Carrot
The carrot (Daucus carota subsp. sativus) is a root vegetable, typically orange in color, though purple, black, red, white, and yellow cultivars exist,[2][3][4] all of which are domesticated forms of the wild carrot, Daucus carota, native to Europe and Southwestern Asia. The plant probably originated in Persia and was originally cultivated for its leaves and seeds. The most commonly eaten part of the plant is the taproot, although the stems and leaves are also eaten. The domestic carrot has been selectively bred for its enlarged, more palatable, less woody-textured taproot.
| Carrot | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Apiales |
| Family: | Apiaceae |
| Genus: | Daucus |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: | D. c. subsp. sativus |
| Trinomial name | |
| Daucus carota subsp. sativus (Hoffm.) Schübl. & G. Martens | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
The carrot is a biennial plant in the umbellifer family, Apiaceae. At first, it grows a rosette of leaves while building up the enlarged taproot. Fast-growing cultivars mature within three months (90 days) of sowing the seed, while slower-maturing cultivars need a month longer (120 days). The roots contain high quantities of alpha- and beta-carotene, and are a good source of vitamin A, vitamin K, and vitamin B6.
The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) reports that world production of carrots and turnips (these plants are combined by the FAO) for 2018 was 40 million tonnes, with 45% of the world total grown in China. Carrots are commonly consumed raw or cooked in various cuisines.
Etymology

The word is first recorded in English circa 1530 and was borrowed from Middle French carotte,[6] itself from Late Latin carōta, from ancient Greek καρωτόν karōtón), originally from the Proto-Indo-European root *ker- ('horn'), due to its horn-like shape. In Old English, carrots (typically white at the time) were not clearly distinguished from parsnips: the two were collectively called moru or more (from Proto-Indo-European *mork- 'edible root', cf. German Möhre or Russian морковь (morkov)).
Various languages still use the same word for carrot as they do for root; e.g. Dutch wortel.[7]
History
Both written history and molecular genetic studies indicate that the domestic carrot has a single origin in Central Asia.[2][3] Its wild ancestors probably originated in Persia (regions of which are now Iran and Afghanistan), which remains the centre of diversity for the wild carrot Daucus carota. A naturally occurring subspecies of the wild carrot was presumably bred selectively over the centuries to reduce bitterness, increase sweetness and minimise the woody core; this process produced the familiar garden vegetable.[8][9]
When they were first cultivated, carrots were grown for their aromatic leaves and seeds rather than their roots. Carrot seeds have been found in Switzerland and Southern Germany dating back to 2000–3000 BC.[10] Some close relatives of the carrot are still grown for their leaves and seeds, such as parsley, cilantro, coriander, fennel, anise, dill and cumin. The first mention of the root in classical sources is from the 1st century AD;[11] the Romans ate a root vegetable called pastinaca,[12] which may have been either the carrot or the closely related parsnip.[13][14]
The plant is depicted and described in the Eastern Roman Juliana Anicia Codex, a 6th-century AD Constantinopolitan copy of the Greek physician Dioscorides' 1st-century pharmacopoeia of herbs and medicines, De Materia Medica. Three different types of carrots are depicted, and the text states that "the root can be cooked and eaten".[15] Another copy of this work, Codex Neapolitanes from late 6th or early 7th century, has basically the same illustrations but with roots in purple.[16]
The plant was introduced into Spain by the Moors in the 8th century.[17] In the 10th century, roots from West Asia, India and Europe were purple.[18] The modern carrot originated in Afghanistan at about this time.[11] The 11th-century Jewish scholar Simeon Seth describes both red and yellow carrots,[19] as does the 12th-century Arab-Andalusian agriculturist, Ibn al-'Awwam.[20] Cultivated carrots appeared in China in the 12th century,[21] and in Japan in the 16th or 17th century.[22]
There are many claims that Dutch growers created orange carrots in the 17th century to honor the Dutch flag at the time and William of Orange.[18][23] Other authorities argue these claims lack convincing evidence.[24] Modern carrots were described at about this time by the English antiquary John Aubrey (1626–1697): "Carrots were first sown at Beckington in Somersetshire. Some very old Man there [in 1668] did remember their first bringing hither."[25] European settlers introduced the carrot to colonial America in the 17th century.[26]
Outwardly purple carrots, still orange on the inside, were sold in British stores beginning in 2002.[18]
Description
Daucus carota is a biennial plant. In the first year, its rosette of leaves produces large amounts of sugars, which are stored in the taproot to provide energy for the plant to flower in the second year.
