Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes
The Scheduled Castes[2] (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) are officially designated groups of people and among the most disadvantaged socio-economic groups in India.[3] The terms are recognized in the Constitution of India and the groups are designated in one or other of the categories.[4]: 3 For much of the period of British rule in the Indian subcontinent, they were known as the Depressed Classes.[4]: 2
In modern literature, the Scheduled Castes are sometimes referred to as Dalit, meaning "broken" or "dispersed",[5][6] having been popularised by B. R. Ambedkar (1891–1956), a Dalit himself, an economist, reformer, chairman of the Constituent Assembly of India, and Dalit leader during the independence struggle.[5] Ambedkar preferred the term Dalit to Gandhi's term, Harijan, meaning "person of Hari/Vishnu" (or Man of God).[5] In September 2018, the government "issued an advisory to all private satellite channels asking them to 'refrain' from using the nomenclature 'Dalit'", though "rights groups and intellectuals have come out against any shift from 'Dalit' in popular usage".[7]
The Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes comprise about 16.6% and 8.6%, respectively, of India's population (according to the 2011 census).[8][9] The Constitution (Scheduled Castes) Order, 1950 lists 1,108 castes across 28 states in its First Schedule,[10] and the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950 lists 744 tribes across 22 states in its First Schedule.[11]
Since the independence of India, the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes were given Reservation status, guaranteeing political representation, preference in promotion, quota in universities, free and stipended education, scholarships, banking services, various government schemes and the Constitution lays down the general principles of positive discrimination for SCs and STs.[12][13]: 35, 137
History
The evolution of Lower caste to modern-day Scheduled Castes is complex. The caste system as a stratification of classes in India originated about 2,000 years ago, and has been influenced by dynasties and ruling elites, including the Mughal Empire and the British Raj.[14][15] The Hindu concept of Varna historically incorporated occupation-based communities.[14] Some low-caste groups, such as those formerly called untouchables[16] who constitute modern-day Scheduled Castes, were considered outside the Varna system.[17][18]
Since the 1850s, these communities were loosely referred to as Depressed Classes, with the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.The early 20th century saw a flurry of activity in the British authorities assessing the feasibility of responsible self-government for India. The Morley–Minto Reforms Report, Montagu–Chelmsford Reforms Report and the Simon Commission were several initiatives in this context. A highly contested issue in the proposed reforms was the reservation of seats for representation of the Depressed Classes in provincial and central legislatures.[19]
In 1935, the UK Parliament passed the Government of India Act 1935, designed to give Indian provinces greater self-rule and set up a national federal structure. The reservation of seats for the Depressed Classes was incorporated into the act, which came into force in 1937. The Act introduced the term "Scheduled Castes", defining the group as "such castes, parts of groups within castes, which appear to His Majesty in Council to correspond to the classes of persons formerly known as the 'Depressed Classes', as His Majesty in Council may prefer".[4] This discretionary definition was clarified in The Government of India (Scheduled Castes) Order, 1936, which contained a list (or Schedule) of castes throughout the British-administered provinces.[4]
After independence the Constituent Assembly continued the prevailing definition of Scheduled Castes and Tribes, giving (via articles 341 and 342) the president of India and governors of the states a mandate to compile a full listing of castes and tribes (with the power to edit it later, as required). The complete list of castes and tribes was made via two orders: The Constitution (Scheduled Castes) Order, 1950[20] and The Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950,[21] respectively. Furthermore, independent India's quest for inclusivity was incident through the appointment of B. R. Ambedkar as the chair of the drafting committee for the Constitution. Ambedkar was a scheduled caste constitutional lawyer, a member of the low caste.[22]
Government initiative to improve the situation of SCs and STs
The Constitution provides a three-pronged strategy[23] to improve the situation of SCs and STs:
- Protective arrangements: Such measures as are required to enforce equality, to provide punitive measures for transgressions, and to eliminate established practices that perpetuate inequities. A number of laws were enacted to implement the provisions in the Constitution. Examples of such laws include the Untouchability Practices Act, 1955, Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989, The Employment of Manual Scavengers and Construction of Dry Latrines (Prohibition) Act, 1993, etc. Despite legislation, social discrimination and atrocities against the backward castes continued to persist.[24]
- Affirmative action: Provide positive treatment in allotment of jobs and access to higher education as a means to accelerate the integration of the SCs and STs with mainstream society. Affirmative action is popularly known as reservation. Article 16 of the Constitution states "nothing in this article shall prevent the State from making any provisions for the reservation of appointments or posts in favor of any backward class of citizens, which, in the opinion of the state, is not adequately represented in the services under the State". The Supreme Court upheld the legality of affirmative action and the Mandal Commission (a report that recommended that affirmative action not only apply to the Untouchables, but the other backward castes as well). However, the reservations from affirmative action were only allotted in the public sector, not the private.[25]
- Development: Provide resources and benefits to bridge the socioeconomic gap between the SCs and STs and other communities. Legislation to improve the socioeconomic situation of SCs and STs because twenty-seven percent of SC and thirty-seven percent of ST households lived below the poverty line, compared to the mere eleven percent among other households. Additionally, the backward castes were poorer than other groups in Indian society, and they suffered from higher morbidity and mortality rates.[26]
National commissions
To effectively implement the safeguards built into the Constitution and other legislation, the Constitution under Articles 338 and 338A provides for two constitutional commissions: the National Commission for Scheduled Castes,[27] and the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes.[28] The chairpersons of both commissions sit ex officio on the National Human Rights Commission.Scheduled Castes in India.
