Patras
Patras (Greek: Πάτρα, romanized: Pátra [ˈpatra]; Katharevousa and Ancient Greek: Πάτραι;[lower-alpha 1] Latin: Patrae[lower-alpha 2]) is Greece's third-largest city and the regional capital of Western Greece, in the northern Peloponnese, 215 km (134 mi) west of Athens. The city is built at the foot of Mount Panachaikon, overlooking the Gulf of Patras.
Patras
Πάτρα | |
|---|---|
 Clockwise from top: Panoramic view of downtown Ethnikis Antistaseos Square area from Agiou Nikolaou Stairs, Rio-Antirio Bridge and Gulf of Corinth, Lighthouse of Patras, Night view of Patras from Romanos Mona Forest Park, Apollon Theatre and Georgiou I Square, Castle of Patras. | |
 Seal | |
 Patras Location within Greece  Patras Location within Europe  Patras Patras (Europe) | |
| Coordinates: 38°15′N 21°44′E | |
| Country | |
| Geographic region | Peloponnese |
| Administrative region | Western Greece |
| Regional unit | Achaia |
| Districts | 5 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–council government |
| • Mayor | Kostas Peletidis (KKE) |
| Area | |
| • Municipality | 334.9 km2 (129.3 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 125.4 km2 (48.4 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 2,928.717 km2 (1,130.784 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 10 m (30 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Municipality | 213,984 |
| • Urban | 167,446 |
| • Urban density | 1,300/km2 (3,500/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 314,567[1] |
| Demonym | Patrinos (Greek: Πατρινός) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal codes | 26x xx |
| Telephone | 261 |
| Vehicle registration | ΑXx, ΑZx, AOx, AYx |
| Patron saint | Saint Andrew (30 November) |
| Website | www.e-patras.gr |



As of the 2011 census, the city of Patras has a population of 167,446 and the municipal unit has 170,896 inhabitants; the municipality has 213,984 inhabitants. The population of its functional urban area was 217,555 in 2011.[2] The core settlement has a history spanning four millennia. In the Roman period, it had become a cosmopolitan center of the eastern Mediterranean whilst, according to the Christian tradition, it was also the place of Saint Andrew's martyrdom.
Dubbed as Greece's 'Gate to the West', Patras is a commercial hub, while its busy port is a nodal point for trade and communication with Italy and the rest of Western Europe. The city has three public universities, hosting a large student population and rendering Patras an important scientific centre with a field of excellence in technological education. The Rio-Antirio Bridge connects Patras' easternmost suburb of Rio to the town of Antirrio, connecting the Peloponnese peninsula with mainland Greece.
Every year, in February, the city hosts one of Europe's largest carnivals. Notable features of the Patras Carnival include its mammoth satirical floats and balls and parades, enjoyed by hundreds of thousands of visitors in a Mediterranean climate. Patras is also famous for supporting an indigenous cultural scene active mainly in the performing arts and modern urban literature. It was European Capital of Culture in 2006.[3]
Geography
