Femoral artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery or profunda femoris artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh.[1]
| Femoral artery | |
|---|---|
 Thigh with and without the sartorius muscle, revealing the femoral artery and vein underneath | |
| Details | |
| Source | External iliac artery |
| Branches | Superficial epigastric artery, superficial iliac circumflex, superficial external pudendal, deep external pudendal, deep femoral artery, continues as popliteal artery |
| Vein | Femoral vein |
| Supplies | Anterior compartment of thigh |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arteria femoralis |
| MeSH | D005263 |
| TA98 | A12.2.16.010 |
| TA2 | 4674 |
| FMA | 70248 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure
The femoral artery enters the thigh from behind the inguinal ligament as the continuation of the external iliac artery.[2] Here, it lies midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the symphysis pubis (Mid-inguinal point).
Segments

In clinical parlance, the femoral artery has the following segments:
- The common femoral artery (CFA) is the segment of the femoral artery between the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament and the branching point of the deep femoral artery/profunda femoris artery. Its first three or four centimetres are enclosed, with the femoral vein, in the femoral sheath. In 65% of people, the common femoral artery lies anterior to the femoral vein in the upper thigh.[3]
- The subsartorial artery[4] or superficial femoral artery[5] are designations for the segment between the branching point of the deep femoral artery and the adductor hiatus, passing through the subsartorial canal. However, usage of the term superficial femoral is discouraged by many physicians because it leads to confusion among general medical practitioners, at least for the femoral vein that courses next to the femoral artery.[6] In particular, the adjacent femoral vein is clinically a deep vein, where deep vein thrombosis indicates anticoagulant or thrombolytic therapy, but the adjective "superficial" leads many physicians to falsely believe it is a superficial vein, which has resulted in patients with femoral thrombosis being denied proper treatment.[7][8][9] Therefore, the terms subsartorial artery and subsartorial vein have been suggested for the femoral artery and vein, respectively, distally to the branching points of the deep femoral artery and vein.[4] The subaortorial artery passes through the adductor hiatus to enter popliteal fossa and continue as popliteal artery.[10]
Relations
The relations of the femoral artery are as follows:
- Anteriorly: In the upper part of its course, it is superficial and is covered by skin and fascia. In the lower part of its course, it passes behind the sartorius muscle.
- Posteriorly: The artery lies on the psoas, which separates it from the hip joint, the pectineus, and the adductor longus. The femoral vein intervenes between the artery and the adductor longus.
- Medially: It is related to the femoral vein in the upper part of its course.
- Laterally: The femoral nerve and its branches.
Branches

Common femoral artery
- The superficial circumflex iliac artery[10] is a small branch that runs up to the region of the anterior superior iliac spine.
- The superficial epigastric artery[10] is a small branch that crosses the inguinal ligament and runs to the region of the umbilicus.
- The superficial external pudendal artery[10] is a small branch that runs medially to supply the skin of the scrotum or labium majus as.
- The deep external pudendal artery runs medially and supplies the skin of the scrotum or labium majus.
- The profunda femoris artery is a large and important branch that arises from the lateral side of the femoral artery about 1.5 in. (4 cm) below the inguinal ligament. It passes medially behind the femoral vessels and enters the medial fascial compartment of the thigh. It ends by becoming the fourth perforating artery. At its origin, it gives off the medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries, and during its course it gives off three perforating arteries.[10]
Subaortorial artery/superficial femoral artery
- The descending genicular artery is a small branch that arises from the femoral artery near its termination within the adductor canal. It assists in supplying the knee joint.
Clinical significance
Clinical examination
The site for optimally palpating the femoral pulse is in the inner thigh, at the mid-inguinal point, halfway between the pubic symphysis and anterior superior iliac spine. Presence of a femoral pulse indicates a systolic blood pressure of more than 50 mmHg.[11]
Vascular access
Femoral artery is the frequent site of access in angiography. As the pulsation of the common femoral artery can often be palpated through the skin; and the site of maximum pulsation is used as a point of puncture for catheter access.[3] From here, wires and catheters can be directed anywhere in the arterial system for intervention or diagnostics, including the heart, brain, kidneys, arms and legs. The direction of the needle in the femoral artery can be against blood flow (retro-grade), for intervention and diagnostic towards the heart and opposite leg, or with the flow (ante-grade or ipsi-lateral) for diagnostics and intervention on the same leg. Access in either the left or right femoral artery is possible and depends on the type of intervention or diagnostic.
To image the lower limb vascular anatomy, common femoral artery (CFA) is chosen as the site of entry. However, CFA entry can only be assessed by retrograde puncture. Therefore, a catheter is advanced retrogradely through the contralateral common femoral artery into common iliac artery, crossing the midline into ipsilateral CFA. The SFA can then be assessed by antegrade puncture.[12]
The femoral artery can be used to draw arterial blood when the blood pressure is so low that the radial or brachial arteries cannot be located.