.jpg.webp)
Soon after germination, carrot seedlings show a distinct demarcation between taproot and stem: the stem is thicker and lacks lateral roots. At the upper end of the stem is the seed leaf. The first true leaf appears about 10–15 days after germination. Subsequent leaves are alternate (with a single leaf attached to a node), spirally arranged, and pinnately compound, with leaf bases sheathing the stem. As the plant grows, the bases of the seed leaves, near the taproot, are pushed apart. The stem, located just above the ground, is compressed and the internodes are not distinct. When the seed stalk elongates for flowering, the tip of the stem narrows and becomes pointed, and the stem extends upward to become a highly branched inflorescence up to 60–200 cm (20–80 in) tall.[27]
Most of the taproot consists of a pulpy outer cortex (phloem) and an inner core (xylem). High-quality carrots have a large proportion of cortex compared to core. Although a completely xylem-free carrot is not possible, some cultivars have small and deeply pigmented cores; the taproot can appear to lack a core when the colour of the cortex and core are similar in intensity. Taproots are typically long and conical, although cylindrical and nearly-spherical cultivars are available. The root diameter can range from 1 cm (3⁄8 in) to as much as 10 cm (4 in) at the widest part. The root length ranges from 5 to 50 cm (2 to 20 in), although most are between 10 and 25 cm (4 and 10 in).[27]


Flower development begins when the flat meristem changes from producing leaves to an uplifted, conical meristem capable of producing stem elongation and a cluster of flowers. The cluster is a compound umbel, and each umbel contains several smaller umbels (umbellets). The first (primary) umbel occurs at the end of the main floral stem; smaller secondary umbels grow from the main branch, and these further branch into third, fourth, and even later-flowering umbels.[27]
A large, primary umbel can contain up to 50 umbellets, each of which may have as many as 50 flowers; subsequent umbels have fewer flowers. Individual flowers are small and white, sometimes with a light green or yellow tint. They consist of five petals, five stamens, and an entire calyx. The stamens usually split and fall off before the stigma becomes receptive to receive pollen. The stamens of the brown, male, sterile flowers degenerate and shrivel before the flower fully opens. In the other type of male sterile flower, the stamens are replaced by petals, and these petals do not fall off. A nectar-containing disc is present on the upper surface of the carpels.[27]
.jpg.webp)
Flowers change sex in their development, so the stamens release their pollen before the stigma of the same flower is receptive. The arrangement is centripetal, meaning the oldest flowers are near the edge and the youngest flowers are in the center. Flowers usually first open at the outer edge of the primary umbel, followed about a week later on the secondary umbels, and then in subsequent weeks in higher-order umbels.[27]
The usual flowering period of individual umbels is 7 to 10 days, so a plant can be in the process of flowering for 30–50 days. The distinctive umbels and floral nectaries attract pollinating insects. After fertilization and as seeds develop, the outer umbellets of an umbel bend inward causing the umbel shape to change from slightly convex or fairly flat to concave, and when cupped it resembles a bird's nest.[27]

The fruit that develops is a schizocarp consisting of two mericarps; each mericarp is a true seed. The paired mericarps are easily separated when they are dry. Premature separation (shattering) before harvest is undesirable because it can result in seed loss. Mature seeds are flattened on the commissural side that faced the septum of the ovary. The flattened side has five longitudinal ribs. The bristly hairs that protrude from some ribs are usually removed by abrasion during milling and cleaning. Seeds also contain oil ducts and canals. Seeds vary somewhat in size, ranging from less than 500 to more than 1000 seeds per gram.[27]
The carrot is a diploid species, and has nine relatively short, uniform-length chromosomes (2n=18).[2][3] The genome size is estimated to be 473 mega base pairs, which is four times larger than Arabidopsis thaliana, one-fifth the size of the maize genome, and about the same size as the rice genome.[28]
Chemistry
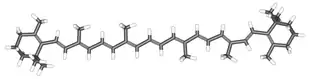
Polyacetylenes can be found in Apiaceae vegetables like carrots where they show cytotoxic activities.[29][30] Falcarinol and falcarindiol (cis-heptadeca-1,9-diene-4,6-diyne-3,8-diol)[31] are such compounds. This latter compound shows antifungal activity towards Mycocentrospora acerina and Cladosporium cladosporioides.[31] Falcarindiol is the main compound responsible for bitterness in carrots.[32]
Other compounds such as pyrrolidine (present in the leaves),[33] 6-hydroxymellein,[34] 6-methoxymellein, eugenin, 2,4,5-trimethoxybenzaldehyde (gazarin) or (Z)-3-acetoxy-heptadeca-1,9-diene-4,6-diin-8-ol (falcarindiol 3-acetate) can also be found in carrot.
