Orhan
Orhan Ghazi (Ottoman Turkish: اورخان غازی; Turkish: Orhan Gazi, also spelled Orkhan, c. 1281 – March 1362) was the second bey of the Ottoman Beylik from 1323/4 to 1362. He was born in Söğüt, as the son of Osman I.
| Orhan | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bey Gazi | |||||
 16th century Ottoman miniature of Orhan Gazi | |||||
| 2nd Sultan of the Ottoman Empire | |||||
| Reign | 1323/4 – 1362 | ||||
| Predecessor | Osman I | ||||
| Successor | Murad I | ||||
| Born | c. 1281 | ||||
| Died | March 1362 (aged 80–81) Bursa, Ottoman Beylik | ||||
| Burial | |||||
| Spouses | Nilüfer Hatun Asporça Hatun Theodora Hatun Eftandise Hatun | ||||
| Issue | See below | ||||
| |||||
| Ottoman Turkish | اورخان غازی | ||||
| Turkish | Orhan Gazi | ||||
| Dynasty | Ottoman | ||||
| Father | Osman I | ||||
| Mother | Malhun Hatun (unclear)[1] | ||||
| Religion | Islam | ||||
| Tughra |  | ||||
In the early stages of his reign, Orhan focused his energies on conquering most of northwestern Anatolia. The majority of these areas were under Byzantine rule and he won his first battle at Pelekanon against the Byzantine Emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos. Orhan also occupied the lands of the Karasids of Balıkesir and the Ahis of Ankara.
A series of civil wars surrounding the ascension of the nine-year-old Byzantine emperor John V Palaiologos greatly benefited Orhan. In the Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347, the regent John VI Kantakouzenos married his daughter Theodora to Orhan and employed Ottoman warriors against the rival forces of the empress dowager, allowing them to loot Thrace. In the Byzantine civil war of 1352–1357, Kantakouzenos used Ottoman forces against John V, granting them the use of a European fortress at Çimpe around 1352.[2][3] A major earthquake devastated Gallipoli (modern Gelibolu) two years later, after which Orhan's son, Süleyman Pasha, occupied the town, giving the Ottomans a strong bridgehead into mainland Europe.
According to Muslim scholar Ibn Battuta, Orhan was "the greatest of the Turkmen kings and the richest in wealth, lands, and military forces".[4]
Passage of power
Osman Gazi died in either 1323 or 1324,[5] and Orhan succeeded him. According to Ottoman tradition, when Orhan succeeded his father, he proposed to his brother, Alaeddin, that they should share the emerging empire. The latter refused on the grounds that their father had designated Orhan as sole successor, and that the empire should not be divided. He only accepted as his share the revenues of a single village near Bursa.
Orhan then told him, "Since, my brother, thou will not take the flocks and the herds that I offer thee, be thou the shepherd of my people; be my Vizier." The word vizier, vezir in the Ottoman language, from Arabic wazīr, meant the bearer of a burden. Alaeddin, in accepting the office, accepted his brother's burden of power, according to oriental historians. Alaeddin, like many of his successors in that office, did not often command the armies in person, but he occupied himself with the foundation and management of the civil and military institutions of the state.
Government
According to some authorities, it was in Alaeddin's time, and by his advice, that the Ottomans ceased acting like vassals to the Seljuk ruler: they no longer stamped money with his image or used his name in public prayers. These changes are attributed by others to Osman himself, but the vast majority of the oriental writers concur in attributing to Alaeddin the introduction of laws respecting the costume of the various subjects of the empire, and the creation and funding of a standing army of regular troops. It was by his advice and that of a contemporary Turkish statesman that the celebrated corps of Janissaries was formed, an institution which European writers erroneously fix at a later date, and ascribe to Murad I.