Constitutional history
In the original Constitution, Article 338 provided for a special officer (the Commissioner for SCs and STs) responsible for monitoring the implementation of constitutional and legislative safeguards for SCs and STs and reporting to the president. Seventeen regional offices of the Commissioner were established throughout the country.
There was an initiative to replace the Commissioner with a committee in the 48th Amendment to the Constitution, changing Article 338. While the amendment was being debated, the Ministry of Welfare established the first committee for SCs and STs (with the functions of the Commissioner) in August 1978. These functions were modified in September 1987 to include advising the government on broad policy issues and the development levels of SCs and STs. Now it is included in Article 342.
In 1990, Article 338 was amended for the National Commission for SCs and STs with the Constitution (Sixty fifth Amendment) Bill, 1990.[29] The first commission under the 65th Amendment was constituted in March 1992, replacing the Commissioner for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes and the commission established by the Ministry of Welfare's Resolution of 1989. In 2003, the Constitution was again amended to divide the National Commission for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes into two commissions: the National Commission for Scheduled Castes and the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes. Due to the spread of Christianity and Islam among schedule caste community converted are not protected as castes under Indian Reservation policy. Hence, these societies usually forge their community certificate as Hindus and practice Christianity or Islam afraid for their loss of reservation.[30]
Scheduled Castes Sub-Plan
The Scheduled Castes Sub-Plan (SCSP) of 1979 mandated a planning process for the social, economic and educational development of Scheduled Castes and improvement in their working and living conditions. It was an umbrella strategy, ensuring the flow of targeted financial and physical benefits from the general sector of development to the Scheduled Castes.[31] It entailed a targeted flow of funds and associated benefits from the annual plan of states and Union Territories (UTs) in at least a proportion to the national SC population. Twenty-seven states and UTs with sizable SC populations are implementing the plan. Although the Scheduled Castes population according to the 2001 Census was 16.66 crores (16.23% of the total population), the allocations made through SCSP have been lower than the proportional population.[32] A strange factor has emerged of extremely lowered fertility of scheduled castes in Kerala, due to land reform, migrating (Kerala Gulf diaspora) and democratization of education.[33]
Demographics
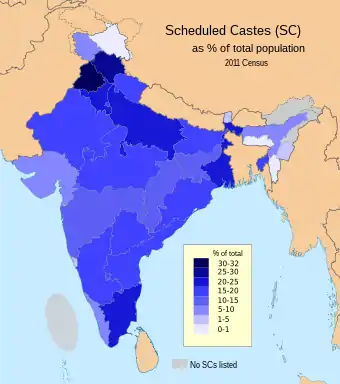
Scheduled Caste Population by State
| State | Population | Scheduled Caste (%) | Scheduled Caste Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| India | 1,210,854,977 | 16.63 | 201,378,086 |
| Andhra Pradesh | 84,580,777 | 16.41 | 13,878,078 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | 1,383,727 | 0.00 | 0 |
| Assam | 31,205,576 | 7.15 | 2,231,321 |
| Bihar | 104,099,452 | 15.91 | 16,567,325 |
| Chhattisgarh | 25,545,198 | 12.82 | 3,274,269 |
| Goa | 1,458,545 | 1.74 | 25,449 |
| Gujarat | 60,439,692 | 6.74 | 4,074,447 |
| Haryana | 25,351,462 | 20.17 | 5,113,615 |
| Himachal Pradesh | 6,864,602 | 25.19 | 1,729,252 |
| Jammu & Kashmir | 12,541,302 | 7.38 | 924,991 |