Cultivation

Carrots are grown from seed and can take up to four months (120 days) to mature, but most cultivars mature within 70 to 80 days under the right conditions.[35] They grow best in full sun but tolerate some shade.[36] The optimum temperature is 16 to 21 °C (61 to 70 °F).[37] The ideal soil is deep, loose and well-drained, sandy or loamy, with a pH of 6.3 to 6.8.[38]
Fertilizer should be applied according to soil type because the crop requires low levels of nitrogen, moderate phosphate and high potash. Rich or rocky soils should be avoided, as these will cause the roots to become hairy and/or misshapen.[39] Irrigation is applied when needed to keep the soil moist. After sprouting, the crop is eventually thinned to a spacing of 8 to 10 cm (3 to 4 in) and weeded to prevent competition beneath the soil.[35][40]
Cultivation problems
There are several diseases that can reduce the yield and market value of carrots. The most devastating carrot disease is Alternaria leaf blight, which has been known to eradicate entire crops. A bacterial leaf blight caused by Xanthomonas campestris can also be destructive in warm, humid areas. Root knot nematodes (Meloidogyne species) can cause stubby or forked roots, or galls.[41] Cavity spot, caused by the oomycetes Pythium violae and Pythium sulcatum, results in irregularly shaped, depressed lesions on the taproots.[42]
Physical damage can also reduce the value of carrot crops. The two main forms of damage are splitting, whereby a longitudinal crack develops during growth that can be a few centimetres to the entire length of the root, and breaking, which occurs postharvest. These disorders can affect over 30% of commercial crops. Factors associated with high levels of splitting include wide plant spacing, early sowing, lengthy growth durations, and genotype.[43]
Companion planting
Carrots benefit from strongly scented companion plants. The pungent odour of onions, leeks and chives help repel the carrot root fly,[38] and other vegetables that team well with carrots include lettuce, tomatoes and radishes, as well as the herbs rosemary and sage.[44] Carrots thrive in the presence of caraway, coriander, chamomile, marigold and Swan River daisy.[38] They can also be good companions for other plants; if left to flower, the carrot, like any umbellifer, attracts predatory wasps that kill many garden pests.[45]
Cultivars


Carrot cultivars can be grouped into two broad classes, eastern carrots and western carrots.[46] A number of novelty cultivars have been bred for particular characteristics.[2][3]
"Eastern" (a European and American continent reference) carrots were domesticated in Persia (probably in the lands of modern-day Iran and Afghanistan within West Asia) during the 10th century, or possibly earlier. Specimens of the "eastern" carrot that survive to the present day are commonly purple or yellow, and often have branched roots. The purple colour common in these carrots comes from anthocyanin pigments.[47]
The western carrot emerged in the Netherlands in the 17th century.[48] There is a popular belief that its orange colour made it popular in those countries as an emblem of the House of Orange and the struggle for Dutch independence, although there is little evidence for this.[24][23] The orange colour results from abundant carotenes in these cultivars.
Western carrot cultivars are commonly classified by their root shape. The four general types are:
- Chantenay carrots. Although the roots are shorter than other cultivars, they have vigorous foliage and greater girth, being broad in the shoulders and tapering towards a blunt, rounded tip. They store well, have a pale-coloured core and are mostly used for processing.[40] Cultivars include 'Carson Hybrid' and 'Red Cored Chantenay'.
- Danvers carrots. These have strong foliage and the roots are longer than Chantenay types, and they have a conical shape with a well-defined shoulder, tapering to a point. They are somewhat shorter than Imperator cultivars, but more tolerant of heavy soil conditions. Danvers cultivars store well and are used both fresh and for processing.[40] They were developed in 1871 in Danvers, Massachusetts.[49] Cultivars include 'Danvers Half Long' and 'Danvers 126'.
- Imperator carrots. This cultivar has vigorous foliage, is of high sugar content, and has long and slender roots, tapering to a pointed tip. Imperator types are the most widely cultivated by commercial growers.[40] Cultivars include 'Imperator 58' and 'Sugarsnax Hybrid'.
- Nantes carrots. These have sparse foliage, are cylindrical, short with a more blunt tip than Imperator types, and attain high yields in a range of conditions. The skin is easily damaged and the core is deeply pigmented. They are brittle, high in sugar and store less well than other types.[40] Cultivars include 'Nelson Hybrid', 'Scarlet Nantes' and 'Sweetness Hybrid'.
