New London, Connecticut
New London is a seaport city and a port of entry on the northeast coast of the United States, located at the mouth of the Thames River in New London County, Connecticut. It was one of the world's three busiest whaling ports for several decades beginning in the early 19th century, along with Nantucket and New Bedford, Massachusetts. The wealth that whaling brought into the city furnished the capital to fund much of the city's present architecture. The city subsequently became home to other shipping and manufacturing industries, but it has gradually lost most of its industrial heart.
City of New London | |
|---|---|
City | |
 New London skyline from Fort Griswold | |
 Seal | |
| Nickname: The Whaling City | |
| Motto: Mare Liberum | |
 Location in New London County, Connecticut | |
 New London Location in the United States and Connecticut  New London New London (Connecticut) | |
| Coordinates: 41°21′20″N 72°05′58″W | |
| State | |
| County | New London |
| Metropolitan area | New London |
| Settle | 1646 (Pequot Plantation) |
| Named | 1658 (New London) |
| Incorporated (city) | 1784 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–council |
| • Mayor | Michael E. Passero
City Council |
| Area | |
| • City | 10.61 sq mi (27.47 km2) |
| • Land | 5.62 sq mi (14.56 km2) |
| • Water | 4.99 sq mi (12.91 km2) |
| • Urban | 123.03 sq mi (318.66 km2) |
| Elevation | 56 ft (17 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • City | 27,367 |
| • Density | 4,868/sq mi (1,879.6/km2) |
| • Metro | 274,055 |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| ZIP code | 06320 |
| Area code | 860 |
| FIPS code | 09-52280 |
| GNIS feature ID | 0209237 |
| Airport | Groton–New London Airport |
| Major highways | |
| Commuter rail | |
| Website | |
New London is home to the United States Coast Guard Academy, Connecticut College, Mitchell College, and The Williams School. The Coast Guard Station New London and New London Harbor is home port to the Coast Guard Cutter Coho and the Coast Guard's tall ship Eagle. The city had a population of 27,367 at the 2020 census.[4] The Norwich–New London metropolitan area includes 21 towns and 274,055 people.
History



Colonial era
The area was called Nameaug by the Pequot Indians. John Winthrop, Jr. founded the first English settlement here in 1646, making it about the 13th town settled in Connecticut. Inhabitants informally referred to it as Nameaug or as Pequot after the tribe. In the 1650s, the colonists wanted to give the town the official name of London after London, England, but the Connecticut General Assembly wanted to name it Faire Harbour. The citizens protested, declaring that they would prefer it to be called Nameaug if it could not be officially named London.[5][6] The legislature relented, and the town was officially named New London on March 10, 1658.
American Revolution
The harbor was considered to be the best deep water harbor on Long Island Sound,[7] and consequently New London became a base of American naval operations during the American Revolutionary War and privateers where it has been said no port took more prizes than New London with between 400–800 being credited to New London privateers including the 1781 taking of supply ship Hannah, the largest prize taken during the war. Famous New Londoners during the American Revolution include Nathan Hale, William Coit, Richard Douglass, Thomas and Nathaniel Shaw, Gen. Samuel Parsons, printer Timothy Green, and Bishop Samuel Seabury.
New London was raided and much of it burned to the ground on September 6, 1781 in the Battle of Groton Heights by Norwich native Benedict Arnold in an attempt to destroy the Revolutionary privateer fleet and supplies of goods and naval stores within the city. It is often noted that this raid on New London and Groton was intended to divert General George Washington and the French Army under Rochambeau from their march on Yorktown, Virginia. The main defensive fort for New London was Fort Griswold, located across the Thames River in Groton. It was well known to Arnold, who sold its secrets to the British fleet so that they could avoid its artillery fire. The British overran New London's Fort Trumbull, while other soldiers moved in to attack Ft. Griswold across the river, commanded by Lieutenant Colonel William Ledyard. The British suffered great casualties at Ft. Griswold before the Americans were finally forced to surrender—whereupon the British stormed into and slaughtered most of the militia who defended it, including Colonel Ledyard. All told, more than 52 British soldiers and 83 defenders were killed, and more than 142 British and 39 defenders were wounded, many mortally. New London suffered over 6 defenders killed and 24 wounded, while Arnold and the British and Hessian raiding party suffered an equal amount.[8]
Connecticut's independent legislature made New London one of the first two cities brought from de facto to formalized incorporations in its January session of 1784, along with New Haven.