Janissaries
Alaeddin, by his military legislation, may be truly said to have organized victory for the Ottoman dynasty. He organised for the Ottoman Beylik a standing army of regularly paid and disciplined infantry and horses, a full century before Charles VII of France established his fifteen permanent companies of men-at-arms, which are generally regarded as the first modern standing army.[6]
Orhan's predecessors, Ertuğrul and Osman I, had made war at the head of the armed vassals and volunteers. This army rode on horseback to their prince's banner when summoned for each expedition, and were disbanded as soon as the campaign was over. Alaeddin determined to ensure any future success by forming a corps of paid infantry, which was to be kept in constant readiness for service. These troops were called Yaya, or piyade. They were divided into tens, hundreds, and thousands with their commanders. Their pay was high, and their pride soon caused their sovereign some anxiety. Orhan wished to provide a check to them, and he took counsel for this purpose with his brother Alaeddin and Kara Khalil Çandarlı (of House of Candar), who was connected with the royal house by marriage. Çandarlı laid before his master and the vizier a project. Out of this arose the renowned corps of Janissaries, which was considered the scourge of the Balkans and Central Europe for a long time, until it was abolished by Sultan Mahmud II in 1826.
Çandarlı proposed to Orhan to create an army entirely composed of the children of conquered places. Çandarlı argued that:
The conquered are the responsibility of the conqueror, who is the lawful ruler of them, of their lands, of their goods, of their wives, and of their children. We have a right to do, same as what we do with our own; and the treatment which I propose is not only lawful, but benevolent. By enforcing the enrolling them in the ranks of the army, we consult both their temporal and eternal interests, as they will be educated and given better life conditions.
He also claimed that the formation of Janissary out of conquered children would induce other people to adopt, not only out of the children of the conquered nations, but out of a crowd of their friends and relations, who would come as volunteers to join the Ottoman ranks. Acting on this advice, Orhan selected a thousand of the finest boys from conquered Christian families. The recruits were trained according to their individual abilities, and employed in posts ranging from professional soldier to Grand Vizier. This practice continued for centuries, until the reign of Sultan Mehmet IV.
Politics
Initial expansion
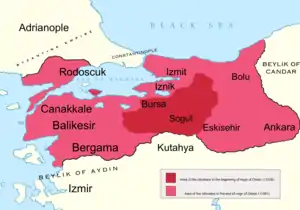
Orhan, with the help of Ghazi commanders at the head of his forces of light cavalry, started a series of conquests of Byzantine territories in northwest Anatolia. First, in 1321 Mudanya, the port of Bursa on the Sea of Marmara coast was captured. He then sent a column under Konur Alp towards the west Black Sea coast; another column under Aqueda to capture Kocaeli, and finally a column to capture the southeast coast of the Sea of Marmara. Then, he captured the city of Bursa through diplomatic negotiations. The Byzantine commander of Bursa fort, called Evrenos Bey, became a commander of a light cavalry force and his sons and grandsons also served the Ottoman Beylik in this capacity to conquer and hold many areas in the Balkans. Once the city of Bursa was captured, Orhan sent cavalry troops towards the Bosphorus, capturing Byzantine coastal towns of Marmara. There were even sightings of Ottoman light cavalry along the Bosphoros coast.
The Byzantine Emperor Andronicus III gathered together a mercenary army and set off towards Anatolia on the peninsular lands of Kocaeli. But at the present towns of Darica, at a site then called Pelekanon, not too far from Üsküdar, he met with Orhan's troops. In the ensuing battle of Pelekanon, the Byzantine forces were routed by Orhan's disciplined troops. Thereafter Andronicus abandoned the idea of getting the Kocaeli lands back and never again conducted a field battle against Ottoman forces.
The city of Nicaea (second only to Constantinople in the Byzantine Empire) surrendered to him after a three-year siege that concluded in 1331. The city of Nicomedia (now Izmit) was also captured in 1337. Orhan gave the command of it to his eldest son, Suleyman Pasha, who had directed the operations of the siege. In 1338 by capturing Scutari (now Üsküdar) most of northwest Anatolia was in Ottoman hands. The Byzantines still controlled the coastal strip from Şile on the Black Sea to Scutari and the city of Amastris (now Amasra) in Paphlagonia, but these were so scattered and isolated as to be no threat to the Ottomans.
Then, there was a change of strategy in 1345. Instead of aiming to gain land from non-Muslims, Orhan took over a Turkish principality, Karesi (present Balıkesir and surroundings). According to Islamic philosophy of war, the areas under Islamic rule were to be abodes of peace and the other areas abodes of war. Conducting a war in abodes of war was considered a good deed. Karesi principality was a state governed by a Turkish emir and its main inhabitants were Turkish so it was an abode of peace. The Ottomans had to have special justification for conquering fellow Muslim Turkish principalities.