Carrot breeding programs have developed new cultivars to have dense amounts of chemically-stable acylated pigments, such as anthocyanins, which enrich carrot color based on the density and types of anthocyanin to produce different carrot colors.[2][3] One particular cultivar lacks the usual orange pigment due to carotene, owing its white colour to a recessive gene for tocopherol (vitamin E), but this cultivar and wild carrots do not provide nutritionally significant amounts of vitamin E.[50]
Production
| Carrot and turnip* production – 2020 | |
|---|---|
| Country | (Millions of tonnes) |
| 18.1 | |
| 2.9 | |
| 1.6 | |
| 1.4 | |
| 0.7 | |
| 0.6 | |
| 0.6 | |
| World | 41 |
| * carrots and turnips combined Source: FAOSTAT of the UN[51] | |
In 2020, world production of carrots (combined with turnips) was 41 million tonnes, with China producing 44% of the world total (table).[51] Other major producers were Uzbekistan and the United States.[51]
Storage
Carrots can be stored for several months in the refrigerator or over winter in a moist, cool place. For long term storage, unwashed carrots can be placed in a bucket between layers of sand, a 50/50 mix of sand and wood shavings, or in soil. A temperature range of 0 to 4 °C (32 to 40 °F) and 98% humidity is best.[52][53][54]
Consumption

Carrots can be eaten in a variety of ways. Only 3 percent of the β-carotene in raw carrots is released during digestion: this can be improved to 39% by pulping, cooking and adding cooking oil.[55] Alternatively they may be chopped and boiled, fried or steamed, and cooked in soups and stews, as well as baby and pet foods. A well-known dish is carrots julienne.[56] Together with onion and celery, carrots are one of the primary vegetables used in a mirepoix to make various broths.[57]
The greens are edible as a leaf vegetable,[58][59] but are rarely eaten by humans;[60] some sources suggest that the greens contain toxic alkaloids.[61][62] When used for this purpose, they are harvested young in high-density plantings, before significant root development, and typically used stir-fried, or in salads.[60] Some people are allergic to carrots. In a 2010 study on the prevalence of food allergies in Europe, 3.6 percent of young adults showed some degree of sensitivity to carrots.[63] Because the major carrot allergen, the protein Dauc c 1.0104, is cross-reactive with homologues in birch pollen (Bet v 1) and mugwort pollen (Art v 1), most carrot allergy sufferers are also allergic to pollen from these plants.[64]
In India carrots are used in a variety of ways, as salads or as vegetables added to spicy rice or dal dishes. A popular variation in north India is the Gajar Ka Halwa carrot dessert, which has carrots grated and cooked in milk until the whole mixture is solid, after which nuts and butter are added.[65] Carrot salads are usually made with grated carrots with a seasoning of mustard seeds and green chillies popped in hot oil. Carrots can also be cut in thin strips and added to rice, can form part of a dish of mixed roast vegetables or can be blended with tamarind to make chutney.[66]
Since the late 1980s, baby carrots or mini-carrots (carrots that have been peeled and cut into uniform cylinders) have been a popular ready-to-eat snack food available in many supermarkets.[67] Carrots are puréed and used as baby food, dehydrated to make chips, flakes, and powder, and thinly sliced and deep-fried, like potato chips.[68]
The sweetness of carrots allows the vegetable to be used in some fruit-like roles. Grated carrots are used in carrot cakes, as well as carrot puddings, an English dish thought to have originated in the early 19th century.[69] Carrots can also be used alone or blended with fruits in jams and preserves. Carrot juice is also widely marketed, especially as a health drink, either stand-alone or blended with juices extracted from fruits and other vegetables.[70]
Highly excessive consumption over a period of time can result in carotenemia, a yellow-orange discoloration of the skin caused by a build up of carotenoids.[71]
Nutrition
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 173 kJ (41 kcal) |
9.6 g | |
| Sugars | 4.7 g |
| Dietary fiber | 2.8 g |
0.24 g | |
0.93 g | |
| Vitamins | Quantity %DV† |
| Vitamin A equiv. lutein zeaxanthin | 104% 835 μg77% 8285 μg256 μg |
| Thiamine (B1) | 6% 0.066 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) | 5% 0.058 mg |
| Niacin (B3) | 7% 0.983 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) | 5% 0.273 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 11% 0.138 mg |
| Folate (B9) | 5% 19 μg |
| Vitamin C | 7% 5.9 mg |
| Vitamin E | 4% 0.66 mg |