19th century
During the War of 1812, torpedoes were employed in attempts to destroy British vessels and protect American harbors. In fact, a submarine-deployed torpedo was used in an unsuccessful attempt to destroy HMS Ramillies while in New London's harbor. This prompted British Capt. Hardy to warn the Americans to cease efforts with the use of any "torpedo boat" in this "cruel and unheard-of warfare", or he would "order every house near the shore to be destroyed".[9]: 693
For several decades beginning in the early 19th century, New London was one of the three busiest whaling ports in the world, along with Nantucket and New Bedford, Massachusetts. The wealth that whaling brought into the city furnished the capital to fund much of the city's present architecture.
The New Haven and New London Railroad connected New London by rail to New Haven and points beyond by the 1850s. The Springfield and New London Railroad connected New London to Springfield, Massachusetts, by the 1870s.
Military presence
Several military installations have been part of New London's history, including the United States Coast Guard Academy and Coast Guard Station New London.[10] Most of these military installations have been located at Fort Trumbull. The first Fort Trumbull was an earthwork built 1775–1777 that took part in the Revolutionary War. The second Fort Trumbull was built 1839–1852 and still stands. By 1910, the fort's defensive function had been superseded by the new forts of the Endicott Program, primarily located on Fishers Island. The fort was turned over to the Revenue Cutter Service and became the Revenue Cutter Academy. The Revenue Cutter Service was merged into the United States Coast Guard in 1915, and the Academy relocated to its current site in 1932. During World War II, the Merchant Marine Officers Training School was located at Fort Trumbull. From 1950 to 1990, Fort Trumbull was the location for the Naval Underwater Sound Laboratory, which developed sonar and related systems for US Navy submarines. In 1990, the Sound Laboratory was merged with the Naval Underwater Systems Center in Newport, Rhode Island, and the New London facility was closed in 1996.[11][12]
The Naval Submarine Base New London is physically located in Groton, but submarines were stationed in New London during World War II and from 1951 to 1991. The submarine tender Fulton and Submarine Squadron 10 were based at State Pier in New London during this time. Squadron Ten was usually composed of eight to ten submarines and was the first all-nuclear submarine squadron. USS Fulton was decommissioned, after 50 years of service, in 1991 and Submarine Squadron 10 was disbanded at the same time. In the 1990s, State Pier was rebuilt as a container terminal.
During the Red Summer of 1919, there were a series of racial riots between white and black Navy men stationed in New London and Groton.[13][14][15]
Fort Trumbull

The neighborhood of Fort Trumbull once consisted of nearly two-dozen homes, but they were seized by the City of New London using eminent domain. This measure was supported in a 5–4 ruling in the 2005 Supreme Court case Kelo v. City of New London, and the homes were ultimately demolished by the city as part of an economic development plan. The site was slated to be redeveloped under this plan, but the chosen developer was not able to get financing and the project failed. The empty landscape of the Fort Trumbull area has been widely characterized as an example of government overreach and inefficiency.[16][17][18][19]
Geography

In terms of land area, New London is one of the smallest cities in Connecticut. Of the whole 10.76 square miles (27.9 km2), nearly half is water; 5.54 square miles (14.3 km2) is land.[20]
The town and city of New London are coextensive. Sections of the original town were ceded to form newer towns between 1705 and 1801. The towns of Groton, Ledyard, Montville, and Waterford, and portions of Salem and East Lyme, now occupy what had earlier been the outlying area of New London.[21]
New London is bounded on the west and north by the town of Waterford on the east by the Thames River and Groton and on the south by Long Island Sound.