In the case of Karesi, the ruler had died and had left two sons whose claims to the post of emir were equally valid. So there was a fight between the armed supporters of the two claimant princes. Orhan's pretext for invasion was that he was acting as a bringer of peace. In the end of the invasion by Ottoman troops the two brothers were pushed to the castle of their capital city of Pergamum (now Bergama). One was killed and the other was captured. The territories around Pergamum and Palaeocastro (Balıkesir) were annexed to Orhan's domains. This conquest was particularly important since it brought Orhan's territories to Çanakkale, the Anatolian side of the Dardanelles Straits.
With the conquest of Karesi, nearly the whole of northwestern Anatolia was included in the Ottoman Beylik, and the four cities of Bursa, Nicomedia İzmit, Nicaea, İznik, and Pergamum (Bergama) had become strongholds of its power. At this stage of his conquests, Orhan's Ottoman Principality had four provinces:[7]
- Original land grant area of Söğüt and Eskişehir;
- Hüdavendigar (Domain of the Sultan) area of Bursa and İznik;
- Koca Eli peninsular area around İzmit;
- former principality of Karesi around Balıkesir and Bergama.
Consolidation period

A twenty-year period of peace followed the acquisition of Karesi. During this time, the Ottoman sovereign was actively occupied in perfecting the civil and military institutions which his brother had introduced, in securing internal order, in founding and endowing mosques and schools, and in the construction of vast public edifices, many of which still stand. Orhan did not continue with any other conquests in Anatolia except taking over Ankara from the commercial-religious fraternity guild of Ahis.
The general diffusion of Turkish populations over Anatolia, before Osman's time, was in main part a push from the Mongol conquest of Central Asia, Iran and then East Anatolia. Turkish peoples had founded a number of principalities after the demise of the Anatolian Sultanate of Rum, after its defeat by the Ilkhanate Mongols. Although they were all of Turkish stock, they were all rivals for dominant status in Anatolia.
After the Byzantine defeat of the Battle of Pelekanon, Orhan developed friendly relations with Andronicus III Palaeologus, and maintained them with some of his successors. Therefore, the Ottoman power experienced a twenty-year period of general repose.
However, as the Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347 dissipated the last resources of the Byzantine Empire, the auxiliary armies of the Emirs of Turkish principalities were frequently called over and employed in Europe. In 1346, The Emperor John VI Cantacuzene recognised Orhan as the most powerful sovereign of the Turks. He aspired to attach the Ottoman forces permanently to his interests, and hoped to achieve this by giving his second daughter, Theodora, in marriage to their ruler, despite differences of creed and the disparity of age. However, in Byzantine and in Western European history, dynastic marriages were quite usual and there are many examples which were much more strange.[8]
The splendour of the wedding between Orhan and Theodora at Selymbria (Silivri) is elaborately described by Byzantine writers. In the following year, Orhan and Theodora visited his imperial father-in-law at Üsküdar, (then Chrysopolis) the suburb of Constantinople on the Asiatic side of the Bosporus where there was a display of festive splendor. However, this close relationship soured when Byzantines suffered from marauding migrant Turcoman bands that had crossed the Marmara Sea and Dardanelles and pillaged several towns in Thrace. After a series of such raids, the Byzantines had to use superior forces to deal with them.
Ibn Battuta gave the following account of Orhan during his reign:
"The greatest of the kings of the Turkmens and the richest in wealth, lands and military forces. Of fortresses he possesses nearly a hundred, and for most of his time he is continually engaged in making a round of them, staying in each fortress for some days to put it in good order and examine its condition. It is said that he has never stayed for a whole month in any one town. He also fights with the infidels continually and keeps them under siege."
— Ibn Battuta, [9]
Decline of Byzantine Empire
During Orhan's reign as the Ottoman emir, the Byzantine Empire declined – partly due to the ambitions of Italian maritime states and to the aggression of the Turcomans and other city Turks, but also due to civil wars within the empire.