| Jharkhand | 32,988,134 | 12.08 | 3,985,644 |
| Karnataka | 61,095,297 | 17.15 | 10,474,992 |
| Kerala | 33,406,061 | 9.10 | 3,039,573 |
| Madhya Pradesh | 72,626,809 | 15.62 | 11,342,320 |
| Maharashtra | 112,374,333 | 11.81 | 13,275,898 |
| Manipur | 2,570,390 | 3.78 | 97,042 |
| Meghalaya | 2,966,889 | 0.58 | 17,355 |
| Mizoram | 1,097,206 | 0.11 | 1,218 |
| Nagaland | 1,978,502 | 0.00 | 0 |
| Odisha | 41,974,218 | 17.13 | 7,190,184 |
| Punjab | 27,743,338 | 31.94 | 8,860,179 |
| Rajasthan | 68,548,437 | 17.83 | 12,221,593 |
| Sikkim | 610,577 | 4.63 | 28,275 |
| Tamil Nadu | 72,147,030 | 20.01 | 14,438,445 |
| Tripura | 3,673,917 | 17.83 | 654,918 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 199,812,341 | 20.70 | 41,357,608 |
| Uttarakhand | 10,086,292 | 18.76 | 1,892,516 |
| West Bengal | 91,276,115 | 23.51 | 21,463,270 |
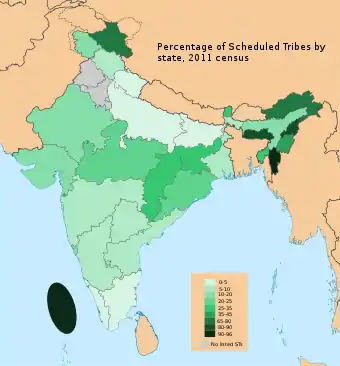
Scheduled Tribe Population by State
| State | Population | Scheduled Tribe (%) | Scheduled Tribe Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| India | 1,210,854,977 | 8.61 | 104,254,613 |
| Andhra Pradesh | 84,580,777 | 7.00 | 5,920,654 |
| Arunachal Pradesh | 1,383,727 | 68.79 | 951,865 |
| Assam | 31,205,576 | 12.45 | 3,885,094 |
| Bihar | 104,099,452 | 1.28 | 1,332,472 |
| Chhattisgarh | 25,545,198 | 30.62 | 7,821,939 |
| Goa | 1,458,545 | 10.21 | 148,917 |
| Gujarat | 60,439,692 | 14.75 | 8,914,854 |
| Haryana | 25,351,462 | 0.00 | 0 |
| Himachal Pradesh | 6,864,602 | 5.71 | 391,968 |
| Jammu & Kashmir | 12,541,302 | 11.90 | 1,492,414 |
| Jharkhand | 32,988,134 | 26.21 | 8,646,189 |
| Karnataka | 61,095,297 | 6.95 | 4,246,123 |
| Kerala | 33,406,061 | 1.45 | 484,387 |
| Madhya Pradesh | 72,626,809 | 21.09 | 15,316,994 |
| Maharashtra | 112,374,333 | 9.35 | 10,507,000 |
| Manipur | 2,570,390 | 35.14 | 903,235 |
| Meghalaya | 2,966,889 | 86.15 | 2,555,974 |
| Mizoram | 1,097,206 | 94.44 | 1,036,201 |
| Nagaland | 1,978,502 | 86.46 | 1,710,612 |
| Odisha | 41,974,218 | 22.85 | 9,591,108 |
| Punjab | 27,743,338 | 0.00 | 0 |
| Rajasthan | 68,548,437 | 13.48 | 9,240,329 |
| Sikkim | 610,577 | 33.72 | 205,886 |
| Tamil Nadu | 72,147,030 | 1.10 | 793,617 |
| Tripura | 3,673,917 | 31.76 | 1,166,836 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 199,812,341 | 0.57 | 1,138,930 |
| Uttarakhand | 10,086,292 | 2.90 | 292,502 |
| West Bengal | 91,276,115 | 5.80 | 5,294,014 |
See also
- Forward caste
- Inter-caste marriages in India
- List of Scheduled Tribes in India
- Other Backward Classes
- Socio Economic Caste Census 2011
References
- Census of India 2011, Primary Census Abstract
 PPT, Scheduled castes and scheduled tribes, Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, Government of India (28 October 2013).
PPT, Scheduled castes and scheduled tribes, Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, Government of India (28 October 2013). - "Scheduled Caste Welfare – List of Scheduled Castes". Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment. Archived from the original on 13 September 2012. Retrieved 16 August 2012.
- "Scheduled Castes And Scheduled Tribes". UNITED NATIONS IN INDIA. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - "Scheduled Communities: A social Development profile of SC/ST's (Bihar, Jharkhand & West Bengal)" (PDF). Planning Commission (India). Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 October 2019. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
- Roychowdhury, Adrija (5 September 2018). "Why Dalits want to hold on to Dalit, not Harijan, not SC". The Indian Express.