Principal communities
- Downtown New London
- Ocean Beach
Other minor communities and geographic features include Bates Woods Park, Fort Trumbull, Glenwood Park, Green's Harbor Beach, Mitchell's Woods, Pequot Colony, Riverside Park, Old Town Mill.
Towns created from New London
New London originally had a larger land area when it was established. Towns set off since include:
- Stonington in 1649
- This large area ran from the Mystic River to the Pawcatuck River, including Pawcatuck, Wequetequock, and the easterly half of Mystic. It stretched inland from Long Island Sound to Lantern Hill.
- North Stonington was created from the northern half of Stonington in 1807.
- Groton in 1705
- Ledyard (originally North Groton) created from a part of Groton in 1836.
- Montville in 1786.
- Salem created from parts of Montville, Colchester, and Lyme in 1819
- Waterford in 1801.
- East Lyme created from parts of Waterford and Lyme in 1839.
- Fishers Island officially left Connecticut and became part of New York in 1879.
Climate
Using the Köppen climate classification New London has a temperate climate (called Humid Subtropical in some climate classifications). This zone is defined as having a monthly mean temperature above 26.4 °F (−3 C) but below 64.4 °F (18 C) in the coldest month.
The city experiences long, hot and humid summers, and cool to cold winters with snowfall on occasion. The city averages 2,300 hours of sunshine annually (higher than the USA average). New London lies in the broad transition zone between continental climates to the north in New England and southern Canada, and the Humid subtropical climates to the south of the middle and south Atlantic states.
From May to late September, the southerly flow from the Bermuda High creates hot and humid tropical weather conditions. Daytime heating produces occasional thunderstorms with heavy but brief downpours. Daytime highs in summer are normally near 80 °F, with occasional heat waves bringing high temperatures into the 90's °F. Spring and Fall are mild in New London, with daytime highs in the 55° to 70 °F range and lows in the 40° to 50 °F range. The seaside location of the city creates a long growing season compared to areas inland. The first frost in the New London area is normally not until late October or early November, almost three weeks later than parts of northern Connecticut. Winters are cool with a mix of rainfall and snowfall, or mixed precipitation. New London normally sees fewer than 25 days annually with snow cover. In mid-winter, there can be large differences in low temperatures between areas along the coastline and areas well inland, sometimes as much as 15 °F.
Tropical cyclones (hurricanes/tropical storms) have struck Connecticut and the New London metropolitan area, although infrequently. Hurricane landfalls have occurred along the Connecticut coast in 1903, 1938, 1944, 1954 (Carol), 1960 (Donna), 1985 (Gloria). Tropical Storm Irene (2011) also caused moderate damage along the Connecticut coast, as did Hurricane Sandy (which made landfall in New Jersey) in 2012.

The Connecticut shoreline (including New London) lies within the broad transition zone where so-called "subtropical indicator" plants and other broadleaf evergreens can successfully be cultivated. New London averages about 90 days annually with freeze, about the same as Baltimore, Maryland. As such, many varieties of Southern Magnolia, Needle Palms, Loblolly and Longleaf Pines, Crape Myrtles, Aucuba japonica, Camellia, trunking Yucca, hardy bananas, Monkey Puzzle, copious types of evergreen Hollies, many East Asian (non-holly) broadleaf evergreen trees and shrubs, and certain varieties of figs may be grown in private and public gardens. The growing season is quite long in New London. Like much of coastal Connecticut and Long Island, NY, it averages close to 200 frost free days.
New London lies at the cusp of USDA hardiness zones 6 and 7 (6b and 7a), with the southern quarter or so of land area in the city being in zone 7 according to the latest released hardiness zone map, making it similar in expected extreme minimum annual temperature to places like Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, Trenton, New Jersey, the Shenandoah Valley of Virginia, much of north-central Tennessee and the Ozarks of northern Arkansas. By the mid-to-late 21st century, the area is expected to fall within USDA zone 8 according to some models.[22][23][24]
Due to climate change, certain low-lying areas such as Ocean Beach in the southern part of the city are susceptible to rising sea levels and increasingly powerful fall/winter noreasters and summer/fall hurricanes.
