Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
| Abdominal pain | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Stomach ache, tummy ache, belly ache, belly pain |
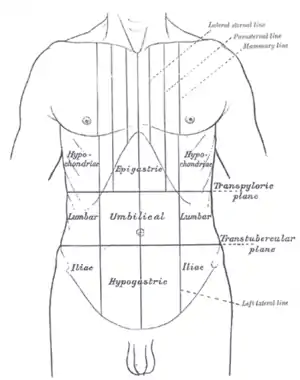 | |
| Abdominal pain can be characterized by the region it affects | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology General surgery |
| Causes | Serious: Appendicitis, perforated stomach ulcer, pancreatitis, ruptured diverticulitis, ovarian torsion, volvulus, ruptured aortic aneurysm, lacerated spleen or liver, ischemic colitis, ischaemic myocardial conditions[1] Common: Gastroenteritis, irritable bowel syndrome[2] |
Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome.[2] About 15% of people have a more serious underlying condition such as appendicitis, leaking or ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm, diverticulitis, or ectopic pregnancy.[2] In a third of cases the exact cause is unclear.[2]
Given that a variety of diseases can cause some form of abdominal pain, a systematic approach to the examination of a person and the formulation of a differential diagnosis remains important.[3]
Differential diagnosis
The most frequent reasons for abdominal pain are gastroenteritis (13%), irritable bowel syndrome (8%), urinary tract problems (5%), inflammation of the stomach (5%) and constipation (5%). In about 30% of cases, the cause is not determined. About 10% of cases have a more serious cause including gallbladder (gallstones or biliary dyskinesia) or pancreas problems (4%), diverticulitis (3%), appendicitis (2%) and cancer (1%).[2] More common in those who are older, ischemic colitis,[4] mesenteric ischemia, and abdominal aortic aneurysms are other serious causes.[5]
Acute abdominal pain
Acute abdomen can be defined as severe, persistent abdominal pain of sudden onset that is likely to require surgical intervention to treat its cause. The pain may frequently be associated with nausea and vomiting, abdominal distention, fever and signs of shock. One of the most common conditions associated with acute abdominal pain is acute appendicitis.[6]
Selected causes
- Traumatic: blunt or perforating trauma to the stomach, bowel, spleen, liver, or kidney
- Inflammatory:
- Infections such as appendicitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, pyelonephritis, Peritonitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, hepatitis, mesenteric adenitis, or a subdiaphragmatic abscess
- Perforation of a peptic ulcer, a diverticulum, or the caecum
- Complications of inflammatory bowel disease such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis
- Mechanical:
- Small bowel obstruction secondary to adhesions caused by previous surgeries, intussusception, hernias, benign or malignant neoplasms
- Large bowel obstruction caused by colorectal cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, volvulus, fecal impaction or hernia
- Vascular: occlusive intestinal ischemia, usually caused by thromboembolism of the superior mesenteric artery
By system
A more extensive list includes the following:
- Gastrointestinal
- GI tract
- Inflammatory: gastroenteritis, appendicitis, gastritis, esophagitis, diverticulitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, microscopic colitis
- Obstruction: hernia, intussusception, volvulus, post-surgical adhesions, tumors, severe constipation, hemorrhoids
- Vascular: embolism, thrombosis, hemorrhage, sickle cell disease, abdominal angina, blood vessel compression (such as celiac artery compression syndrome), superior mesenteric artery syndrome, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome
- Digestive: peptic ulcer, lactose intolerance, celiac disease, food allergies, indigestion
- Glands
- Bile system
- Inflammatory: cholecystitis, cholangitis
- Obstruction: cholelithiasis, tumours
- Liver
- Inflammatory: hepatitis, liver abscess
- Pancreatic
- Inflammatory: pancreatitis
- Bile system
- GI tract
- Renal and urological
- Inflammation: pyelonephritis, bladder infection
- Obstruction: kidney stones, urolithiasis, urinary retention, tumours
- Vascular: left renal vein entrapment
- Gynaecological or obstetric
- Inflammatory: pelvic inflammatory disease
- Mechanical: ovarian torsion
- Endocrinological: menstruation, Mittelschmerz
- Tumors: endometriosis, fibroids, ovarian cyst, ovarian cancer
- Pregnancy: ruptured ectopic pregnancy, threatened abortion
- Abdominal wall
- muscle strain or trauma
- muscular infection
- neurogenic pain: herpes zoster, radiculitis in Lyme disease, abdominal cutaneous nerve entrapment syndrome (ACNES), tabes dorsalis
- Referred pain
- from the thorax: pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, ischemic heart disease, pericarditis
- from the spine: radiculitis
- from the genitals: testicular torsion
- Metabolic disturbance
- uremia, diabetic ketoacidosis, porphyria, C1-esterase inhibitor deficiency, adrenal insufficiency, lead poisoning, black widow spider bite, narcotic withdrawal
