Dnieper
The Dnieper (/ˈ(d)niːpər/) or Dnipro (/(d)niːˈproʊ/)[lower-alpha 1] is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus and the fourth-longest river in Europe, after the Volga, Danube, and Ural rivers.[2] It is approximately 2,200 km (1,400 mi) long,[3] with a drainage basin of 504,000 square kilometres (195,000 sq mi).
| Dnieper | |
|---|---|
 Dnieper Reservoir downstream from Dnipro city, Ukraine | |
 Dnieper River drainage basin | |
| Native name |
|
| Location | |
| Countries |
|
| Cities | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Valdai Hills, Russia |
| • coordinates | 55°52′18.08″N 33°43′27.08″E |
| • elevation | 220 m (720 ft) |
| Mouth | Dnieper Delta |
• location | Ukraine |
• coordinates | 46°30′00″N 32°20′00″E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 2,201 km (1,368 mi) |
| Basin size | 504,000 km2 (195,000 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Kherson |
| • average | 1,670 m3/s (59,000 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Sozh, Desna, Trubizh, Supiy, Sula, Psel, Vorskla, Samara, Konka, Bilozerka |
| • right | Drut, Berezina, Pripyat, Teteriv, Irpin, Stuhna, Ros, Tiasmyn, Bazavluk, Inhulets |
| Protection status | |
Ramsar Wetland | |
| Official name | Dnieper River Floodplain |
| Designated | 29 May 2014 |
| Reference no. | 2244[1] |
| Settlements next to the Dnieper Towns/villages blank spaces indicate as place above (") | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In antiquity, the river was part of the Amber Road trade routes. During the Ruin in the later 17th century, the area was contested between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia, dividing Ukraine into areas described by its right and left banks. During the Soviet period, the river became noted for its major hydroelectric dams and large reservoirs. The 1986 Chernobyl disaster occurred on the Pripyat, immediately above that tributary's confluence with the Dnieper. The Dnieper is an important navigable waterway for the economy of Ukraine and is connected by the Dnieper–Bug Canal to other waterways in Europe.
Names

.jpg.webp)
In English, the initial D in Dnieper is generally silent, although it may be sounded: /(d)ˈniːpər/ (D)NEE-pər. Nonrhotic accents will generally omit the final /r/ as well.[4][5] The name derives from the French transcription of the Russian form of the river's name. The pronunciation of Dnipro is usually with the accent on the second syllable: /(d)niːˈproʊ/ (d)nee-PRO.[6] Less commonly, it is pronounced with the accent on the first syllable, the second vowel becoming a schwa: /ˈ(d)niːprə/ (D)NEE-prə.[7]
The name varies slightly in the local Slavic languages of the three countries through which it flows:
- Belarusian: Дняпро, romanized: Dnyapro, [dnʲaˈprɔ], or Днепр Dnyepr,[8] [ˈdnʲɛpr]
- Russian: Днепр, tr. Dnepr, IPA: [dʲnʲepr]; formerly spelled Днѣпръ[9]
- Ukrainian: Дніпро, romanized: Dnipro, IPA: [ɟɲiˈprɔ] (
 listen); poetic Дніпр, Dnipr; formerly Дніпер[10] Dniper, [ˈɟɲiper], or older Днѣпръ (Dnipr, [ˈd(j)n(j)ipr])
listen); poetic Дніпр, Dnipr; formerly Дніпер[10] Dniper, [ˈɟɲiper], or older Днѣпръ (Dnipr, [ˈd(j)n(j)ipr])
These names are all cognate, deriving from Old East Slavic Дънѣпръ (Dŭněprŭ). The origin of this name is disputed but generally derived from either Sarmatian *Dānu Apara ("Farther River") in parallel with the Dniester ("Nearer River") or from Scythian *Dānu Apr ("Deep River") in reference to its lack of fords,[11][12] from which was also derived the Late Antique name of the river, Danapris (Δαναπρις).[13]
Another Scythian language name of the Dnipro was *Varustāna, meaning "having broad space," from which were derived:[14]
- the Graeco-Roman name of the river, Borysthenes (Βορυσθενης Borusthenēs; Latin: Borysthenes). This name was connected to the Graeco-Roman name of the Volga river, Oarus (Ancient Greek: Οαρος Oaros; Latin: Oarus), which was derived from Scythian *Varu, meaning "Broad."