| Climate data for New London (Groton) 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1957–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 69 (21) |
67 (19) |
78 (26) |
88 (31) |
91 (33) |
95 (35) |
101 (38) |
99 (37) |
93 (34) |
87 (31) |
79 (26) |
69 (21) |
101 (38) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 38.8 (3.8) |
40.8 (4.9) |
47.3 (8.5) |
56.9 (13.8) |
66.4 (19.1) |
75.2 (24.0) |
80.8 (27.1) |
79.8 (26.6) |
73.6 (23.1) |
63.3 (17.4) |
53.2 (11.8) |
44.1 (6.7) |
60.0 (15.6) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 31.3 (−0.4) |
32.9 (0.5) |
39.5 (4.2) |
48.9 (9.4) |
58.1 (14.5) |
67.3 (19.6) |
73.4 (23.0) |
72.5 (22.5) |
65.8 (18.8) |
55.2 (12.9) |
45.5 (7.5) |
36.8 (2.7) |
52.3 (11.3) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 23.8 (−4.6) |
24.9 (−3.9) |
31.6 (−0.2) |
40.9 (4.9) |
49.9 (9.9) |
59.3 (15.2) |
65.9 (18.8) |
65.1 (18.4) |
58.0 (14.4) |
47.1 (8.4) |
37.9 (3.3) |
29.5 (−1.4) |
44.5 (6.9) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −14 (−26) |
−12 (−24) |
0 (−18) |
14 (−10) |
30 (−1) |
38 (3) |
47 (8) |
41 (5) |
29 (−2) |
22 (−6) |
8 (−13) |
−10 (−23) |
−14 (−26) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.91 (99) |
3.42 (87) |
4.92 (125) |
4.40 (112) |
3.67 (93) |
3.93 (100) |
3.42 (87) |
4.19 (106) |
4.29 (109) |
4.42 (112) |
3.75 (95) |
4.59 (117) |
48.91 (1,242) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 5.8 (15) |
8.3 (21) |
3.9 (9.9) |
0.8 (2.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.5 (1.3) |
5.2 (13) |
24.5 (62) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 11.4 | 9.7 | 11.5 | 11.6 | 11.9 | 9.5 | 9.7 | 9.3 | 10.2 | 10.4 | 10.0 | 12.4 | 127.6 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 3.1 | 2.7 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 1.9 | 9.9 |
| Source: NOAA[25][26] | |||||||||||||
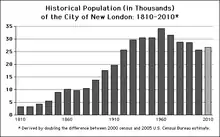
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1800 | 5,150 | — | |
| 1810 | 3,238 | −37.1% | |
| 1820 | 3,330 | 2.8% | |
| 1830 | 4,335 | 30.2% | |
| 1840 | 5,519 | 27.3% | |
| 1850 | 8,991 | 62.9% | |
| 1860 | 10,115 | 12.5% | |
| 1870 | 9,576 | −5.3% | |
| 1880 | 10,537 | 10.0% | |
| 1890 | 13,757 | 30.6% | |
| 1900 | 17,548 | 27.6% | |
| 1910 | 19,659 | 12.0% | |
| 1920 | 25,688 | 30.7% | |
| 1930 | 29,640 | 15.4% | |
| 1940 | 30,456 | 2.8% | |
| 1950 | 30,551 | 0.3% | |
| 1960 | 34,182 | 11.9% | |
| 1970 | 31,630 | −7.5% | |
| 1980 | 28,842 | −8.8% | |
| 1990 | 28,540 | −1.0% | |
| 2000 | 25,671 | −10.1% | |
| 2010 | 27,620 | 7.6% | |
| 2020 | 27,367 | −0.9% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
Demographics
Recent estimates on demographics and economic status
According to the 2006–2008 American Community Survey, non-Hispanic whites made up 54.6% of New London's population. Non-Hispanic blacks made up 14.0% of the population. Asians of non-Hispanic origin made up 4.6% of the city's population. Multiracial individuals of non-Hispanic origin made up 4.3% of the population; people of mixed black and white ancestry made up 1.7% of the population. In addition, people of mixed black and Native American ancestry made up 1.0% of the population. People of mixed white and Native American ancestry made up 0.7% of the population; those of mixed white and Asian ancestry made up 0.4% of the populace. Hispanics and Latinos made up 21.9% of the population, of which 13.8% were Puerto Rican.[27]
The top five largest European ancestry groups were Italian (10.5%), Irish (9.7%), German (7.4%), English (6.8%) and Polish (5.0%)
According to the survey, 74.4% of people over the age of 5 spoke only English at home. Approximately 16.0% of the population spoke Spanish at home.[28]
In 2012, the population reached 27,700. The median household income was $44,100, with 20% of the population below the poverty line.