Patras is 215 km (134 mi) west of Athens by road, 94 km (58 mi) northeast of Pyrgos, 7 km (4.3 mi) south of Rio, 134 km (83 miles) west of Corinth, 77 km (48 miles) northwest of Kalavryta and 144 km (89 mi) northwest of Tripoli.
A central feature of the urban geography of Patras is its division into upper and lower sections. This is the result of an interplay between natural geography and human settlement patterns; the lower section of the city (Kato Poli), which includes the 19th-century urban core and the port, is adjacent to the sea and stretches between the estuaries of the rivers of Glafkos and Haradros. It is built on what was originally a bed of river soils and dried-up swamps. The older upper section (Ano Poli) covers the area of the pre-modern settlement, around the Fortress, on what is the last elevation of Mount Panachaikon (1,926 m (6,319 ft))[4] before the Gulf of Patras.
Hydrology
The largest river in the area is the Glafkos, flowing to the south of Patras. Glafkos springs in Mount Panachaikon and its water is, since 1925, collected in a small mountainous reservoir-dam near the village of Souli and subsequently pumped in order to provide energy for the country's first hydroelectric plant.[5] Other smaller streams are Charadros, Meilichos, Kallinaos, Panagitsa and the mountain torrent Diakoniaris.
Climate
Patras has a Mediterranean climate. It features the typical mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers, with spring and autumn being pleasant transitional seasons. Autumn in Patras, however, is wetter than spring.
| Climate data for Patras (1955–1997) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 14.5 (58.1) |
15.0 (59.0) |
16.8 (62.2) |
19.7 (67.5) |
24.2 (75.6) |
28.0 (82.4) |
30.1 (86.2) |
30.9 (87.6) |
28.2 (82.8) |
24.1 (75.4) |
19.5 (67.1) |
16.1 (61.0) |
22.3 (72.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 10.3 (50.5) |
10.7 (51.3) |
12.3 (54.1) |
15.0 (59.0) |
19.1 (66.4) |
22.7 (72.9) |
24.8 (76.6) |
25.3 (77.5) |
22.7 (72.9) |
18.9 (66.0) |
14.9 (58.8) |
11.9 (53.4) |
17.4 (63.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 6.1 (43.0) |
6.4 (43.5) |
7.7 (45.9) |
10.2 (50.4) |
13.9 (57.0) |
17.4 (63.3) |
19.4 (66.9) |
19.6 (67.3) |
17.2 (63.0) |
13.8 (56.8) |
10.3 (50.5) |
7.6 (45.7) |
12.5 (54.5) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 89.1 (3.51) |
81.7 (3.22) |
63.3 (2.49) |
47.8 (1.88) |
28.9 (1.14) |
7.5 (0.30) |
4.6 (0.18) |
5.2 (0.20) |
28.3 (1.11) |
72.2 (2.84) |
118.0 (4.65) |
116.1 (4.57) |
662.7 (26.09) |
| Average rainy days | 12.0 | 10.6 | 9.9 | 8.4 | 5.3 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 3.6 | 7.8 | 11.0 | 13.2 | 86 |
| Source: Hellenic National Meteorological Service[6] | |||||||||||||
Ecology
Of great importance for the biological diversity of the area and the preservation of its climate is the swamp of Agyia, a small and coastal aquatic ecosystem of only 30 ha (74 acres), north of the city centre. The main features of this wetland are its apparent survival difficulty, being at the heart of a densely populated urban centre that features a relatively arid climate and its admittedly high level of biodiversity, with over 90 species of birds being observed until the early 1990s, according to a study by the Patras Bureau of the Hellenic Ornithological Society.[7]
History
.jpg.webp)