| Vitamin K | 13% 13.2 μg |
| Minerals | Quantity %DV† |
| Calcium | 3% 33 mg |
| Iron | 2% 0.3 mg |
| Magnesium | 3% 12 mg |
| Manganese | 7% 0.143 mg |
| Phosphorus | 5% 35 mg |
| Potassium | 7% 320 mg |
| Sodium | 5% 69 mg |
| Zinc | 3% 0.24 mg |
| Other constituents | Quantity |
| Water | 88 g |
| |
| †Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. | |
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 147 kJ (35 kcal) |
8.22 g | |
| Sugars | 3.45 g |
| Dietary fiber | 3 g |
0.18 g | |
0.76 g | |
| Vitamins | Quantity %DV† |
| Vitamin A equiv. lutein zeaxanthin | 107% 852 μg77% 8330 μg687 μg |
| Thiamine (B1) | 6% 0.066 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) | 4% 0.044 mg |
| Niacin (B3) | 4% 0.645 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) | 5% 0.232 mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 12% 0.153 mg |
| Folate (B9) | 4% 14 μg |
| Vitamin C | 4% 3.6 mg |
| Vitamin E | 7% 1.03 mg |
| Vitamin K | 13% 13.7 μg |
| Minerals | Quantity %DV† |
| Calcium | 3% 30 mg |
| Iron | 3% 0.34 mg |
| Magnesium | 3% 10 mg |
| Manganese | 7% 0.155 mg |
| Phosphorus | 4% 30 mg |
| Potassium | 5% 235 mg |
| Sodium | 4% 58 mg |
| Zinc | 2% 0.2 mg |
| Other constituents | Quantity |
| Water | 90.2 g |
| |
| †Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. | |
Raw carrots are 88% water, 9% carbohydrates, 0.9% protein, 2.8% dietary fiber, 1% ash and 0.2% fat.[72] Carrot dietary fiber comprises mostly cellulose, with smaller proportions of hemicellulose, lignin and starch.[68] Free sugars in carrot include sucrose, glucose, and fructose.[72]
The carrot gets its characteristic, bright orange colour from β-carotene, and lesser amounts of α-carotene, γ-carotene, lutein, and zeaxanthin.[73] α- and β-carotenes are partly metabolized into vitamin A,[74][75] providing more than 100% of the Daily Value (DV) per 100 g serving of carrots (right table). Carrots are also a good source of vitamin K (13% DV) and vitamin B6 (11% DV), but otherwise have modest content of other essential nutrients (table).[72]
Night vision
The provitamin A beta-carotene from carrots does not actually help people to see in the dark unless they suffer from vitamin A deficiency.[76] This myth was propaganda used by the Royal Air Force during the Second World War to explain why British pilots had improved night vision which enabled their success during nighttime air battles.[77]
Nevertheless, the consumption of carrots was advocated in Britain at the time as part of a Dig for Victory campaign. A radio programme called The Kitchen Front encouraged people to grow, store and use carrots in various novel ways, including making carrot jam and Woolton pie, named after the Lord Woolton, the Minister for Food.[78] The British public during WWII generally believed that eating carrots would help them see better at night and in 1942 there was a 100,000-ton surplus of carrots from the extra production.[79]
See also
- Carrot and stick – Metaphor for the use of punishment and reward to induce a desired behavior
- Carrot fly – Species of fly
- Carrot harvester – Harvesting machine
- Carrot seed oil
- Turnip
- List of carrot dishes
 Food portal
Food portal
References
Citations
- "Daucus carota subsp. sativus (Hoffm.) Arcang". theplantlist.org. The Plant List. Retrieved 12 July 2020.
- Iorizzo, Massimo; Curaba, Julien; Pottorff, Marti; Ferruzzi, Mario G.; Simon, Philipp; Cavagnaro, Pablo F. (7 August 2020). "Carrot Anthocyanins Genetics and Genomics: Status and Perspectives to Improve Its Application for the Food Colorant Industry". Genes. 11 (8): 906. doi:10.3390/genes11080906. ISSN 2073-4425. PMC 7465225. PMID 32784714.
- Iorizzo, Massimo; Senalik, Douglas A.; Ellison, Shelby L.; Grzebelus, Dariusz; Cavagnaro, Pablo F.; Allender, Charlotte; Brunet, Johanne; Spooner, David M.; Van Deynze, Allen; Simon, Philipp W. (2013). "Genetic structure and domestication of carrot (Daucus carota subsp. sativus) (Apiaceae)". American Journal of Botany. 100 (5): 930–938. doi:10.3732/ajb.1300055. PMID 23594914.
- Sifferlin, Alexandra. "Eat This Now: Rainbow Carrots". Time. Archived from the original on 23 January 2018. Retrieved 27 January 2018.
- Folio 312, Juliana Anicia Codex
- "Carrot". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 30 November 2014.
- van Wely, F. Prick (1959). Wortel. Van Goor's English-Dutch and Dutch-English dictionary. David Mckay Company, New York. Retrieved 7 August 2016.
- Rose, F. (2006). The Wild Flower Key. London: Frederick Warne. p. 346. ISBN 978-0-7232-5175-0.
- Mabey, R. (1997). Flora Britannica. London: Chatto and Windus. p. 298. ISBN 978-1-85619-377-1.