Peripheral arterial disease
The femoral artery is susceptible to peripheral arterial disease.[13] When it is blocked through atherosclerosis, percutaneous intervention with access from the opposite femoral may be needed. Endarterectomy, a surgical cut down and removal of the plaque of the femoral artery is also common. If the femoral artery has to be ligated surgically to treat a popliteal aneurysm, blood can still reach the popliteal artery distal to the ligation via the genicular anastomosis. However, if flow in the femoral artery of a normal leg is suddenly disrupted, blood flow distally is rarely sufficient. The reason for this is the fact that the genicular anastomosis is only present in a minority of individuals and is always undeveloped when disease in the femoral artery is absent.[14]
See also
- Brachial artery, an arm based artery with a similar function
References
- Schulte, Erik; Schumacher, Udo (2006). "Arterial Supply to the Thigh". In Ross, Lawrence M.; Lamperti, Edward D. (eds.). Thieme Atlas of Anatomy: General Anatomy and Musculoskeletal System. Thieme. p. 490. ISBN 978-3-13-142081-7.
- Jacob, S. (January 1, 2008), Jacob, S. (ed.), "Chapter 6 - Lower limb", Human Anatomy, Churchill Livingstone, pp. 135–179, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-10373-5.50009-9, ISBN 978-0-443-10373-5, retrieved January 18, 2021
- van den Berg, Jos C (January 2013). "Optimal Technique for Common Femoral Artery Access". Endovascular Today. Archived from the original on August 6, 2021. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- Mikael Häggström (2019). "Subsartorial Vessels as Replacement Name for Superficial Femoral Vessels" (PDF). International Journal of Anatomy, Radiology and Surgery: AV01–AV02.
- Snell, Richard S. (2008). Clinical Anatomy By Regions (8 ed.). Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 581–582. ISBN 978-0-7817-6404-9.
- Bundens, WP; Bergan, JJ; Halasz, NA; Murray, J; Drehobl, M (1995). "The superficial femoral vein. A potentially lethal misnomer". JAMA. 274 (16): 1296–8. doi:10.1001/jama.1995.03530160048032. PMID 7563535.
- Hammond, I (2003). "The superficial femoral vein". Radiology. 229 (2): 604, discussion 604-6. doi:10.1148/radiol.2292030418. PMID 14595157.
- Kitchens CS (2011). "How I treat superficial venous thrombosis". Blood. 117 (1): 39–44. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-05-286690. PMID 20980677.
- Thiagarajah R, Venkatanarasimha N, Freeman S (2011). "Use of the term "superficial femoral vein" in ultrasound". J Clin Ultrasound. 39 (1): 32–34. doi:10.1002/jcu.20747. PMID 20957733. S2CID 23215861.
- Ryan, Stephanie (2011). "Chapter 8". Anatomy for diagnostic imaging (Third ed.). Elsevier Ltd. p. 306. ISBN 9780702029714.
- Deakin, Charles D.; Low, J. Lorraine (September 2000). "Accuracy of the advanced trauma life support guidelines for predicting systolic blood pressure using carotid, femoral, and radial pulses: observational study". BMJ. 321 (7262): 673–4. doi:10.1136/bmj.321.7262.673. PMC 27481. PMID 10987771.
- Berman, Hl; Katz, Sg; Tihansky, Dp (September 1986). "Guided direct antegrade puncture of the superficial femoral artery". American Journal of Roentgenology. 147 (3): 632–634. doi:10.2214/ajr.147.3.632. ISSN 0361-803X. PMID 2943146.
- MacPherson, D. S.; Evans, D. H.; Bell, P. R. F. (January 1984). "Common femoral artery Doppler wave-forms: a comparison of three methods of objective analysis with direct pressure measurements". British Journal of Surgery. 71 (1): 46–9. doi:10.1002/bjs.1800710114. PMID 6689970. S2CID 30352039.
- Sabalbal, M.; Johnson, M.; McAlister, V. (September 2013). "Absence of the genicular arterial anastomosis as generally depicted in textbooks". Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England. 95 (6): 405–9. doi:10.1308/003588413X13629960046831. PMC 4188287. PMID 24025288.
Additional images
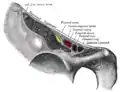 Structures passing behind the inguinal ligament. (Femoral artery labeled at upper right.)
Structures passing behind the inguinal ligament. (Femoral artery labeled at upper right.) Cross-section showing structures surrounding right hip-joint.
Cross-section showing structures surrounding right hip-joint.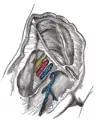 Femoral sheath laid open to show its three compartments.
Femoral sheath laid open to show its three compartments. The femoral artery.
The femoral artery. The spermatic cord in the inguinal canal.
The spermatic cord in the inguinal canal. Front of right thigh, showing surface markings for bones, femoral artery and femoral nerve.
Front of right thigh, showing surface markings for bones, femoral artery and femoral nerve. Femoral artery and its major branches - right thigh, anterior view.
Femoral artery and its major branches - right thigh, anterior view. Illustration depicting main leg arteries (anterior view).
Illustration depicting main leg arteries (anterior view). Femoral artery - deep dissection.
Femoral artery - deep dissection. Femoral artery - deep dissection.
Femoral artery - deep dissection.
External links
- Anatomy photo:12:05-0101 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Cross section image: pelvis/pelvis-e12-15—Plastination Laboratory at the Medical University of Vienna
- Image at umich.edu - pulse
- Diagram at MSU
- QuantaFlo vs ABI in Peripheral Arterial Disease