- "Dalit". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 6 October 2022.
- Union minister: Stick to SC, avoid the term 'Dalit' "Union social justice minister Thawarchand Gehlot said media should stick to the constitutional term "Scheduled Castes" while referring to Dalits as there are objections to the term to the term "Dalit" – backing the government order which has significant sections of scheduled caste civil society up in arms." Times of India 5 September 2018.
- "2011 Census Primary Census Abstract" (PDF). Censusindia.gov.in. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
- "Half of India's dalit population lives in 4 states". Timesofindia.indiatimes.com. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
- "Text of the Constitution (Scheduled Castes) Order, 1950, as amended". Lawmin.nic.in. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
- "Text of the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950, as amended". Lawmin.nic.in. Archived from the original on 20 September 2017. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
- Kumar, K Shiva (17 February 2020). "Reserved uncertainty or deserved certainty? Reservation debate back in Mysuru". The New Indian Express.
- "THE CONSTITUTION OF INDIA [As on 9th December, 2020]" (PDF). Legislative Department.
- "What is India's caste system?". 20 July 2017. Retrieved 6 April 2019.
- Bayly, Susan (July 1999). Caste, Society and Politics in India from the Eighteenth Century to the Modern Age by Susan Bayly. Cambridge Core. doi:10.1017/CHOL9780521264341. ISBN 9780521264341. Retrieved 6 April 2019.
- Pletcher, Ken; Staff of EB (2010). "Untouchable - social class, India". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved 25 June 2021.
- "Civil rights | society". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 6 April 2019.
- "Jati: The Caste System in India". Asia Society. Retrieved 6 April 2019.
- Jyoti, Dhrubo (1 October 2019). "Gandhi, Ambedkar and the 1932 Poona Pact". Hindustan Times.
- "THE CONSTITUTION (SCHEDULED CASTES) ORDER, 1950". lawmin.nic.in.
- "1. THE CONSTITUTION (SCHEDULED TRIBES)". lawmin.nic.in. Archived from the original on 20 September 2017.
- Metcalf, Barbara D.; Metcalf, Thomas R. (2012). A Concise History of Modern India. New York: Cambridge. p. 232. ISBN 978-1-107-67218-5.
- Archived 8 May 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- Sengupta, Chandan (2013). Democracy, Development, and Decentralization in India: Continuing Debates. Routledge. p. 23. ISBN 978-1136198489.
- Metcalf, Barbara D.; Metcalf, Thomas R. (2012). A Concise History of Modern India. New York: Cambridge. p. 274. ISBN 978-1-107-67218-5.
- Sengupta, Chandan (2013). Democracy, Development and Decentralization in India: Continuing Debates. Routledge. p. 23. ISBN 9781136198489.
- "National Commission for Schedule Castes". Indiaenvironmentportal.org. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
- "THE CONSTITUTION (EIGHTY-NINTH AMENDMENT) ACT, 2003". Indiacode.nic.in. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
- "Constitution of India as of 29 July 2008" (PDF). The Constitution of India. Ministry of Law & Justice. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 September 2014. Retrieved 13 April 2011.
- "Community status lapses on conversion, rules Madras High Court". Thehindu.com. 24 June 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
- Sridharan, R (31 October 2005). "Letter from Joint Secretary (SP) to Planning Secretaries of All States/UTs". Planning Commission (India). Archived from the original on 26 February 2009. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - Bone, Omprakash S. (2015). Mannewar: A Tribal Community in India. Notion Press. ISBN 978-9352063444.
- S., Pallikadavath; C., Wilson (1 July 2005). "A paradox within a paradox: Scheduled caste fertility in Kerala". Economic and Political Weekly. 40 (28): 3085–3093. Retrieved 1 October 2017.
- Government of India, Ministry of Social Justice website
- Statewise Total & Tribal Population of India (As per 2011 Census)
Further reading
- Mandal, Mahitosh (2022). "Dalit Resistance during the Bengal Renaissance: Five Anti-Caste Thinkers from Colonial Bengal, India". Caste: A Global Journal on Social Exclusion. 3 (1): 11–30. doi:10.26812/caste.v3i1.367. S2CID 249027627.
- Srivastava, Vinay Kumar; Chaudhury, Sukant K. (2009). "Anthropological Studies of Indian Tribes". In Atal, Yogesh (ed.). Sociology and Social Anthropology in India. Indian Council of Social Science Research/Pearson Education India. ISBN 9788131720349.