2000 census
As of the census[29] of 2000, there were 25,671 people, 10,181 households, and 5,385 families residing in the city. The population density was 4,635.5 per square mile (1,789.8/km2). There were 11,560 housing units at an average density of 2,087.4 per square mile (805.9/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 63.5% White, 19.7% Hispanic or Latino of any race, 18.6% African American, 0.9% Native American, 2.1% Asian, 0.1% Pacific Islander, 9.1% from other races, and 5.7% from two or more races.
There were 10,181 households, out of which 27.6% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 30.4% were married couples living together, 17.8% had a female householder with no husband present, and 47.1% were non-families. 37.8% of all households were made up of individuals, and 10.7% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.26 and the average family size was 3.00.
In the city, the population was spread out, with 22.8% under the age of 18, 17.6% from 18 to 24, 29.6% from 25 to 44, 17.9% from 45 to 64, and 12.1% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 31 years. For every 100 females, there were 95.5 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 93.8 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $33,809, and the median income for a family was $38,942. Males had a median income of $31,405 versus $25,426 for females. The per capita income for the city was $18,437. About 13.4% of families and 15.8% of the population were below the poverty line, including 23.5% of those under age 18 and 11.4% of those age 65 or over.
Arts and culture

Eugene O'Neill
Nobel laureate and Pulitzer Prize-winning playwright Eugene O'Neill (1888–1953) lived in New London and wrote several plays in the city. An O'Neill archive is located at Connecticut College, and the family home, Monte Cristo Cottage,[30] is a museum and national historic landmark operated by the Eugene O'Neill Theater Center.
Music
Notable artists and ensembles include:
- Eastern Connecticut Symphony Orchestra, founded in 1946 and led by Toshiyuki Shimada, who is also conductor of the Yale Symphony Orchestra in New Haven.
- The Idlers of the United States Coast Guard Academy, an all-male vocal group specializing in sea shanties and patriotic music.
- United States Coast Guard Band, founded in 1925 with the assistance of John Philip Sousa. Stationed at the United States Coast Guard Academy and attracting talented musicians from all parts of the country, the band is the official musical representative of the nation's oldest continuous seagoing service.
- The Can Kickers, a folk punk band.
Sites of interest


- Lyman Allyn Art Museum
- Ocean Beach Park[31]
- New London County Historical Society, Shaw-Perkins Mansion (1758)[32]
- New London Maritime Society, U.S. Custom House (1833),[33] landing site of Amistad (1839)
- Fishers Island (7 miles off the coast of New London, but part of New York)[34]
- Connecticut College Arboretum
- Fort Griswold (Groton)
- Fort Trumbull
- United States Coast Guard Academy
- Coast Guard Station New London
- Flock Theatre[35]
- Garde Arts Center[36]
- Hygienic Arts Gallery[37]
- Joshua Hempsted House (1678)[38]
- Monte Cristo Cottage & Eugene O'Neill Theater Center (Waterford)[39]
- USS Nautilus (Groton)
- Ye Antientist Burial Ground
- Winthrop Mill (1650)
- Former Second Congregational Church (1870)[40]
- The Pequot Chapel (1872)
Government

In 2010, New London changed their form of government from council-manager to strong mayor-council after a charter revision.[41] Distinct town and city government structures formerly existed and technically continue; however, they now govern exactly the same territory and have elections on the same ballot on Election Day in November.
