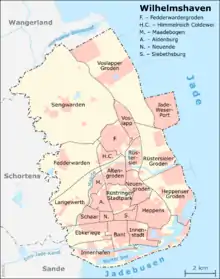
Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven (German pronunciation: [vɪlhɛlmsˈhaːfn̩] (![]() listen), lit. Wilhelm's Harbour; Northern Low Saxon: Willemshaven) is a coastal town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the western side of the Jade Bight, a bay of the North Sea, and has a population of 76,089.[3] Wilhelmshaven is the centre of the "Jade Bay" business region (which has around 330,000 inhabitants) and is Germany's main military port.
listen), lit. Wilhelm's Harbour; Northern Low Saxon: Willemshaven) is a coastal town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the western side of the Jade Bight, a bay of the North Sea, and has a population of 76,089.[3] Wilhelmshaven is the centre of the "Jade Bay" business region (which has around 330,000 inhabitants) and is Germany's main military port.
Wilhelmshaven | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Wilhelmshaven  | |
 Wilhelmshaven  Wilhelmshaven | |
| Coordinates: 53°31′43″N 08°06′20″E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Lower Saxony |
| District | Urban district |
| Government | |
| • Lord mayor (2019–24) | Carsten Feist[1] (Ind.) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 106.91 km2 (41.28 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 2 m (7 ft) |
| Population (2020-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 75,189 |
| • Density | 700/km2 (1,800/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 26351–26389 |
| Dialling codes | 04421, 04423, and 04425 (each partially) |
| Vehicle registration | WHV |
| Website | www.wilhelmshaven.de |
The adjacent Lower Saxony Wadden Sea National Park (part of the Wattenmeer UNESCO World Natural Heritage Site) provides the basis for the major tourism industry in the region.
History
The Siebethsburg castle, built before 1383, operated as a pirate stronghold; the Hanseatic League destroyed it in 1433. Four centuries later, the Kingdom of Prussia planned a fleet and a harbour on the North Sea. In 1853, Prince Adalbert of Prussia, a cousin of the Prussian King Frederick William IV, arranged the Jade Treaty (Jade-Vertrag) with the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg, in which Prussia and the Grand Duchy entered into a contract whereby Oldenburg ceded 3.13 km2 (1.21 sq mi) of its territory at the Jade Bight to Prussia. In 1869 King William I of Prussia (later also German Emperor) founded the town as an exclave of the Province of Hanover and a naval base for Prussia's developing fleet. All the hinterland of the city remained as part of the Duchy of Oldenburg.
A shipbuilding yard developed at Wilhelmshaven, the Kaiserliche Werft Wilhelmshaven (Wilhelmshaven Imperial Shipyard). On 30 June 1934 the "pocket battleship" Admiral Graf Spee was launched at Wilhelmshaven.
In 1937 Wilhelmshaven and the adjacent village Rüstringen merged[4] and the united city, named Wilhelmshaven, became a part of the Free State of Oldenburg.
World War II
In World War II (1939–1945), Allied bombing destroyed two thirds of the town's buildings while the main target, the Naval Shipyard Wilhelmshaven, remained operational despite serious damage.[5] A major attack on residential areas of Wilhelmshaven was carried out on 15 October 1944. Various churches, hospitals, schools and many residential buildings were destroyed or severely damaged.[6] On 28 April 1945, the Canadian First Army captured Emden and the Polish First Armored Division captured Wilhelmshaven, and took the surrender of the entire garrison, including some 200 ships of the Kriegsmarine. The Poles remained as part of the Allied occupation forces until 1947. During the war, Alter Banter Weg (No. 1582 Wilhelmshaven), functioned as a subcamp of the Neuengamme concentration camp.
Since 1945
In 1947 the city council decided to seek a new emblem for the city. After the Control Commission for Germany – British Element (CCG/BE) had rejected several designs, Wilhelmshaven selected the image of a Frisian warrior (Rüstringer Friese), designed after a nail man erected in the city during the First World War to collect war donations.