- Rubatsky, Quiros & Siman (1999), p. 6
- Simon et al. (2008), p. 328
- Encyclopedia of Food and Health. Elsevier Science. 2015. p. 387. ISBN 978-0-12-384953-3.
- Zohary, Daniel; Hopf, Maria (2000). Domestication of Plants in the Old World (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 203.
- Linnaeus later used the word as a scientific name for the genus Pastinaca, which includes parsnips.
- Folio 312, 313, 314, Juliana Anicia Codex
- Janick, Jules; Stolarczyk, John (May 2012). "Ancient Greek Illustrated Dioscoridean Herbals: Origins and Impact of the Juliana Anicia Codex and the Codex Neopolitanus". Not Bot Horti Agrobo. 40 (1): 9–17. doi:10.15835/nbha4017767.
- Krech III, Shepard; Merchant, Carolyn; McNeill, John Robert, eds. (2004). Encyclopedia of World Environmental History. Vol. 3: O–Z, Index. Routledge. pp. 1071–. ISBN 978-0-415-93735-1.
- "Carrots return to purple roots". BBC. 16 May 2002. Retrieved 5 December 2013.
- Dalby, Andrew (2003). Food in the Ancient World from A to Z. Psychology Press. p. 75. ISBN 978-0-415-23259-3.
- Staub, Jack E. (2010). Alluring Lettuces: And Other Seductive Vegetables for Your Garden. Gibbs Smith. p. 230. ISBN 978-1-4236-0829-5.
- 王繼先. 紹興校定經史證類備急本草.
- 主婦の友社編 (20 February 2011). 野菜まるごと大図鑑. 主婦の友社. pp. 68–73. ISBN 978-4-07-273608-1.
- "How did carrots become orange?". The Economist. 26 September 2018. ISSN 0013-0613. Retrieved 16 December 2019.
- Greene, Wesley (2012). Vegetable Gardening the Colonial Williamsburg Way: 18th-Century Methods for Today's Organic Gardeners. Rodale. p. 81. ISBN 978-1-60961-162-0.
- Oliver Lawson Dick, ed. Aubrey's Brief Lives. Edited from the Original Manuscripts, 1949, p. xxxv.
- Rubatsky, Quiros & Siman (1999), pp. 6–7
- Rubatsky, Quiros & Siman (1999), pp. 22–28
- Bradeen & Simon (2007), p. 162
- Zidorn, Christian; Jöhrer, Karin; Ganzera, Markus; Schubert, Birthe; Sigmund, Elisabeth Maria; Mader, Judith; Greil, Richard; Ellmerer, Ernst P.; Stuppner, Hermann (2005). "Polyacetylenes from the Apiaceae vegetables carrot, celery, fennel, parsley, and parsnip and their cytotoxic activities". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 53 (7): 2518–2523. doi:10.1021/jf048041s. PMID 15796588.
- Baranska, Malgorzata; Schulz, Hartwig; Baranski, Rafal; Nothnagel, Thomas; Christensen, Lars P. (2005). "In situ simultaneous analysis of polyacetylenes, carotenoids and polysaccharides in carrot roots". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 53 (17): 6565–6571. doi:10.1021/jf0510440. PMID 16104767.
- Garrod, B.; Lewis, B.G.; Coxon, D.T. (1978). "Cis-heptadeca-1,9-diene-4,6-diyne-3,8-diol, an antifungal polyacetylene from carrot root tissue". Physiological Plant Pathology. 13 (2): 241–246. doi:10.1016/0048-4059(78)90039-5.
- Czepa, Andreas; Hofmann, Thomas (2003). "Structural and sensory characterization of compounds contributing to the bitter off-taste of carrots (Daucus carota L.) and carrot puree". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 51 (13): 3865–3873. doi:10.1021/jf034085+. PMID 12797757.
- Boyd, O'Neil, M.J., ed. (2006). The Merck Index – An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (14th ed.). Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1.
- Kurosaki, Fumiya; Nishi, Arasuke (1988). "A methyltransferase for synthesis of the phytoalexin 6-methoxymellein in carrot cells". FEBS Letters. 227 (2): 183–186. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(88)80894-9. S2CID 86402868.
- "Your Guide To Growing Carrots". Rodale's Organic Life. Retrieved 23 December 2015.
- Elzer-Peters, K. (2014). Midwest Fruit & Vegetable Gardening: Plant, Grow, and Harvest the Best Edibles – Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio, South Dakota & Wisconsin. Cool Springs Press. p. 136. ISBN 978-1-61058-960-4.