Antiquity
The first traces of settlement in Patras date to as early as the third millennium BC, in the area of modern Aroi. Patras flourished for the first time in the Post-Helladic or Mycenean period (1580–1100 BC). Ancient Patras was formed by the unification of three Mycenaean villages in modern Aroi, namely ancient Aroe, Antheia (from mythological Antheia) and Mesatis. Mythology has it that after the Dorian invasion, a group of Achaeans from Laconia led by the eponymous Patreus established a colony. In antiquity Patras remained a farming city. It was in Roman times that it became an important port.
After 280 BC and prior to the Roman occupation of Greece, Patras played a significant role in the foundation of the second "Achaean League" (Achaiki Sympoliteia), along with the cities of Dyme, Tritaea and Pharai. Later on, and following the Roman occupation of Greece in 146 BC, Patras played a key role, and Augustus refounded the city as a Roman colony in the area. In addition, Patras has been a Christian centre since the early days of Christianity, and it is the city where Saint Andrew was crucified.
Middle Ages and early modern

In the Byzantine era Patras continued to be an important port as well as an industrial centre. One of the most scholarly philosophers and theologians of the time, Arethas of Caesarea was born at Patrae, at around 860. By the 9th century, there are strong signs the city was prosperous: the widow Danielis from Patras had accumulated immense wealth in land ownership, the carpet and textile industry, and offered critical support in the ascent of Basil I the Macedonian to the Byzantine throne.
In 1205 the city was captured by William of Champlitte and Villehardouin, and became a part of the principality of Achaea. It became the seat of the Barony of Patras, and its Latin archbishop primate of the principality. In 1408, Patras became Venetian, until it was recaptured in 1430 by the Despotate of Morea and its despot Constantine Palaiologos, who thus succeeded in recovering for the Byzantine Empire the whole of the Morea, apart from Venetian possessions. The administration of Patras was given to George Sphrantzes, while Constantine was immediately contested by the Ottoman Empire and later, in 1449, became emperor of the Byzantine empire.[8]
Patras remained a part of the Despotate of Morea until 1458, when it was conquered by the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire, Mehmet II. Under the Ottomans, it was known as "Baliabadra", from the Greek: Παλαιά Πάτρα ('Old Patras'), as opposed to Νέα Πάτρα ('new Patra'), the town of Ypati in Central Greece. Though Mehmet granted the city special privileges and tax reductions, it never became a major centre of commerce. Venice and Genoa attacked and captured it several times in the 15th and 16th centuries, but never re-established their rule effectively, except for a period of Venetian rule in 1687–1715 after the Morean War.[9]
In 1772 a naval battle took place off the city between the Russians and Ottomans.
Modern era
Patras was one of the first cities in which the Greek Revolution began in 1821;[10] the Ottoman garrison, confined to the citadel, held out until 1828. Finally the city was surrendered on 7 October 1828 to the French expeditionary force in the Peloponnese, under the command of General Maison. After the war, most of the city and its buildings were completely destroyed. The new city was planned under the supervision of Stamatis Voulgaris following orders by Ioannis Kapodistrias.
Patras developed quickly into the second-largest urban centre in late-19th-century Greece.[11] The city benefited from its role as the main export port for the agricultural produce of the Peloponnese.[12]
In the early 20th century, Patras developed fast and became the first Greek city to introduce public streetlights and electrified tramways.[13] The war effort necessitated by the First World War hampered the city's development and also created uncontrollable urban sprawl after the influx of displaced persons from Asia Minor after the 1922 population exchange between Greece and Turkey. In the Second World War, the city was a major target of Italian air raids. In the Axis occupation period, a German military command was established and German and Italian troops stationed in the city. After the liberation in 1944, the city recovered, but in later years was increasingly overshadowed by the urban pole of Athens. Since 2014, the city's mayor is Kostas Peletidis.
Urban landscape

The city is divided into the upper and the lower section, connected with roads and broad stairs. The upper section (Ano Poli) is the older and the more picturesque; however, the lower section (Kato Poli) is laid out according to the 1858 city plan, featuring a variety of squares. The most notable of these are the Psila Alonia and the Georgiou I Square. A number of notable neoclassical buildings are to be found, including the Apollon Theatre in Georgiou I Square, the City Hall, the headquarters of the Local Trade Association and the Court of Justice. A replica of Patras Lighthouse, the city's emblematic old lighthouse – which was at the dock of Ayios Nikolaos – rises at the end of Trion Navarchon street, near the temple of Saint Andreas.

In general, much of Patras' coastline is framed by roads and avenues running alongside; these include Dymaion Coast to the south and Iroon Polytechneiou Street to the north.
Main sights