- From Borysthenes was derived the river's poetic Latin name, Boristhenius[15]
- the Huns' name for the river, Var, from Scythian *Varu, "Broad."
During the period of Old Great Bulgaria, it was known as Buri-Chai and, under the Kievan Rus' it was known as Славу́тич (Slavútytch), a name still used poetically in Ukrainian due to the influence of the Old East Slavic epic The Tale of Igor's Campaign and its modern adaptations on Ukrainian literature. This usage also lent its name to the city of Slavutych, founded in the wake of the Chernobyl disaster in 1986 to house displaced workers.[16] The Kipchak Turks called it the Uzeu, the Crimean Tatars the Özü, and modern Turks the Özü or Özi.[17]
Geography
The total length of the river is variously given as 2,145 kilometres (1,333 mi)[3] or 2,201 km (1,368 mi),[18][19][20][21] of which 485 km (301 mi) are within Russia, 700 km (430 mi) are within Belarus,[3] and 1,095 km (680 mi) are within Ukraine. Its basin covers 504,000 square kilometres (195,000 sq mi), of which 289,000 km2 (112,000 sq mi) are within Ukraine,[22] 118,360 km2 (45,700 sq mi) are within Belarus.[3]
The source of the Dnieper is the sedge bogs (Akseninsky Mokh) of the Valdai Hills in central Russia, at an elevation of 220 m (720 ft).[22] For 115 km (71 mi) of its length, it serves as the border between Belarus and Ukraine. Its estuary, or liman, used to be defended by the strong fortress of Ochakiv.
The southernmost point in Belarus is on the Dnieper to the south of Kamaryn in Brahin Raion.[23]
Tributaries of the Dnieper

The Dnieper has many tributaries (up to 32,000) with 89 being rivers of 100+ km.[24] The main ones are, from its source to its mouth, with left (L) or right (R) bank indicated:

- Vyazma (L)
- Vop (R)
- Khmost (R)
- Myareya (L)
- Drut (R)
- Berezina (R)
- Sozh (L)
- Pripyat (R)
- Teteriv (R)
- Irpin (R)
- Desna (L)
- Stuhna (R)
- Trubizh (L)
- Ros (R)
- Tiasmyn (R)
- Supii (L)
- Sula (L)
- Psyol (L)
- Vorskla (L)
- Oril (L)
- Samara (L)
- Konka (L)
- Bilozerka (L)
- Bazavluk (R)
- Inhulets (R)
Many small direct tributaries also exist, such as, in the Kyiv area, the Syrets (right bank) in the north of the city, the historically significant Lybid (right bank) passing west of the centre, and the Borshahivka (right bank) to the south.
The water resources of the Dnieper basin compose around 80% out of all Ukraine.[24]
Rapids

.jpg.webp)
The Dnieper Rapids were part of the trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks, first mentioned in the Kyiv Chronicle. The route was probably established in the late eighth and early ninth centuries and gained significant importance from the tenth until the first third of the eleventh century. On the Dnieper the Varangians had to portage their ships round seven rapids, where they had to be on guard for Pecheneg nomads.
Along this middle flow of the Dnieper, there were 9 major rapids (although some sources cite a fewer number of them), obstructing almost the whole width of the river, about 30 to 40 smaller rapids, obstructing only part of the river, and about 60 islands and islets.
After the Dnieper hydroelectric station was built in 1932, they were inundated by Dnieper Reservoir.
Canals
There are a number of canals connected to the Dnieper:
- The Dnieper–Donbas Canal;
- The Dnieper–Kryvyi Rih Canal;
- The Kakhovka Canal (southeast of the Kherson region);
- The Krasnoznamianka Irrigation System in the southwest of the Kherson region;
- The North Crimean Canal—will largely solve the water problem of the peninsula, especially in the arid northern and eastern Crimea;
- The Inhulets Irrigation System.
Fauna
The river is part of the quagga mussel's native range.[25] The mussel has been accidentally introduced around the world, where it has become an invasive species.[25]
Estuary

The city of Kherson is nearest to the Dnieper estuary. It has no large port facilities.
Ecology
Nowadays the Dnieper River suffers from anthropogenic influence and obtain numerous emissions of pollutants.[26] The Dnieper is close to the Prydniprovsky Chemical Plant radioactive dumps (near Kamianske) and susceptible to leakage of its radioactive waste. The river is also close to the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Station (Chernobyl Exclusion Zone) that is located next to the mouth of the Pripyat River.