- Benjamin, McGarry & Gray (1997), p. 557
- Cunningham, Sally Jean (2000). Great Garden Companions: A Companion-Planting System for a Beautiful, Chemical-Free Vegetable Garden. Rodale. pp. 195–196. ISBN 978-0-87596-847-6.
- Abbott, Catherine (2012). The Year-Round Harvest: A Seasonal Guide to Growing, Eating, and Preserving the Fruits and Vegetables of Your Labor. Adams Media. pp. 54–55. ISBN 978-1-4405-2816-3.
- Production guidelines for carrot (PDF) (Report). Agriculture, Forestry & Fisheries Department: Republic of South Africa.
- Davis, R. Michael (2004). "Carrot diseases and their management". In Naqvi S.A.M.H. (ed.). Diseases of Fruits and Vegetables: Diagnosis and Management. Springer. pp. 397–439. ISBN 978-1-4020-1822-0.
- "Carrot cavity spot". University of California Agriculture & Natural Resources. September 2012. Retrieved 21 March 2013.
- Benjamin, McGarry & Gray (1997), pp. 570–571
- Riotte, L. (1998). Carrots Love Tomatoes: Secrets of Companion Planting for Successful Gardening. Storey Publishing, LLC. p. 10. ISBN 978-1-60342-396-0.
- Carr, Anna (1998). Rodale's Illustrated Encyclopedia of Herbs. Rodale. p. 112. ISBN 978-0-87596-964-0.
- Grubben, G.J.H. (2004). Vegetables. Plant Resources of Tropical Africa. p. 282. ISBN 978-90-5782-147-9.
- Tiwari, B.K.; Brunton, Nigel P.; Brennan, Charles (2012). Handbook of Plant Food Phytochemicals: Sources, Stability and Extraction. John Wiley & Sons. p. 405. ISBN 978-1-118-46467-0.
- "Scientists unveil 'supercarrot'". BBC News. 15 January 2008. Retrieved 22 March 2013.
- "Carrots History" Retrieved on 2009-02-26
- Luby, C. H; Maeda, H. A; Goldman, I. L (2014). "Genetic and phenological variation of tocochromanol (vitamin E) content in wild (Daucus carota L. Var. Carota) and domesticated carrot (D. Carota L. Var. Sativa)". Horticulture Research. 1: 14015–. doi:10.1038/hortres.2014.15. PMC 4596321. PMID 26504534.
- "Production of carrots and turnips in 2020, Crops/Regions/World list/Production Quantity (pick lists)". UN Food and Agriculture Organization, Corporate Statistical Database (FAOSTAT). 2022. Retrieved 13 April 2022.
- Gist, Sylvia. "Successful Cold Storage". Backwoods Home Magazine. Archived from the original on 6 September 2011. Retrieved 21 March 2013.
- Owen, Marion. "What's Up Doc? Carrots!". UpBeat Gardener. PlanTea. Retrieved 21 March 2013.
- "Carrot Harvesting, Handling & Storage | Johnny's Selected Seeds".
- Hedrén, E.; Diaz, V.; Svanburg, U. (2002). "Estimation of carotenoid accessibility from carrots determined by an in vitro digestion method". European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 56 (5): 425–430. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601329. PMID 12001013.
- Martino, Robert S. (2006). Enjoyable Cooking. AuthorHouse. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-4259-6658-4.
- Gisslen, Wayne (2010). Professional Cooking, College Version. John Wiley & Sons. p. 146. ISBN 978-0-470-19752-3.
- Jeanine Donofrio (2019). "Waste not, want not". Love and Lemons Every Day: More than 100 Bright, Plant-Forward Recipes for Every Meal: A Cookbook. Penguin. ISBN 978-0-7352-1985-4.
- Michel Richard (2006). Happy in the Kitchen. Artisan Books. pp. 74 & 76. ISBN 978-1-57965-299-9.
- Rubatsky, Quiros & Siman (1999), p. 253
- Yeager, Selene; Editors of Prevention (2008). The Doctors Book of Food Remedies: The Latest Findings on the Power of Food to Treat and Prevent Health Problems – From Aging and Diabetes to Ulcers and Yeast Infections. Rodale. p. 366. ISBN 978-1-60529-506-0.
{{cite book}}:|author2=has generic name (help) - Brown, Ellen (2012). The Complete Idiot's Guide to Smoothies. DK Publishing. p. 21. ISBN 978-1-4362-9393-8.
- Burney, P.; Summers, C.; Chinn, S.; Hooper, R.; Van Ree, R.; Lidholm, J. (2010). "Prevalence and distribution of sensitization to foods in the European Community Respiratory Health Survey: A EuroPrevall analysis". Allergy. 65 (9): 1182–1188. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02346.x. PMID 20180791. S2CID 22718444.