Patras and its region is home to various Ancient Greek, Roman and Byzantine Monuments, including the Roman Odeon, the Fortress of Rio and the Fortress (castle) of Patras.[14] More specifically, the main sights of the city are:
- The Patras Archaeological Museum focuses on the exhibition of various archaeological finds, from the Mycenaean to the Late Roman era, discovered in Patras and the wider Achaea region. The museum is housed in a modern and special architectural building designed by the architect Theophanis Bobotis.[15]
- The Mycenaean cemetery of Voudeni (Skioessa), 8 km (5.0 mi) from the center of Patras, is one of the most important sites of the Mycenaean world, showing active use for nearly five hundred years (1500–1000 BC). The site itself appears to have been inhabited from the Bronze Age until middle Roman times (1800 BC–AD 400).
- The Roman Odeon, the most significant ancient monument, is in the upper town and was built around 160 AD, in the reign of either Antoninus Pius or Marcus Aurelius. It has been restored and partially reconstructed, and is used as an open-air theatre for performances and concerts in the summer.
- The Roman Amphitheatre, near the Roman Odeon, in Ifestou street, dating from the 1st century AD, at a period of the biggest development of Roman Patras. Its area has been only partially excavated.[16]
- The Roman aqueduct[17] that led from the springs of Romanos to the acropolis. The aqueduct measured 6.5 km (4.04 mi) from the water cistern to the castle. For the greater part of this distance, the water passed through an underground channel, passing over valleys and gorges on carefully constructed archways, parts of which still stand, in the area of Aroi.[18]
- Other Roman monuments include the ruins of the Roman stadium, remains of the Roman wall and a preserved bridge over the river Kallinaos.
- The medieval Patras Castle, in the ancient acropolis overlooking the city, was initially built in the 6th century AD by the Byzantine emperor Justinian, having many additions from the period of the Frankish and Venetian rule of the city, up to as far as the time of the Despotate of Morea and later the Ottoman Empire. Its current outline dates back to the second Venetian rule of the town (1687–1715). Today, its interior is used as a public garden.
- The church of Saint Andrew of Patras was founded in 1908 by King George I and was inaugurated in 1974. It is dedicated to Saint Andrew, the patron of the city.[19] It is the second-largest temple of Byzantine style in the Balkans (after the Cathedral of Saint Sava in Belgrade). The central cupola is 46 m (151 ft) tall and is the base for a 5 m (16 ft) gold-plated cross and twelve smaller ones, symbolising Christ and the twelve apostles. A congregation of at least 5,000 can attend a sermon within the church.[20]
- The municipal Theatre Apollon, built in 1872 designed by architect Ernst Ziller. The building is characteristic of the 19th-century neoclassical style and is in the central square of the city.
- The Achaia Clauss wine industry and tasting center, which is on the outskirts in Petroto village. It was founded in 1861 by the Bavarian Gustav Clauss and is most famous for its Mavrodaphne.This place also houses the oldest wine of Greece, the old mavrodaphne of 1873.
- Residence of Kostis Palamas, a preserved neoclassical building on 241 Corinthou Street in the city center, where Kostis Palamas and the Italian painter Matilde Serao were born. It is an aesthetic building and the creation of the museum there fulfilled the great vision of businessman Athanasios Stefanopoulos, who bought the collapsing building on Corinthou Street to create the Cultural Center Kostis Palamas.
- The Ottoman baths (16th century), still retain their initial use, and are one of the oldest Ottoman baths surviving in Europe.[21]
- The Patras Lighthouse, a reconstructed "Faros" (Lighthouse), a landmark of the city.
- The Agiou Nikolaou Stairs, Gerokostopoulou Stairs, Patreos Stairs and Trion Navarchon Stairs, outdoor grand staircases all over the centre of the city dividing the upper town from downtown.
Parks and squares
- Georgiou I Square, the central square and the heart of the city. It was named after King George I. The square's fountains were installed in 1875 at a cost of 70,000 drachmas each, a huge amount for the finances of Greece and Patra at the time. It was and continues to be the center of political and cultural life in the city, hosting all significant activities, political gatherings, rallies, cultural events and, most importantly for some, its carnival.
- Ethnikis Antistaseos ("National Resistance Square")

- Kapodistria Square in the district of Markato.
- Trion Symmachon Square bears the name of the three Allied Powers who fought in the Battle of Navarino; Britain, France and Russia. The square features a flower clock and links the Agiou Nikolaou pedestrian way with the seaside front and the dock of Agios Nikolaos.
- Psilalonia Square (Ψηλαλώνια or formally Πλατεία Υψηλών Αλωνίων) is one of Patras's most popular squares. It is 1.5 km (0.93 mi) from downtown Patras, next to the city's main north–south street, Gounari Street. It features a fountain, many sidewalks, palm trees and playgrounds. A bronze statue of Germanos of Patras stands on the northern end, while a memorial plaque to people executed during the Axis occupation of Greece stands on the south-western corner. It is surrounded by several shops, restaurants and cafes and a number of modernist buildings. It was completed in the mid-to-late 19th century, when trees were added, along with neoclassical buildings. After World War II and the Greek Civil War, however, and through the 1960s and 1970s, most neoclassical buildings were replaced by eight-storey residential buildings. In the west end, a 15-metre-tall (49 ft) cliff overlooks the pedestrian Trion Navarchon Street, and offers a wide vista across the western Gulf of Patras, including the mountains of Aitoloakarnania.
- Saint George Square (Πλατεία Αγίου Γεωργίου). There is the monument to the fighters of 1821 on which is engraved the "declaration of the revolutionaries of Patras to the states of Europe" (22/3/1821).
- The Spinney of Patras (Δασύλλιο), is in a pine-tree-covered hill, which is dubbed "the Gulf of Patras' veranda" because of the panoramic view it offers. The spinney is ideal for recreational walks and jogging, with its specially formed paths and the shade offered by the tall trees. The pine trees that cover the spinney were planted in March 1916 by students of Patras' primary schools under the supervision of the Austrian forest specialist Steggel.
Architecture