- Blood vessels
- aortic dissection, abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Immune system
- sarcoidosis
- vasculitis
- familial Mediterranean fever
- Idiopathic
- irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)(affecting up to 20% of the population, IBS is the most common cause of recurrent and intermittent abdominal pain)
By location
The location of abdominal pain can provide information about what may be causing the pain. The abdomen can be divided into four regions called quadrants. Locations and associated conditions include:[7][8]
- Diffuse
- Peritonitis
- Vascular: mesenteric ischemia, ischemic colitis, Henoch-Schonlein purpura, sickle cell disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, polyarteritis nodosa
- Small bowel obstruction
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Metabolic disorders: ketoacidosis, porphyria, familial Mediterranean fever, adrenal crisis
- Epigastric
- Heart: myocardial infarction, pericarditis
- Stomach: gastritis, stomach ulcer, stomach cancer
- Pancreas: pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer
- Intestinal: duodenal ulcer, diverticulitis, appendicitis
- Right upper quadrant
- Liver: hepatomegaly, fatty liver, hepatitis, liver cancer, abscess
- Gallbladder and biliary tract: inflammation, gallstones, worm infection, cholangitis
- Colon: bowel obstruction, functional disorders, gas accumulation, spasm, inflammation, colon cancer
- Other: pneumonia, Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome
- Left upper quadrant
- Splenomegaly
- Colon: bowel obstruction, functional disorders, gas accumulation, spasm, inflammation, colon cancer
- Peri-umbilical (the area around the umbilicus, aka the belly button)
- Appendicitis
- Pancreatitis
- Inferior myocardial infarction
- Peptic ulcer
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Vascular: aortic dissection, aortic rupture
- Bowel: mesenteric ischemia, Celiac disease, inflammation, intestinal spasm, functional disorders, small bowel obstruction
- Lower abdominal pain
- Right lower quadrant
- Colon: intussusception, bowel obstruction, appendicitis (McBurney's point)
- Renal: kidney stone (nephrolithiasis), pyelonephritis
- Pelvic: cystitis, bladder stone, bladder cancer, pelvic inflammatory disease, pelvic pain syndrome
- Gynecologic: endometriosis, intrauterine pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy, ovarian cyst, ovarian torsion, fibroid (leiomyoma), abscess, ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer
- Left lower quadrant
- Bowel: diverticulitis, sigmoid colon volvulus, bowel obstruction, gas accumulation, Toxic megacolon
- Right low back pain
- Liver: hepatomegaly
- Kidney: kidney stone (nephrolithiasis), complicated urinary tract infection
- Left low back pain
- Spleen
- Kidney: kidney stone (nephrolithiasis), complicated urinary tract infection
- Low back pain
- kidney pain (kidney stone, kidney cancer, hydronephrosis)
- Ureteral stone pain
Pathophysiology
| Region | Blood supply[9] | Innervation[10] | Structures[9] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foregut | Celiac artery | T5 - T9 | Pharynx
Lower respiratory tract Proximal duodenum Biliary tract |
| Midgut | Superior mesenteric artery | T10 - T12 | Distal duodenum
Cecum Ascending colon Proximal transverse colon |
| Hindgut | Inferior mesenteric artery | L1 - L3 | Distal transverse colon
Descending colon Sigmoid colon Superior anal canal |
Abdominal pain can be referred to as visceral pain or peritoneal pain. The contents of the abdomen can be divided into the foregut, midgut, and hindgut.[9] The foregut contains the pharynx, lower respiratory tract, portions of the esophagus, stomach, portions of the duodenum (proximal), liver, biliary tract (including the gallbladder and bile ducts), and the pancreas.[9] The midgut contains portions of the duodenum (distal), cecum, appendix, ascending colon, and first half of the transverse colon.[9] The hindgut contains the distal half of the transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, and superior anal canal.[9]
Each subsection of the gut has an associated visceral afferent nerve that transmits sensory information from the viscera to the spinal cord, traveling with the autonomic sympathetic nerves.[11] The visceral sensory information from the gut traveling to the spinal cord, termed the visceral afferent, is non-specific and overlaps with the somatic afferent nerves, which are very specific.[12] Therefore, visceral afferent information traveling to the spinal cord can present in the distribution of the somatic afferent nerve; this is why appendicitis initially presents with T10 periumbilical pain when it first begins and becomes T12 pain as the abdominal wall peritoneum (which is rich with somatic afferent nerves) is involved.[12]
Diagnosis
A thorough patient history and physical examination is used to better understand the underlying cause of abdominal pain.