During these years the Byzantine Empire became so weak that commercial supremacy in the surrounding seas around it became a bone of contention for the Italian maritime commercial city states. The Republic of Genoa possessed Galata, a separate Genoese city across the Golden Horn from Constantinople itself. The Genoese had fought the Byzantines earlier in 1348 when the Byzantines had decreased their customs tariffs in order to attract trade to the Byzantine side of the Golden Horn. In 1352 the rivalry for trade led to a war between Genoa and Venice. The Genoese, in trying to repel a Venetian fleet from destroying their ships in Golden Horn, bombarded the sea walls of Constantinople and pushed the Byzantines to ally with the Venetians. The Venetians assembled a large naval force, including hired fleets from Peter IV of Aragon and from the Byzantine Empire of John VI Cantacuzene. The sea battle between the Venetian fleet under the command of Niccolo Pisani and the Genoese fleet under Paganino Doria led to defeat of Venetians and their Byzantine allies.[10] Orhan opposed the Venetians, whose fleets and piratical raids were disrupting his seaward provinces, and who had met his diplomatic overtures with contempt. The Venetians were allies of John VI, so Orhan sent an auxiliary force across the straits to Galata, which there co-operated with the Genoese.
In the midst of the distress and confusion that the Byzantine Empire now suffered, Orhan's eldest son, Suleyman Pasha, captured the Castle of Tzympe (Cinbi) in a bold move which gave the Turks a permanent foothold on the European side of the Dardanelles Straits. He also started to settle migrant Turcomans and town-dwelling Turks in the strategic city and castle of Gelibolu (Gallipoli), which had been devastated by a severe earthquake and was therefore evacuated by its inhabitants. Suleyman refused various financial inducements offered by John VI to empty the castle and the city. The emperor pleaded with his son-in-law Orhan to meet personally and discuss the matter, but the request was either rejected or could not be carried out due to Orhan's age and ill-health.[11]
This military situation remained unresolved, in part because of the eruption of hostilities between John VI and his co-emperor and son-in-law John V Palaeologus. John V was dismissed from his imperial post and exiled to Tenedos; Cantacuzene's son Matthew was crowned as the co-emperor. But very soon John V returned from exile with Venetian help and conducted a coup, taking over the government of Constantinople. Although the two men came to an agreement to share power, John VI resigned from his imperial post and became a monk. Each of these two contestants for power was continually soliciting Orhan's aid against the other, and Orhan supported whichever side would benefit the Ottomans.[12]
Last years


Orhan was the longest living and one of the longest reigning of the future Ottoman Sultans. In his last years he had left most of the powers of state in the hands of his second son Murad and lived a secluded life in Bursa.
In 1356 Orhan and Theodora's son, Khalil, was abducted somewhere on the Bay of Izmit. A Genoese commercial boat captain, which was conducting acts of piracy alongside commercial activity, was able to capture the young prince and take him over to Phocaea on the Aegean Sea, which was under Genoese rule. Orhan was very much upset by this kidnapping and conducted talks with his brother-in-law and now sole Byzantine Emperor John V Palaeologos. As to the agreement, John V with a Byzantine naval fleet went to Phocaea, paid the ransom demanded of 100,000 hyperpyra, and brought Khalil back to Ottoman territory.
In 1357 Orhan's eldest and most experienced son and likely heir, Suleyman Pasha, died after injuries sustained from a fall from a horse near Bolayir on the coast of the sea of Marmara. The horse that Suleyman fell from was buried alongside him and their tombs can still be seen today. Orhan was said to have been greatly affected by the death of his son.
Orhan died soon after, likely from natural causes. It seems rather likely that the death of his son was taxing on his health, however. Orhan died in 1362, in Bursa, at the age of eighty, after a reign of thirty-six years. He is buried in the türbe (tomb) with his wife and children, called Gümüşlü Kumbet in Bursa.
Wives and children
- Hatice Hatun, married Süleyman Bey, son of Savji Bey and through him grandson of Osman I.
- In 1299 Orhan married (1359) Nilüfer Hatun, daughter of the Prince of Yarhisar or Byzantine Princess Helen (Nilüfer), who was of ethnic Greek descent,[13][14][15] and had three sons:
Süleyman Pasha (c. 1316 – 1357). Eldest known son and the intended heir who was the architect of the Ottoman expansion into Thrace. He died, shortly after his brother Khalil's capture by the Genoese pirates, as the result of a fall from his horse. His steed was buried next to him in Bolayir, north of Gallipoli, where their graves can still be seen.