As a part of the 2006 European Capital of Culture programme, there was a project for the restoration of the city's architectural heritage.
Patras' center is characterised by a composition of architectural currents and trends. During the 19th century many neoclassical buildings were constructed in the city. Α representative example are the façades around the central square of the city (Georgiou I square). The neoclassical Apollo Theatre, a work of Ernst Ziller, is next to the modernist building of the Hall of Literature and Art (Μέγαρο Λόγου και Τέχνης).

Patra is a relatively newly built city, as its medieval buildings were completely destroyed in the Greek War of Independence. The oldest surviving buildings (apart from ancient monuments and the castle) are the church of Pantocrator in Ano Poli and a residential building (Tzini's house) at the corner of Agiou Nikolaou and Maisonos street, built in 1832. The area on the south of the castle, around the Roman Odeon, the church of Pantokrator, in the Upper Town (Ano Poli), is the most appealing of the city, because of its status as the only area where construction height is limited to two-storey buildings.[22] Ιn Ano Poli is interesting the old school complex "Georgios Glarakis" work of the architect Georgios Petrιtsopoulos in 1931 which is built with stone and recently became a nice bioclimatic school. At the beginning of the 20th century, outside the school complex "Georgios Glarakis", line 2 of the tram ended, starting from Agios Dionysios, going up Dimitriou Gounari Street, passing behind the church of Pantanassa, entering Roman Odeon and finished outside the Glarakis school complex.

Historical buildings and mansions of the city, apart Tzini's house, include also the Prapopoulos building, Golfinopoulos mansion (Alhambra), Perivolaropoulos mansion, Palamas house, while among the demolished after WWII were Tsiklitiras mansion, Kanellopoulos house, Chaidopoulos building, Frangopoulos house, Green mansion and Mineyko mansion.[23]
Districts and neighbourhoods
Nowadays, the municipal units of Rio, Paralia, Messatida and Vrachnaiika have functionally become a part of the wider urban complex of Patras. Apart from the city center, the main districts of Patras are:
|
Patras municipal unit:
|
|
Rio municipal unit:
|
Paralia:
|
Messatida:
|
Vrachneika:
|
Government

Patras is the regional capital of Western Greece and the capital of the Achaea regional unit. Since 2011, the city is also the capital of the administrative division, which includes (along with Western Greece) the regions of Peloponnese and the Ionian Islands.
Municipality
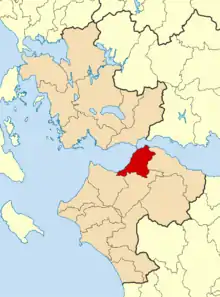
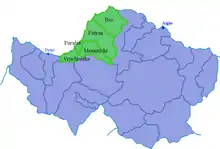
The current municipality of Patras was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of 5 municipalities that made up the Patras Urban Area. These former municipalities, which became municipal units, are:[24] (in parenthesis their population, 2011)
- Messatida (13,852)
- Paralia (9,987)
- Patras (170,896)
- Rio (14,034)
- Vrachnaiika (4,627)
The municipality has an area of 334.858 km2 (129 sq mi), the municipal unit 125.420 km2 (48 sq mi).[25]
Demographics
The following list presents demographic data on the municipality of Patras over the years 2012.
| Historical Population[26][27][28] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Patras municipality | |||
| 1853 | 15,854 | |||
| 1861 | 18,342 | |||
| 1870 | 16,641 | |||
| 1879 | 25,494 | |||
| 1889 | 33,529 | |||
| 1896 | 37,985 | |||
| 1907 | 37,728 | |||
| 1920 | 52,174 | |||
| 1928 | 61,278 | |||
| 1951 | 87,570 | |||
| 1961 | 96,100 | |||
| 1971 | 112,228 | |||
| 1981 | 142,163 | |||
| 1991 | 161,782 | |||
| 2001 | 171,616 | |||
| 2007 | 180,000 | |||
| 2011 | 213,984 | |||
| 2021 | 211,593 | |||
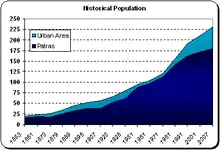
From 2011 on, can data also reflect the city's urban area population, as all the municipalities that made up the Patras Urban Area were joined to create the new larger Patras municipality, formed at the 2011 local government reform.
Infrastructure
Heavy infrastructure works performed in the 2000s include the Peiros-Parapeiros dam (to provide water supply for Patras and surrounding towns)[29] and a "small industries" park that will be constructed next to the Glaykos river and provide an easy connection with the new port.
The city is one of the main Greek internet and GRNET hubs and is connected with high speed lines to Athens as part of the backbone. A metropolitan optical network will be deployed in the city, with a total length of 48 km (30 mi).[30]
Two major state hospitals operate in the city: the Agios Andreas Hospital is the oldest of the two; and General University Hospital of Patras. There also exists two smaller state hospitals, Karamandanio - a children's hospital, and the Center of Chest Diseases of Southwestern Greece. A large range of private hospitals and clinics operate in parallel.
Numerous art venues[31] and an ultra-modern archaeological museum[32] were constructed for the needs of European Culture Capital designation. The cultural and educational facilities include the Municipal Library, the university libraries, many theatres, the municipal art gallery,[33] the University of Patras's facilities, the Hellenic Open University and the Technical Institute of Patras. A number of research facilities are also established in the university campus area.
Economy