The process of gathering a history may include:[13]
- Identifying more information about the chief complaint by eliciting a history of present illness; i.e. a narrative of the current symptoms such as the onset, location, duration, character, aggravating or relieving factors, and temporal nature of the pain. Identifying other possible factors may aid in the diagnosis of the underlying cause of abdominal pain, such as recent travel, recent contact with other ill individuals, and for females, a thorough gynecologic history.
- Learning about the patient's past medical history, focusing on any prior issues or surgical procedures.
- Clarifying the patient's current medication regimen, including prescriptions, over-the-counter medications, and supplements.
- Confirming the patient's drug and food allergies.
- Discussing with the patient any family history of disease processes, focusing on conditions that might resemble the patient's current presentation.
- Discussing with the patient any health-related behaviors (e.g. tobacco use, alcohol consumption, drug use, and sexual activity) that might make certain diagnoses more likely.
- Reviewing the presence of non-abdominal symptoms (e.g., fever, chills, chest pain, shortness of breath, vaginal bleeding) that can further clarify the diagnostic picture.
- Using Carnett's sign to differentiate between visceral pain and pain originating in the muscles of the abdominal wall.[14]
After gathering a thorough history, one should perform a physical exam in order to identify important physical signs that might clarify the diagnosis, including a cardiovascular exam, lung exam, thorough abdominal exam, and for females, a genitourinary exam.[13]
Additional investigations that can aid diagnosis include:[15]
- Blood tests including complete blood count, basic metabolic panel, electrolytes, liver function tests, amylase, lipase, troponin I, and for females, a serum pregnancy test.
- Urinalysis
- Imaging including chest and abdominal X-rays
- Electrocardiogram
If diagnosis remains unclear after history, examination, and basic investigations as above, then more advanced investigations may reveal a diagnosis. Such tests include:[15]
- Computed tomography of the abdomen/pelvis
- Abdominal or pelvic ultrasound
- Endoscopy and/or colonoscopy
Management
The management of abdominal pain depends on many factors, including the etiology of the pain. In the emergency department, a person presenting with abdominal pain may initially require IV fluids due to decreased intake secondary to abdominal pain and possible emesis or vomiting.[16] Treatment for abdominal pain includes analgesia, such as non-opioid (ketorolac) and opioid medications (morphine, fentanyl).[16] Choice of analgesia is dependent on the cause of the pain, as ketorolac can worsen some intra-abdominal processes.[16] Patients presenting to the emergency department with abdominal pain may receive a "GI cocktail" that includes an antacid (examples include omeprazole, ranitidine, magnesium hydroxide, and calcium chloride) and lidocaine.[16] After addressing pain, there may be a role for antimicrobial treatment in some cases of abdominal pain.[16] Butylscopolamine (Buscopan) is used to treat cramping abdominal pain with some success.[17] Surgical management for causes of abdominal pain includes but is not limited to cholecystectomy, appendectomy, and exploratory laparotomy.
Emergencies
Below is a brief overview of abdominal pain emergencies.