Between 1947 and 1972 Wilhelmshaven was the home of Prince Rupert School, a comprehensive boarding school for children of British Army of the Rhine and Royal Air Force Germany personnel serving in West Germany. The school relocated to Rinteln in Lower Saxony in 1972, and closed in 2014. There is an active association of former Wilhelmshaven pupils called The Wilhelmshaven Association. After World War II the shipyard was totally disarmed under the British Commander in Chief, and of course many military buildings were damaged or vacant. While it was prohibited to establish any kind of military-linked businesses, Wilhelmshaven took the opportunity to provide a convenient location for the Olympia Werke, which became one of the most popular quality typewriter factories in the world. A workforce of 7,000 worker was employed there in 1953.[7]
A liquefied natural gas terminal for LNG ships is being built at Wilhelmshaven in 2022. Planning began in 2017,[8] but regulatory impediments delayed construction for years.[9] Following the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, as gas commitments from the Nord Stream 1 and Nord Stream 2 undersea Baltic pipelines became unreliable to unavailable, construction of the Wilhelmshaven LNG terminal was rapidly accelerated, with the aim of being operational to receive LNG in late 2022.[10][9][11]
Largest groups of foreign residents (as of 31 December 2018):
| 1,465 | |
| 594 | |
| 468 | |
| 467 | |
| 423 | |
| 410 | |
| 238 | |
| 190 | |
| 164 | |
Today
Wilhelmshaven is Germany's only deep-water port, and its largest naval base. Concerning the new plans for the Bundeswehr which took shape in 2011 it has become the largest military base in Germany as well.[12] The benefits of the deep shipping channel were already recognised at the end of the 1950s with the construction of the first oil tanker jetty. Wilhelmshaven has been the most important German import terminal for crude oil ever since. Pipelines from here supply refineries in the Rhine-Ruhr region and Hamburg. Other major business operations followed, and constructed jetties for crude oil and oil products, coal, and chemical products. Construction of a liquified natural gas (LNG) import regasification facility began in May 2022 to displace some of the pipeline gas imported from Russia.[13]
One of the main industrial sectors in Wilhelmshaven is the port industry with its wharves, sea port service companies, service providers and repair businesses, transhipment and handling businesses, and agencies, etc. The "JadeWeserPort" – Container Terminal Wilhelmshaven (CTW), operational since 2012 and the development of the neighbouring Freight Village provide prospects for employment in areas such as logistics and distribution. In 2016 Eurogate increased transhipment volume up to 480,000 Container (TEU). And since Volkswagen is interested in using the deep-water facilities the number of employed workers is assumed to rise from 400 to 600.[14]
Another element of the "Wilhelmshaven energy hub" programme is the chemical industry (refinery, PVC, and chlorine gas production), as well as power generation (two coal-fired power stations, wind power).
The German defence forces (German Navy, navy arsenal, logistics centre) together with the public sector, are the main pillars of the local employment market.
Sights





- The Jadestadion, the stadium of Regionalliga Nord club SV Wilhelmshaven
- Wasserturm Wilhelmshaven – water tower built in 1911 and a significant landmark of Wilhelmshaven city.
- Aquarium Wilhelmshaven, located on the Helgolandkai – a view of the oceans and underwater habitats around the world.
- The Botanischer Garten der Stadt Wilhelmshaven, a municipal botanical garden.
- The Deutsches Marinemuseum (Navy Museum), whose main exhibits are the former German Navy destroyer Mölders (D186), a submarine, and some smaller warships as well as an exhibition of German naval history from the 19th century onwards.
- UNESCO World Heritage Site Wadden Sea Visitor center. The large permanent interactive exhibition provides insight into the Wadden Sea environment. One of the special displays is the 14-metre-long skeleton of a sperm whale which beached on the island of Baltrum in 1994 and weighed 39 tonnes when alive. The whale's organs were preserved using plastination by Gunther von Hagens.