.png.webp)


The economy of the city largely depends on its service sector. Its main economic activities include retailing, logistics, financial and public sector services. Patras suffered a severe problem of deindustrialization in the late 1980s and 1990s when a number of major productive units shut down in successive order. As a result, a considerable portion of the city's workforce and the city's economic planning in its entirety had to be re-evaluated and restructured by the authorities giving emphasis on the scientific research and technology sector. The University of Patras contributed by working towards this goal, using its service and technology sectors.
The area still retains some of its traditional winemaking and foodstuff industries as well as a small agricultural sector. Major businesses in Patras include:
Services sector
Most Greek banks have their regional headquarters for Western Greece in Patras.
In 2010, the new Infocenter of Patras was established, inside the neoclassical building of the former market "Agora Argyri", in Ayiou Andreou street. The building includes a conference hall, along with multi-purpose and exhibitional spaces.[34] The regional unit of Achaea has about 4,800 hotels rooms and in 2006, 286,000 tourists, mainly from Greece, stayed in the area for a total of 634,000 days.[35][36]
Manufacturing sector
Patras still has a large manufacturing base for a variety of industries.
The Titan Cement Company operates a large cement factory, with a private port, in Psathopyrgos, a suburb of Patras.
Patras hosts several timber manufacturing companies, and a wood distribution center of Shelman. The largest local company is Abex.[37] The paper sector is also active including a paper factory belonging to Georgia-Pacific (Delica) and two important Greek companies, Elite and El-pack, headquartered in the city.
Patras has several packing and industrial equipment companies. The most important of them are the local Antzoulatos and the multinational Frigoglass, a subsidiary of Coca-Cola, headquartered in the suburbs of Patras. Ideal Bikes is the leading bike producer in Greece, with large export activities.
The once omnipresent textile industry of the city is now almost defunct after the shut-down of the huge factory of Peiraiki-Patraiki (Πειραϊκή-Πατραϊκή), followed by numerous smaller textile industries. This had an important impact on the city's economy and resulted in high levels of unemployment in the 1990s. The remains of the facilities still cover hundreds of acres in the south side of the city.
Patras companies also focus in dress production, the most important among them being DUR.
Food

Some of the largest industries in the city belong to the soft drinks and drinks sector. There are factories from Coca-Cola HBC and Athenian Brewery established in area, along with the facilities of the largest local company in soft-drinks production, Loux (ΛΟΥΞ). The city is also home to many leading Greek wineries and distilleries, among them the venerable Achaia Clauss and Parparoussi located in Rio. In the food sector, Friesland Foods, through the local subsidiary NoyNoy, operates a new yogurt factory in the city's industrial area. Patras is also home to important fish-farming companies (Andromeda, Nireus).[38][39] ECOFEED operates in the industrial zone of Patras, the largest fish-feeds factory in the Mediterranean.[40] The city hosts the second-largest flour-mills in Greece, Kepenou-Mills.[41]
Energy sector