- Murad I (1319/1326 – 15 June 1389). Assassinated by Miloš Obilić during the Battle of Kosovo.[16][17]
- [[Şehzade kasim] (D 1346)
- Orhan married Asporça Hatun. Her parentage is unknown.[18] The resting place of Asporça is in the tomb of Orhan in Bursa, Turkey. They had at least four children:
- Ibrahim Bey, Governor of Eskişehir (1316–1362). Executed by order of his half-brother Murad I.
- Şerefullah Bey
- Fatma Hatun
- Selçuk Hatun
- Orhan married in 1346 Theodora Kantakouzene, born in 1332. She was a daughter of John VI Kantakouzenos, Emperor of Byzantium, and Irene Asanina.[19] They had at least one son:
- Halil (1347–1362). When still only a child he was captured by Genoese pirates for ransom. The Byzantine emperor and his future father-in-law John V Palaeologus was instrumental in his eventual release. Halil married Irene, who was a daughter of John V Palaeologus and Helena Kantakouzene.
- Orhan married Eftandise Hatun, daughter of Mahmud Alp.
In 1351, Orhan and Stefan Uroš IV Dušan of Serbia were negotiating about a potential alliance. There was a proposal to marry Dušan's daughter Theodora to Orhan, or one of his sons. However, the Serbian diplomats were attacked by Nikephoros Orsini, after which the negotiations broke down, the marriage didn't take place, and Serbia and the Ottoman state resumed hostilities.[20]
In popular culture
In the Turkish television series Kuruluş "Osmancık" (1988), Orhan Gazi has been portrayed.[21]
References
- Incorporates text from "History of Ottoman Turks" (1878)
- Feridun Emecen (2019). "Mal Hatun". İslâm Ansiklopedisi (3rd ed.) (in Turkish). Vol. Annex 2.
It is generally accepted that she is the mother of Orhan Bey.
- Nicolle, David and Hook, Adam. Ottoman Fortifications 1300-1710. Osprey Publishing, 2010. Retrieved 3 Sep 2011.
- Goffman, Daniel. The Ottoman Empire and Early Modern Europe. Cambridge University Press, 2002. Retrieved 3 September 2011.
- Henry Glassie (1991). Turkish Traditional Art Today. p. 370.
- Kafadar, Cemal (1995). Between Two Worlds: The Construction of the Ottoman State. p. 16.
- Edward S. Creasy, History of the Ottoman Turks. (Beirut: Khayats, 1961), 13
- S.J.Shaw (19760, History of the Empire and Modern Turkey. Vol. 1: Empire of Ghazis, Cambridge U.P., pp. 15–16
- J.J.Norwich (1996) Byzantium: the Decline and Fall, Penguin, London Chp.18
- A Social History of Ottoman Istanbul - Ebru Boyar, Kate Fleet Cambridge University Press
- J.J.Norwich (1996) Byzantium: the Decline and Fall, Penguin, London Chp.19
- J.J.Norwich (1996) Byzantium: the Decline and Fall, Penguin, London p.320
- J.J.Norwich (1996) Byzantium: the Decline and Fall, Penguin, London pp. 321–2
- The Fall of Constantinople, Steven Runciman, Cambridge University Press, p.36
- The Nature of the Early Ottoman State, Heath W. Lowry, 2003 SUNY Press, p.153
- History of the Ottoman Empire and Modern Turkey, Stanford Jay Shaw, Cambridge University Press, p.24
- Helmolt, Ferdinand. The World's History, p.293. W. Heinemann, 1907.
- Fine, John. The Late Medieval Balkans, p.410. University of Michigan Press, 1994. ISBN 0-472-08260-4
- Peirce, L.P., The Imperial Harem: Women and Sovereignty in the Ottoman Empire (OUP: New York/Oxford, 1993), p. 34
- Peter F. Sugar, 15-16.
- George Ostrogorsky (1986), Byzantine sources on the history of the peoples of Yugoslavia, (Institute of Byzantine Studies), VI-280.
- "Full Cast & Crew: Kurulus". IMDb. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
External links
- Cawley, Charles, His listing ., Medieval Lands database, Foundation for Medieval Genealogy The project "involves extracting and analysing detailed information from primary sources, including contemporary chronicles, cartularies, necrologies and testaments."
- A listing of descendants of Ertuğrul, alongside other royalty
.svg.png.webp)