Infrastructure
Transportation

Downtown New London is served by regional Southeast Area Transit buses, the Estuary Transit District public transit service between the New London transportation center and Old Saybrook, and interstate Greyhound Lines buses. Interstate 95 passes through New London.
New London has frequent passenger rail service. New London Union Station is served by Amtrak's Northeast Regional and Acela Express regional rail services, plus Shore Line East (SLE) commuter rail service. The Providence & Worcester Railroad and the New England Central Railroad handle freight.
The city is also served by Cross Sound Ferry to Long Island, the Fishers Island Ferry District, and the Block Island Express ferry. New London is also visited by cruise ships.[42]
The Groton-New London Airport, a general aviation facility, is located in Groton. Scheduled commercial flights are available at T. F. Green and the much smaller Tweed New Haven Regional Airport. The larger Bradley International Airport is 75 minutes driving time.
Mayors of New London
Notable mayors include:
- Richard Law (1784–1806)[43]
- Elias Perkins (1829–1832)[43]
- Noyes Billings (1835–1837)[43]
- John Perkins Cushing Mather (1845–1850)[43]
- Hiram Willey (1862–1865)[43]
- Augustus Brandegee (1871–1873)[43]
- Thomas M. Waller (1873–1879)[43]
- Bryan F. Mahan (1903–1906)[43]
- Bryan F. Mahan (1909–1915)[43]
- Ernest E. Rogers (1915–1918)[43]
Notable people

- Eliphalet Adams (1677–1753), clergyman
- Theresa Andrews (born 1962), winner of two Olympic gold medals
- Peter C. Assersen (1839–1906), Rear Admiral in the United States Navy
- James Avery (1620–1700), politician and military commander
- Valerie Azlynn (born 1980), actress
- Gaten Matarazzo (born 2002), actor
- Scott Barlow, professional Baseball Pitcher for the Kansas City Royals
- Nathan Belcher (1813–1891), congressman
- Augustus Brandegee (1828–1904), judge, congressman, abolitionist
- Frank B. Brandegee (1864–1924), congressman and senator
- Amy Brenneman (born 1964), actress
- Henry Burbeck (1754–1848), brigadier general
- Daniel Burrows (1756–1858), congressman
- John Button (soldier) (1772–1861), American-born Upper Canada settler (founder of Buttonville, Ontario), sedentary Canadian militia officer and founder of the 1st York Light Dragoons
- William Colfax, Canadian soldier and settler
- Frances Manwaring Caulkins (1795–1869), historian, genealogist, author
- Thomas Humphrey Cushing (1755–1822), brigadier general in the War of 1812 and collector of customs
- John M. K. Davis, U.S. Army brigadier general; lived in New London during his retirement[44]
- Harry Daghlian (1921–1945), physicist at Los Alamos National Lab, first person to die as a result of a criticality accident
- A. J. Dillon (born 1998), American football running back
- David Dorfman (born 1955), choreographer
- Richard Douglass (1746–1828), cooper and soldier
- Grace L. Drake, Ohio state legislator
- Doug DuBose (born 1964), NFL player
- Kris Dunn (born 1994), point guard for the Chicago Bulls
- Larry Elgart (born 1922), musician
- John Ellis (born 1948), baseball player
- Elsie Ferguson (1883–1961), stage and film actress
- Richard P. Freeman (1869–1944), congressman
- William Goddard (publisher) (1740–1817), Co-founded US Post Office with Benjamin Franklin
- L. Patrick Gray (1916–2005), lawyer and Watergate figure
- Nathan Hale (1755–1776), schoolmaster and patriot
- Doc Hammer (born 1967), multimedium artist and co-creator of the Venture Brothers
- Matt Harvey (born 1989), MLB pitcher for the Cincinnati Reds
- Glenne Headly (1955–2017), actress
- Barkley L. Hendricks (born 1945), painter
- Jedediah Huntington (1743–1818), Revolutionary War General and New London Customs Collector
- Linda Jaivin (born 1955), Australian author[45]
- Sarah Kemble Knight (1666–1727), diarist, teacher and businesswoman
- Madeline Kripke (1943–2020), book collector