Navigation
Almost 2,000 km (1,200 mi) of the river is navigable (to the city of Dorogobuzh).[24] The Dnieper is important for transportation in the economy of Ukraine. Its reservoirs have large ship locks, allowing vessels of up to 270 by 18 metres (886 ft × 59 ft) access as far as the port of Kyiv, and thus are an important transportation corridor. The river is used by passenger vessels as well. Inland cruises on the rivers Danube and Dnieper have had a growing market in recent decades.
Upstream from Kyiv, the Dnieper receives the water of the Pripyat River. This navigable river connects to the Dnieper-Bug canal, the link with the Bug River. Historically, a connection with the Western European waterways was possible, but a weir without any ship lock near the town of Brest, Belarus, has interrupted this international waterway. Poor political relations between Western Europe and Belarus mean there is little likelihood of reopening this waterway in the near future.[27] River navigation is interrupted each year by freezing and severe winter storms.
Reservoirs and hydroelectric power

From the mouth of the Pripyat River to the Kakhovka Hydroelectric Station, there are six sets of dams and hydroelectric stations, which produce 10% of Ukraine's electricity.[24]
The first constructed was the Dnieper Hydroelectric Station (or DniproHES) near Zaporizhzhia, built between 1927 and 1932 with an output of 558 MW.[28] It was destroyed during World War II, but was rebuilt in 1948 with an output of 750 MW.
| Location | Dam | Reservoir area | Hydroelection station | Date of construction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kyiv | Kyiv Reservoir | 922 km2 or 356 sq mi | Kyiv Hydroelectric Station | 1960–1964 |
| Kaniv | Kaniv Reservoir | 675 km2 or 261 sq mi | Kaniv Hydroelectric Station | 1963–1975 |
| Kremenchuk | Kremenchuk Reservoir | 2,250 km2 or 870 sq mi | Kremenchuk Hydroelectric Station | 1954–1960 |
| Kamianske | Kamianske Reservoir | 567 km2 or 219 sq mi | Middle Dnieper Hydroelectric Power Plant | 1956–1964 |
| Zaporizhzhia | Dnieper Reservoir | 420 km2 or 160 sq mi | Dnieper Hydroelectric Station | 1927–1932; 1948 |
| Kakhovka | Kakhovka Reservoir | 2,155 km2 or 832 sq mi | Kakhovka Hydroelectric Station | 1950–1956 |
Regions and cities

Regions
|
|
|
- The Dnieper River in different regions
 The Dnieper River in Kyiv, Ukraine
The Dnieper River in Kyiv, Ukraine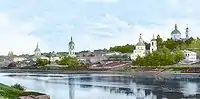 The Dnieper River in Dorogobuzh, Russian Empire, before 1917
The Dnieper River in Dorogobuzh, Russian Empire, before 1917 The Dnieper River in Kremenchuk, Ukraine
The Dnieper River in Kremenchuk, Ukraine
Cities
Major cities, over 100,000 in population, are in bold script. Cities and towns located on the Dnieper are listed in order from the river's source (in Russia) to its mouth (in Ukraine):
|
Arheimar, a capital of the Goths, was located on the Dnieper, according to the Hervarar saga.[29]
In the arts
Literature
The River Dnieper has been a subject of chapter X of a story by Nikolai Gogol A Terrible Vengeance (1831, published in 1832 as a part of the Evenings on a Farm Near Dikanka short stories collection). It is considered as a classical example of description of the nature in Russian literature. The river was also described in the works of Taras Shevchenko.
In the adventure novel The Long Ships (also translated Red Orm), set during the Viking Age, a Scanian chieftain travels to the Dnieper Rapids to retrieve a treasure hidden there by his brother, encountering many difficulties. The novel was very popular in Sweden and is one of few to depict a Viking voyage to eastern Europe.
Visual arts
The River Dnieper has been a subject for artists, great and minor, over the centuries. Major artists with works based on the Dnieper are Arkhip Kuindzhi and Ivan Aivazovsky.
Films
The River Dnieper makes an appearance in the 1964 Hungarian drama film The Sons of the Stone-Hearted Man (based on the novel of the same name by Mór Jókai), where it appears when two characters are leaving Saint Petersburg but get attacked by wolves.