- The Küstenmuseum (Coastal Museum). The exhibition displays a broad spectrum of the past, present and future of the coast.
- The Bontekai, city harbor jetty, featuring the former light vessel "Weser" and the steam engine powered buoy layer "Kapitän Meyer", an active museum ship. During the "Jade Weekend" (late June) it is berth of tall sailing ships, too.
- The double swing bridge Kaiser-Wilhelm-Brücke ("Emperor Wilhelm Bridge") crosses an inlet of the Jade Bight. It was built from 1905 to 1907 and is considered to be one of Wilhelmshaven's landmarks.
- The Town Hall (Rathaus), a large brick building, constructed from 1927 to 1929 by the architect Fritz Höger as the town hall of the city of Rüstringen. It was severely damaged by bombs in 1944 and rebuilt from 1948 to 1953.
- Ruins of Sibetsburg Castle. It was built in 1383, conquered and dismantled in 1435.[15]
- The oldest church of the city is St. Jakobi Church at Neuende which was built about 1383 under the direction of the chieftain of Jever Edo Wiemken.[16] The Christus-und-Garnisionskirche, built in 1869 by the Prussian architect Friedrich Adler was heavily damaged by bombs in 1942 and rebuilt after the war.[17]
- Kopperhörner Mühle is a windmill dating from 1839 which was renovated in 1982 and 2000.[18]
- Kaiser-Wilhelm-Denkmal at the Friedrich-Wilhelm-Platz, a monument erected in memory of emperor Wilhelm I of Prussia in 1896, who was one of the founder of the city. After the statue had been melted down in 1942, it was reconstructed in 1994.
- The entrance building of the former Kaiserliche Marinewerft ("emperor's shipyard"), built in the 1870s.
- The building of the former Kaiserliche Westwerft ("emperor's western shipyard"), completed in 1913.
Every year in the first days of July, the big "Weekend on the Jade" event attracts hundreds of thousands of visitors to the big port, the southern beach and the navy arsenal. Another big event takes place at the end of the sailing season at the beginning of October when two dozen large sailing ships dock in Wilhelmshaven as part of the "JadeWeserPort Cup".
Notable people

- Eilhard Mitscherlich (1794–1863) a chemist, discovered crystallographic isomorphism in 1819.
- Kurt Doerry (1874–1947) track and field athlete, competed at the 1896 & 1900 Summer Olympics.
- Erhard Milch (1892–1972), field marshal who oversaw the development of the Luftwaffe
- Gustav Leffers (1895–1916), flying ace in World War I
- Ernst Paul Heinz Prüfer (1896–1934), Jewish mathematician
- Hans Hellmann (1903–1938), theoretical physicist; associated with the Hellmann–Feynman theorem
- Adalbert von Blanc (1907–1976) naval officer in WWII and admiral in the West German Navy.
- Klaus Riedel (1907–1944), rocket pioneer, worked on the V-2 missile programme at Peenemünde Army Research Center
- Otto von Bülow (1911–2006), U-boat commander in World War II, and captain in the Bundesmarine
- Henry Picker (1912–1988), lawyer, stenographer and author, co-transcribed Hitler's Table Talk
- Wilfried Struve (1914–1992), scientist working in astronomy and acoustics, son of Georg Hermann Struve
- Helmut Heißenbüttel (1921–1996), novelist and poet
- Hans Clarin (1929–2005), actor
- Karl Leister (born 1937), clarinetist with the Berlin Philharmonic Orchestra
- Hans-Michael Bock (born 1947), film historian, translator
- Gert Krawinkel (1947–2014), guitarist, founding member of the rock band Trio
- Rainer Fetting (born 1949), painter and sculptor
- Thomas Hengelbrock (born 1958), violinist, stage director and principal conductor of the NDR Symphony Orchestra
- Nico Beyer (born 1964), film director and producer
- Olaf Lies (born 1964), politician (SPD)
- Niels Högel (born 1976), serial killer
Twin towns – sister cities
Wilhelmshaven is twinned with:[19]
 Vichy, France (1965)
Vichy, France (1965) Norfolk, United States (1976)
Norfolk, United States (1976) Dunfermline, Scotland, United Kingdom (1979)
Dunfermline, Scotland, United Kingdom (1979) Bromberg, Austria (1980)
Bromberg, Austria (1980) Bydgoszcz, Poland (2006)
Bydgoszcz, Poland (2006)
See also
- Lake Bant
Citations
- "Verzeichnis der direkt gewählten Bürgermeister/-innen und Landräte/Landrätinnen". Landesamt für Statistik Niedersachsen. April 2021. Archived from the original on 17 November 2021. Retrieved 17 November 2021.