| Condition | Presentation | Diagnosis | Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appendicitis[18] | Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever
Periumbilical pain, migrates to RLQ |
Clinical (history & physical exam)
Abdominal CT |
Patient made NPO (nothing by mouth)
IV fluids as needed General surgery consultation, possible appendectomy Antibiotics Pain control |
| Cholecystitis[18] | Abdominal pain (RUQ, radiates epigastric), nausea, vomiting, fever, Murphy's sign | Clinical (history & physical exam)
Imaging (RUQ ultrasound) Labs (leukocytosis, transamintis, hyperbilirubinemia) |
Patient made NPO (nothing by mouth)
IV fluids as needed General surgery consultation, possible cholecystectomy Antibiotics Pain, nausea control |
| Acute pancreatitis[18] | Abdominal pain (sharp epigastric, shooting to back), nausea, vomiting | Clinical (history & physical exam)
Labs (elevated lipase) Imaging (abdominal CT, ultrasound) |
Patient made NPO (nothing by mouth)
IV fluids as needed Pain, nausea control Possibly consultation of general surgery or interventional radiology |
| Bowel obstruction[18] | Abdominal pain (diffuse, crampy), bilious emesis, constipation | Clinical (history & physical exam)
Imaging (abdominal X-ray, abdominal CT) |
Patient made NPO (nothing by mouth)
IV fluids as needed Nasogastric tube placement General surgery consultation Pain control |
| Upper GI bleed[18] | Abdominal pain (epigastric), hematochezia, melena, hematemesis, hypovolemia | Clinical (history & physical exam, including digital rectal exam)
Labs (complete blood count, coagulation profile, transaminases, stool guaiac) |
Aggressive IV fluid resuscitation
Blood transfusion as needed Medications: proton pump inhibitor, octreotide Stable patient: observation Unstable patient: consultation (general surgery, gastroenterology, interventional radiology) |
| Lower GI Bleed[18] | Abdominal pain, hematochezia, melena, hypovolemia | Clinical (history & physical exam, including digital rectal exam)
Labs (complete blood count, coagulation profile, transaminases, stool guaiac) |
Aggressive IV fluid resuscitation
Blood transfusion as needed Medications: proton pump inhibitor Stable patient: observation Unstable patient: consultation (general surgery, gastroenterology, interventional radiology) |
| Perforated Viscous[18] | Abdominal pain (sudden onset of localized pain), abdominal distension, rigid abdomen | Clinical (history & physical exam)
Imaging (abdominal X-ray or CT showing free air) Labs (complete blood count) |
Aggressive IV fluid resuscitation
General surgery consultation Antibiotics |
| Volvulus[18] | Sigmoid colon volvulus: Abdominal pain (>2 days, distention, constipation)
Cecal volvulus: Abdominal pain (acute onset), nausea, vomiting |
Clinical (history & physical exam)
Imaging (abdominal X-ray or CT) |
Sigmoid: Gastroenterology consultation (flexibile sigmoidoscopy)
Cecal: General surgery consultation (right hemicolectomy) |
| Ectopic pregnancy[18] | Abdominal and pelvic pain, bleeding
If ruptured ectopic pregnancy, the patient may present with peritoneal irritation and hypovolemic shock |
Clinical (history & physical exam)
Labs: complete blood count, urine pregnancy test followed with quantitative blood beta-hCG Imaging: transvaginal ultrasound |
If patient is unstable: IV fluid resuscitation, urgent obstetrics and gynecology consultation
If patient is stable: continue diagnostic workup, establish OBGYN follow-up |
| Abdominal aortic aneurysm[18] | Abdominal pain, flank pain, back pain, hypotension, pulsatile abdominal mass | Clinical (history & physical exam)
Imaging: Ultrasound, CT angiography, MRA/magnetic resonance angiography |
If patient is unstable: IV fluid resuscitation, urgent surgical consultation
If patient is stable: admit for observation |
| Aortic dissection[18] | Abdominal pain (sudden onset of epigastric or back pain), hypertension, new aortic murmur | Clinical (history & physical exam)
Imaging: Chest X-Ray (showing widened mediastinum), CT angiography, MRA, transthoracic echocardiogram/TTE, transesophageal echocardiogram/TEE |
IV fluid resuscitation
Blood transfusion as needed (obtain type and cross) Medications: reduce blood pressure (sodium nitroprusside plus beta blocker or calcium channel blocker) Surgery consultation |
| Liver injury[18] | After trauma (blunt or penetrating), abdominal pain (RUQ), right rib pain, right flank pain, right shoulder pain | Clinical (history & physical exam)
Imaging: FAST examination, CT of abdomen and pelvis Diagnostic peritoneal aspiration and lavage |
Resuscitation (Advanced Trauma Life Support) with IV fluids (crystalloid) and blood transfusion
If patient is unstable: general or trauma surgery consultation with subsequent exploratory laparotomy |
| Splenic injury[18] | After trauma (blunt or penetrating), abdominal pain (LUQ), left rib pain, left flank pain | Clinical (history & physical exam)
Imaging: FAST examination, CT of abdomen and pelvis Diagnostic peritoneal aspiration and lavage |
Resuscitation (Advanced Trauma Life Support) with IV fluids (crystalloid) and blood transfusion
If patient is unstable: general or trauma surgery consultation with subsequent exploratory laparotomy and possible splenectomy If patient is stable: medical management, consultation of interventional radiology for possible arterial embolization |
Epidemiology
Abdominal pain is the reason about 3% of adults see their family physician.[2] Rates of emergency department (ED) visits in the United States for abdominal pain increased 18% from 2006 through to 2011. This was the largest increase out of 20 common conditions seen in the ED. The rate of ED use for nausea and vomiting also increased 18%.[19]
References
- Patterson JW, Dominique E (14 November 2018). "Acute Abdomenal". StatPearls. PMID 29083722.