- John Law (1796–1873), congressman
- Bryan F. Mahan (1856–1923), congressman
- Richard Mansfield (1857–1907), actor
- John McCain (1936–2018), senator and Republican presidential nominee (lived in New London as a child when his father, John S. McCain, Jr., worked at the naval submarine base)
- Thomas Minor (1608–1690), founder and early New England diarist
- Casey Neistat (born 1981), filmmaker
- James R Newby (born 1844), was a Civil War veteran who served in the first regiment of volunteer African Americans in the United States and a 19th-century African-American missionary to present-day Nigeria, Cameroon, and Liberia[46]
- Hannah Ocuish (1774–1786), believed to be the youngest person executed in the United States
- James O'Neill (1847–1920), actor, father of Eugene O'Neill
- Eugene O'Neill (1888–1953), playwright
- Walter Palmer (1585–1661), founder
- Elias Perkins (1767–1845), congressman
- Mary Philips (1901–1975), actress
- Edward Clark Potter (1857–1923), sculptor
- Ellen Culver Potter (1871–1958), physician, public health official
- Renee Prahar (1879–1962), sculptor
- Art Quimby (1933–2010), basketball player
- Jordan Reed (born 1990), tight end for the Washington Redskins
- Tim Riordan (born 1960), gridiron football player
- Dawn Robinson (born 1965), singer
- Dudley Saltonstall (1738–1796), naval officer
- "Magic Dick" Salwitz (born 1945), musician
- Thomas R. Sargent III (1914–2010), Vice Admiral in the United States Coast Guard
- C. John Satti (1895–1968), Secretary of the State of Connecticut
- Samuel Seabury (1729–1796), bishop
- Benjamin Stark (1820–1898), senator
- Sigmund Strochlitz (1916–2006), activist and Holocaust survivor
- Dana Suesse (1909–1987), composer, songwriter, musician
- Ron Suresha, author and editor
- Flora M. Vare, (1874–1962), Pennsylvania State Senator from 1925 to 1928
- Cassie Ventura (born 1986), singer
- John T. Wait (1811–1899), former U.S. Representative for Connecticut[47]
- Thomas M. Waller (1839–1924), Mayor of New London and 51st Governor of Connecticut
- Mary Way (1769–1833), portrait miniaturist
- John Winthrop the Younger (1606–1676), statesman and founder
- Tyson Wheeler (born 1975), former Denver Nuggets basketball player[48]
- Abisha Woodward (1752–1809), early American lighthouse builder[49]
See also
- National Register of Historic Places in New London County, Connecticut
References
Notes
- "Office of the Mayor". City of New London, Connecticut. Retrieved June 11, 2017.
- "Council Members". City of New London, Connecticut. Retrieved June 11, 2017.
- "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- "Census - Geography Profile: New London town, New London County, Connecticut". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved December 18, 2021.
- Marrin, Richard B. (January 1, 2007). Abstracts from the New London Gazette Covering Southeastern Connecticut, 1763-1769. Heritage Books. p. 242. ISBN 978-0-7884-4171-4.
- Frances Manwaring Caulkins, History of New London, Connecticut, from the first survey of the coast in 1612 to 1860, Library of Congress, 1895.
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 19 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 515–516.
- "The Battle of Groton Heights & Burning of New London". Battleofgrotonheights.com. August 31, 2006. Retrieved October 28, 2011.
- Lossing, Benson (1868). The Pictorial Field-Book of the War of 1812. Harper & Brothers, Publishers. p. 692.
- Coast Guard Station New London official web page
- The History of Fort Trumbull by John Duchesneau
- Fort Trumbull History Site
- Rucker & Upton 2007, p. 554.
- The Greeneville Daily Sun 1919, p. 1.
- Voogd 2008, p. 95.
- Jacoby, Jeff (March 12, 2014). "Eminent disaster: Homeowners in Connecticut town were dispossessed for nothing". The Boston Globe.
- Allen, Charlotte (February 10, 2014). "'Kelo' Revisited". Weekly Standard. Retrieved October 23, 2014.