In 1983, the concert program "Song of the Dnieper" from the "Victory Salute" series was released, dedicated to the 40th anniversary of the liberation of the city of Kiev from the German fascist invaders. The program includes songs by Soviet composers, Ukrainian folk songs, and dances performed by the Song and Dance Ensemble of the Kiev Military District led by A. Pustovalov, P. Virsky Ukrainian National Folk Dance Ensemble, Kyiv Bandurist Capella, the Military Band of the Headquarters of the Kiev Military District led by A. Kuzmenko, singers Anatoliy Mokrenko, Lyudmila Zykina, Anatoliy Solovianenko, Dmytro Hnatyuk, Mykola Hnatyuk. Filming on the battlefield, streets and squares of Kiev. Scriptwriter - Victor Meerovsky. Directed by Victor Cherkasov. Operator - Alexander Platonov.[30]
Volcano (2018 film) was filmed at this river in Beryslav, Kherson Oblast.
Image gallery
- The Dnieper in painting
 Catherine II leaving Kaniów in 1787 by Johann Gottlieb Plersch
Catherine II leaving Kaniów in 1787 by Johann Gottlieb Plersch Dnieper by Arkhip Kuindzhi, 1881
Dnieper by Arkhip Kuindzhi, 1881 Moonlit Night on the Dnieper by Arkhip Kuindzhi, 1882
Moonlit Night on the Dnieper by Arkhip Kuindzhi, 1882 Ice in the Dnieper by Ivan Aivazovsky, 1872
Ice in the Dnieper by Ivan Aivazovsky, 1872 Sapphire Dnieper by Jan Stanisławski, 1904
Sapphire Dnieper by Jan Stanisławski, 1904
Popular culture
- The river is one of the symbols of the Ukrainian nation[32] and is mentioned in the national anthem of Ukraine.
- There are several names that connect the name of the river with Ukraine: Overdnieper Ukraine, Right-bank Ukraine, Left-bank Ukraine, and others. Some of the cities on its banks — Dnipro, Dniprorudne, Kamianka-Dniprovska — are named after the river.
- The Zaporozhian Cossacks lived on the lower Dnieper and their name refers to their location "beyond the rapids".[33]
- The folk metal band Turisas have a song called "The Dnieper Rapids" on their 2007 album The Varangian Way.[34]
See also
- List of rivers of Russia
- List of rivers of Belarus
- List of rivers of Ukraine
- Trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks
Notes
- Russian: Днепр, romanized: Dnepr; Ukrainian: Дніпро, romanized: Dnipro pronounced [dʲnʲiˈprɔ] (
 listen); Belarusian: Дняпро, romanized: Dniapro.
listen); Belarusian: Дняпро, romanized: Dniapro.
References and footnotes
- "Dnieper River Floodplain". Ramsar Sites Information Service. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
- "Dnieper River". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 25 May 2022.
- "Main Geographic Characteristics of the Republic of Belarus. Main characteristics of the largest rivers of Belarus". Land of Ancestors. Data of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environmental Protection of the Republic of Belarus. 2011. Retrieved 27 September 2013.
- "Dnieper". Lexico UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 2 December 2020.
- "Dnieper". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Retrieved 25 July 2018.
- "Dnipro". Lexico Dictionaries | English. Archived from the original on 1 March 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- "Dnipro". Collins English Dictionary. Retrieved 9 March 2022.
- Блакітная кніга Беларусі: Энцыклапедыя. — Мінск: Беларуская Энцыклапедыя, 1994. — С. 144. — 415 с. — 10 000 экз.
- Турбин, Сергей Иванович (1879). "Днѣпр и приднѣпровье: Описаніе губерній, смоленкой, Минской. Черниговской, Киевской, Полтавской, Екатеринославской, Херсонской, Таврической и Курской".
- "Тлумачення / значення слова "ДНІПЕР" | Словник української мови. Словник Грінченка". hrinchenko.com.
- Mallory, J. P.; Mair, Victor H. (2000). The Tarim Mummies: Ancient China and the Mystery of the Earliest Peoples from the West. London: Thames and Hudson. p. 106. ISBN 0-500-05101-1.
- Абаев В. И. Осетинский язык и фольклор (Ossetian language and folklore). Moscow: Publishing house of Soviet Academy of Sciences, 1949. p. 236
- Smith, Philip (1854). "BORY´STHENES". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology. London: John Murray.
- Harmatta, János (1999). "Herodotus, Historian of the Cimmerians and the Scythians". In Reverdin, Olivier; Nenci, Giuseppe (eds.). Hérodote et les Peuples Non Grecs [Herodotus and the Non-Greek Peoples] (in French). Vandœuvres, Switzerland: Fondation Hardt pour l’étude de l’Antiquité classique. pp. 115–130. ISBN 978-3-774-92415-4.