- Viniol A, Keunecke C, Biroga T, Stadje R, Dornieden K, Bösner S, et al. (October 2014). "Studies of the symptom abdominal pain--a systematic review and meta-analysis". Family Practice. 31 (5): 517–29. doi:10.1093/fampra/cmu036. PMID 24987023.
- "differential diagnosis". Merriam-Webster (Medical dictionary). Retrieved 30 December 2014.
- Hung, Alex; Calderbank, Tom; Samaan, Mark A.; Plumb, Andrew A.; Webster, George (1 January 2021). "Ischaemic colitis: practical challenges and evidence-based recommendations for management". Frontline Gastroenterology. 12 (1): 44–52. doi:10.1136/flgastro-2019-101204. ISSN 2041-4137.
- Spangler R, Van Pham T, Khoujah D, Martinez JP (2014). "Abdominal emergencies in the geriatric patient". International Journal of Emergency Medicine. 7: 43. doi:10.1186/s12245-014-0043-2. PMC 4306086. PMID 25635203.
- "Appendicitis". The Lecturio Medical Concept Library. Retrieved 1 July 2021.
- Masters P (2015). IM Essentials. American College of Physicians. ISBN 9781938921094.
- LeBlond RF (2004). Diagnostics. US: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. ISBN 978-0-07-140923-0.
- Moore KL (2016). "11". The Developing Human Tenth Edition. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier, Inc. pp. 209–240. ISBN 978-0-323-31338-4.
- Hansen JT (2019). "4: Abdomen". Netter's Clinical Anatomy, 4e. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier. pp. 157–231. ISBN 978-0-323-53188-7.
- Drake RL, Vogl AW, Mitchell AW (2015). "4: Abdomen". Gray's Anatomy For Students (Third ed.). Churchill Livingstone Elsevier. pp. 253–420. ISBN 978-0-7020-5131-9.
- Neumayer L, Dangleben DA, Fraser S, Gefen J, Maa J, Mann BD (2013). "11: Abdominal Wall, Including Hernia". Essentials of General Surgery, 5e. Baltimore, MD: Wolters Kluwer Health.
- Bickley L (2016). Bates' Guide to Physical Examination & History Taking. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9781469893419.
- ANP-BC, Karen M. Myrick, DNP, APRN, FNP-BC; ANP-BC, Laima Karosas, PhD, APRN, FNP-BC (6 December 2019). Advanced Health Assessment and Differential Diagnosis: Essentials for Clinical Practice. Springer Publishing Company. p. 250. ISBN 978-0-8261-6255-7.
- Cartwright SL, Knudson MP (April 2008). "Evaluation of acute abdominal pain in adults". American Family Physician. 77 (7): 971–8. PMID 18441863.
- Mahadevan SV. Essentials of Family Medicine 6e. p. 149.
- Tytgat GN (2007). "Hyoscine butylbromide: a review of its use in the treatment of abdominal cramping and pain". Drugs. 67 (9): 1343–57. doi:10.2165/00003495-200767090-00007. PMID 17547475. S2CID 46971321.
- Sherman SC, Cico SJ, Nordquist E, Ross C, Wang E (2016). Atlas of Clinical Emergency Medicine. Wolters Kluwer. ISBN 978-1-4511-8882-0.
- Skiner HG, Blanchard J, Elixhauser A (September 2014). "Trends in Emergency Department Visits, 2006-2011". HCUP Statistical Brief #179. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.