- Landesamt für Statistik Niedersachsen, LSN-Online Regionaldatenbank, Tabelle A100001G: Fortschreibung des Bevölkerungsstandes, Stand 31. Dezember 2020.
- "Landesamt für Statistik Niedersachsen". Archived from the original on 20 April 2019. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- "Wilhelmshaven". Luftschutzbunker Wilhelmshaven. Archived from the original on 20 July 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
- "Angriffe und Statistik". Homepage Luftschutzbunker Wilhelmshaven. Archived from the original on 25 April 2018. Retrieved 17 December 2017.
- "Uwe Karwath | Wilhelmshaven – Sehenswürdigkeiten von a bis Z – Teil 3". Archived from the original on 28 March 2022. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- "Olympiawerke jetzt AG = Die Zeit". 22 July 1954. Archived from the original on 12 November 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
- "Zeitung: LNG-Terminal in Wilhelmshaven wieder in Planung". Gas-Magazin (in German). Berlin. 20 October 2015. Archived from the original on 3 August 2017. Retrieved 9 August 2022.
- "Germany to upgrade two ports 'quickly' to receive shipped gas". Politico. 27 February 2022. Retrieved 8 August 2022.
- Oltermann, Philip (8 August 2022). "'We got too comfortable': the race to build an LNG terminal in north Germany". The Guardian. Retrieved 8 August 2022.
- "Germany says fifth floating LNG terminal to be built by end of 2022". Reuters. 19 July 2022. Retrieved 24 September 2022.
- "Wilhelmshaven wächst zum größten Bundeswehrstandort". Hamburger Abendblatt. 4 November 2011. Archived from the original on 29 September 2020. Retrieved 18 December 2017.
- Villegas, Paulina; Morris, Loveday (5 May 2022). "Germany begins construction of liquefied natural gas terminal". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 5 May 2022. Retrieved 5 May 2022.
- Wolschner, Klaus (5 October 2017), "VW entdeckt Wilhelmshaven", Tageszeitung TAZ: 41
- "Uwe Karwath | Wilhelmshaven – Sehenswürdigkeiten von a bis Z – Teil 4". Archived from the original on 10 June 2022. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- de:St.-Jakobi-Kirche (Neuende)
- "Uwe Karwath | Wilhelmshaven – Sehenswürdigkeiten von a bis Z – Teil 1". Archived from the original on 10 June 2022. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- "Uwe Karwath | Wilhelmshaven – Sehenswürdigkeiten von a bis Z – Teil 2". Archived from the original on 22 November 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- "Wilhelmshavens Städtepartnerschaften und Städtefreundschaften". wilhelmshaven.de (in German). Wilhelmshaven. Archived from the original on 28 June 2018. Retrieved 17 February 2021.
General sources
- Official German list of concentration camps Verzeichnis der Konzentrationslager und ihrer Außenkommandos (in German)
- Camp memorial Neuengamme (in German)
External links
- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 28 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 641–642.
 Media related to Wilhelmshaven (category) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Wilhelmshaven (category) at Wikimedia Commons Wilhelmshaven travel guide from Wikivoyage
Wilhelmshaven travel guide from Wikivoyage