- Lewis, Charlton; Short, Charles (1879). "Bŏrysthĕnes, is". A Latin Dictionary. Founded on Andrews' edition of Freund's Latin dictionary. revised, enlarged, and in great part rewritten by. Charlton T. Lewis, Ph.D. and. Charles Short, LL.D. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- Яцик, А. В.; Яковлєв, Є. О.; Осадчук, В. О. (2002). А. В. Яцика (ed.). До питання щодо спуску Київського водосховища (Do pytanni︠a︡ shchodo spusku kyïvsʹkoho vodoskhovyshcha) (in Ukrainian). Kiev: Оріяни (Oriany). pp. 6–12. ISBN 966-7373-78-9.
- Temel Öztürk (1988–2016). "ÖZÜ: Günümüzde Ukrayna sınırları içinde bulunan tarihî bir kale ve şehir.". TDV Encyclopedia of Islam (44+2 vols.) (in Turkish). Istanbul: Turkiye Diyanet Foundation, Centre for Islamic Studies.
- Zastavnyi, F. D. (2000). Physical Geography of Ukraine. Rivers of Ukraine. Dnieper. Forum. Kyiv.
- Masliak, P.; Shyshchenko, P. (1998). Heohrafii︠a︡ Ukraïny [Geography of Ukraine]. Zodiak-eko. Kyiv. ISBN 966-7090-06-X.
- "Website about Dnieper". Archived from the original on 21 February 2014. Retrieved 6 February 2014.
- Mishyna, Liliana. Hydrographic research of Dnieper river Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Derzhhidrohrafiya.
- Kubiyovych, Volodymyr; Ivan Teslia. "Dnieper River". Encyclopedia of Ukraine. Retrieved 19 January 2007.
- "Main Geographic Characteristics of the Republic of Belarus. Coordinates of the extreme points of the state frontier". Land of Ancestors. The Scientific and Production State Republican Unitary Enterprise "National Cadastre Agency" of the State Property Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 2011. Retrieved 20 September 2013.
- Splendid Dnieper. There is no straighter river. Ukrinform. 4 July 2015
- Benson, AJ. "Dreissena rostriformis bugensis Andrusov, 1897". Nonindigenous Aquatic Species. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2 May 2014.
- Snytko, V.; Shirokova, V.; Ozerova, N.; Romanova, O.; Sobisevich, A. (2017). "Hydrological situation of the Upper Dnieper". GeoConference SGEM. 17 (31): 379–384.
- "PC-Navigo – Dé routeplanner voor de binnenwateren". PC Navigo. Archived from the original on 9 November 2005.
- Edward A. Hewett, Victor H. Winston (1991). Milestones in Glasnost and Perestroyka: Politics and people. Brookings Institution. p. 19. ISBN 9780815736240.
The importance of Chernobyl' for Soviet industry is best illustrated by comparing it to the key energy project of Stalin's industrialization, the famous Dnieper hydroelectric station, completed in 1932. The largest European hydroelectric station of its time, it had a capacity of 560 MW.
- "An English translation of Hervar saga by Kershaw". Archived from the original on 28 March 2006. Retrieved 28 March 2006.
- Victory Salute. Song of the Dnieper (1983) on YouTube
- Kyiv Bandurist Capella - Song of the Dnieper on YouTube
- Work on the subject Ukrainian national symbols. Library of Ukrainian literature.
- "...the Zaporohjans whose name meant 'those who live beyond the cataracts'...", Henryk Sienkiewicz, With Fire and Sword, chap. 7.
- "Releases".
External links
- Kropotkin, Peter Alexeivitch; Bealby, John Thomas (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 8 (11th ed.). p. 349.
- Volodymyr Kubijovyč, Ivan Teslia, Dnieper River at the Encyclopedia of Ukraine
- Site about Dnieper—objects over the river, photos, facts
- Dnieper river charts
- "Комсомольская правда" об угрозах плотины Киевской ГЭС и водохранилища Archived 22 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- "Аргументы и факты" о реальных угрозах дамбы Киевского водохранилища и ГЭС Archived 25 January 2021 at the Wayback Machine
- "Известия" о проблематике плотины Киевского водохранилища и ГЭС
- Эксперт УНИАН об угрозах дамбы Киевского водохранилища