- Ballmer-Weber, B.K.; Skamstrup Hansen, K.; Sastre, J.; Andersson, K.; Bätscher, I.; Ostling, J.; Dahl, L.; Hanschmann, K.M.; Holzhauser, T.; Poulsen, L.K.; Lidholm, J.; Vieths, S. (2012). "Component-resolved in vitro diagnosis of carrot allergy in three different regions of Europe". Allergy. 67 (6): 758–766. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2012.02827.x. PMID 22486768. S2CID 23864612.
- Gupta, Niru (2000). Cooking the Up Way. Orient Blackswan. p. 17. ISBN 978-81-250-1558-1.
- Chapman, Pat (2007). India Food and Cooking: The Ultimate Book on Indian Cuisine. New Holland Publishers. pp. 158–230. ISBN 978-1-84537-619-2.
- Bidlack, Wayne R.; Rodriguez, Raymond L. (2011). Nutritional Genomics: The Impact of Dietary Regulation of Gene Function on Human Disease. CRC Press. p. 321. ISBN 978-1-4398-4452-6.
- Rubatsky, Quiros & Siman (1999), p. 256
- Davidson, Alan (1999). The Oxford Companion to Food. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-211579-9.
- Shannon, Nomi (1998). The Raw Gourmet. Book Publishing Company. p. 33. ISBN 978-0-920470-48-0.
- Amy S. Paller; Anthony J. Mancini (23 May 2011). SPEC - Hurwitz Clinical Pediatric Dermatology E -Book 12Month Subscription: A Textbook of Skin Disorders of Childhood and Adolescence. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 264–. ISBN 978-1-4377-3613-7.
- "Nutrition facts for carrots, raw [Includes USDA commodity food A099], per 100 g, USDA Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, version SR-21". Conde Nast. 2014. Retrieved 10 December 2014.
- Abdel-Aal el-SM, Akhtar H, Zaheer K, Ali R (2013). "Dietary sources of lutein and zeaxanthin carotenoids and their role in eye health". Nutrients. 5 (4): 1169–85. doi:10.3390/nu5041169. PMC 3705341. PMID 23571649.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - Strube, Michael; OveDragsted, Lars (1999). Naturally Occurring Antitumourigens. IV. Carotenoids Except β-Carotene. Copenhagen: Nordic Council of Ministers. p. 48. ISBN 978-92-893-0342-2.
- Novotny, Janet A.; Dueker, S.R.; Zech, L.A.; Clifford, A.J. (1995). "Compartmental analysis of the dynamics of β-carotene metabolism in an adult volunteer". Journal of Lipid Research. 36 (8): 1825–1838. doi:10.1016/S0022-2275(20)41501-9. PMID 7595103.
- "Fact sheet for health professionals: Vitamin A". Office of Dietary Supplements, National Institutes of Health. 3 June 2013. Archived from the original on 17 May 2008. Retrieved 8 April 2008.
- Maron DF (23 June 2014). "Fact or Fiction?: Carrots Improve Your Vision". Scientific American. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- "Carrots in the Second World War". Carrot history. World Carrot Museum. Retrieved 8 September 2016.
- "A WWII Propaganda Campaign Popularized the Myth That Carrots Help You See in the Dark". Retrieved 7 July 2017.
Cited literature
- Benjamin, L. R.; McGarry, A.; Gray, D. (1997). "The root vegetables: Beet, carrot, parsnip and turnip". The Physiology of Vegetable Crops. Wallingford, UK: CAB International. pp. 553–580. ISBN 978-0-85199-146-7.
- Bradeen, James M.; Simon, Philipp W. (2007). "Carrot". In Cole, Chittaranjan (ed.). Vegetables. Genome Mapping and Molecular Breeding in Plants. Vol. 5. New York, NY: Springer. pp. 162–184. ISBN 978-3-540-34535-0.
- Rubatsky, V. E.; Quiros, C. F.; Siman, P. W. (1999). Carrots and Related Vegetable Umbelliferae. CABI Publishing. ISBN 978-0-85199-129-0.
- Simon, Philipp W.; Freeman, Roger E.; Vieira, Jairo V.; Boiteux, Leonardo S.; Briard, Mathilde; Nothnagel, Thomas; Michalik, Barbara; Kwon, Young-Seok (2008). "Carrot". Vegetables II. Handbook of Plant Breeding. Vol. 2. New York, NY: Springer. pp. 327–357. ISBN 978-0-387-74108-6.
External links
 Quotations related to Carrot at Wikiquote
Quotations related to Carrot at Wikiquote Media related to Daucus carota at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Daucus carota at Wikimedia Commons Media related to Carrots at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Carrots at Wikimedia Commons