- Somin, Ilya (May 29, 2015). "The story behind Kelo v. City of New London – how an obscure takings case got to the Supreme Court and shocked the nation". The Washington Post.
- Downey, Kirstin (May 22, 2005). "Nation & World | Supreme Court ruling due on use of eminent domain". Seattle Times. Retrieved October 28, 2011.
- "New London County, Connecticut – County Subdivision and Place". American FactFinder. United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 16, 2020. Retrieved October 28, 2011.
- www.sots.ct.gov https://web.archive.org/web/20080314164126/http://www.sots.ct.gov/RegisterManual/SectionVII/townorder.htm. Archived from the original on March 14, 2008.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - "Redrawing the Map: How the World's Climate Zones Are Shifting".
- Parker, Lauren E.; Abatzoglou, John T. (2016). "Projected changes in cold hardiness zones and suitable overwinter ranges of perennial crops over the United States". Environmental Research Letters. 11 (3): 034001. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/11/3/034001.
- Parker, Lauren E.; Abatzoglou, John T. (2016). "Projected changes in cold hardiness zones and suitable overwinter ranges of perennial crops over the United States". Environmental Research Letters. 11 (3): 034001. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/11/3/034001.
- "NowData – NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved June 2, 2021.
- "Station: Groton, CT". U.S. Climate Normals 2020: U.S. Monthly Climate Normals (1991-2020). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved June 2, 2021.
- "New London city, Connecticut – ACS Demographic and Housing Estimates: 2006–2008". American FactFinder. United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 11, 2020. Retrieved October 28, 2011.
- "New London city, Connecticut – Selected Social Characteristics in the United States: 2006–2008". American FactFinder. United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 11, 2020. Retrieved October 28, 2011.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- "Monte Cristo Cottage". theoneill.com.
- Ocean Beach Park
- New London Historical Society
- New London Maritime Society
- Fishers Island
- Flock Theatre
- Garde Arts Center
- Hygienic Arts
- Joshua Hempsted House Archived July 3, 2008, at the Wayback Machine Connecticut Landmarks
- Eugene O'Neill Theater Center
- Morrison, Betty Urban (1985). The Church on the Hill: A history of the Second Congregational Church, New London, Connecticut 1835-1985. New London, Connecticut: Second Congregational Church. p. 17.
- "New Face Stirs Up Historic New London Election". tribunedigital-thecourant. Retrieved November 21, 2017.
- Howard, Lee (September 7, 2013). "Cruise ships returning to New London". The Day. Retrieved August 28, 2018.
- Marshall, Benjamin Tinkham (1922). A Modern History of New London County, Connecticut, Volume 1. New London, Connecticut: Lewis Historical Publishing Company. p. 238.
- "Mrs. John H. K. Davis". Hartford Courant. Hartford, CT. December 28, 1917. p. 8 – via Newspapers.com.
- Bio, Linda Jaivin's web site
- McHardie, Allan, Elizabeth, Andrew (1885). The Prodigal Continent and her Prodigal Son. London: Morgan & Scott.
- "Wait, John Turner". Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Retrieved October 10, 2012.
- Keefe, Gavin (March 20, 2015). "Wheeler on Dunn: New London basketball legend talks about legend-to-be". The New London Day. Retrieved August 13, 2015.
- Griswold, Wick (2012). A History of the Connecticut River. The History Press. pp. 96–97. ISBN 978-1609494056. Retrieved April 13, 2016.
Bibliography
- The Greeneville Daily Sun (May 31, 1919). "Race Riot at New London Naval Base". The Greeneville Daily Sun. Greeneville, Tennessee: W.R. Lyon. pp. 1–4. ISSN 2475-0174. OCLC 37307396. Retrieved July 19, 2019.
- Rucker, Walter C.; Upton, James N. (2007). Encyclopedia of American Race Riots, Volume 2. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 9780313333026. - Total pages: 930
- Voogd, Jan (2008). Race Riots and Resistance: The Red Summer of 1919. Peter Lang. ISBN 9781433100673. - Total pages: 234
External links
- Official website
- . Collier's New Encyclopedia. 1921.