Acciona has completed the largest wind park in Greece, on the Panachaiko mountain, overlooking the city of Patras.[42] The Public Electric Company, operates a small hydroelectric plant on river Glafkos.[43]
IT sector
Intracom (Greece's largest multinational provider of telecommunications products) facilities in Patras house the offices of Telecommunications Software Development, Terminal Equipment Design, Development Programmes, and Support Services divisions. Expansion plans have recently been completed.[44] INTRASOFT, another core company of INTRACOM holdings group, has recently (2018) began operations in Patras and it is expected to expand its activities in 2019.[45] The Corallia Innovation Hub, Innohub hosts many companies focusing on Microelectronics.[46] Among them one of the largest is the multinational software company Citrix Systems which operates a R&D centre with more than 100 computer scientists and engineers. Another company that maintains an R&D center in Patras is Dialog Semiconductor, a UK-based manufacturer of semiconductor-based system solutions. Another large Greek IT company, Unisystems announced recently (October 2018) the signing of a cooperation agreement with the Patras-based IT company Knowledge SA, that lays the foundation for the establishment of a Remote Development Center in Patras.[47]
Research and technology
Patras Science Park is an incubator for many small but upcoming technology companies.[48][49] CBL Patras, a global manufacturer of specialty chemicals and active pharmaceutical ingredients, is a startup from a professor of the University of Patras.
Vianex, owned by Pavlos Giannakopoulos, has its largest production facilities in the industrial area of the city.[50]
Nobacco, a Greek electronic cigarette brand, works mainly with cooperation with the university of Patras.
There has been a significant development in the R&D sector, in the last few years, as a result of the many research institutes and the university impact in the area. The Computer Technology Institute and the Industrial Systems Institute[51] of Greece are headquartered in Patras. The city is also a host to the FORTH-ICE-HT (Institute of Chemical Engineering & High Temperature Chemical Processes)[52] and the Institute of Biomedical Technology.[53]
Media
|
Press
|
Television
|
Culture




The cultural activity of Patras includes the Patras International Festival (with various artistic activities, mainly in the fields of theatre and music), the Patras Carnival and the Poetry Symposium.[54]
The city hosts many museums, including the Patras Archaeological Museum the History and Ethnology Museum, the Folk Art Museum, the Press Museum and the Technology Museum, the latter in the campus of Patras University.
Other cultural institutes are: the Visual Arts Workshop, the icon painting school, the Carnival Float Workshop, the Municipal Library, the Municipal Gallery, along with many private art galleries. The architectural heritage of the city is dominated by neo-classicism, but also includes structures from other periods. Patras is also a pilot city of the Council of Europe and EU Intercultural cities programme.
Theatrical tradition and music
The Patras Municipal and Regional Theatre was founded in June 1988, having as its main stage the city's landmark, the Apollon Theatre. Throughout its existence it has mounted critically acclaimed performances ranging from ancient dramaturgy and modern Greek, to international repertoire. The theatre cooperates with other theatrical groups, such as the Viomichaniki (Industrial) group and the Michani Technis (Art Machine).
The Roman Odeon hosts ancient dramas in the summer, while the Pantheon theater, the Art Factory, the Lithographeion and the Agora theatres provide additional venues. The International Festival of Patras takes place every summer, with a program consisting mostly of plays—both ancient drama and modern theatre—as well as various musical events.
Patras has also a very strong indie rock scene with critically acclaimed bands such as Raining Pleasure, Abbie Gale, Serpentine, Doch an Doris and others.
Carnival
The Patras Carnival (Patrino Karnavali) is the largest event of its kind in Greece and one of the biggest in Europe, with a heritage reaching back 160 years. The events begin in January 17 each year (St. Anthony's nameday), and last until Clean Monday. Hundreds of thousands of visitors from all over the world gather each year for its festivities, which include large events such as the mammoth sized parades of the last two weeks (up to 50.000 participants each), the Hidden Treasure Hunt (Krymmenos Thisavros), concerts, expositions, theatrical, musical, comedy and other artistic contests and events. Patras Carnival was originally introduced as ball-masquee' events in 1835 by the Italian origin merchant family of Moretti.
European Capital of Culture 2006

Patras was chosen by the European Commission to be the European Capital of Culture for the year 2006. The concept of the event revolved around the main theme of "Bridges" and "Dialogues", drawing benefit from the city's rich history and its position as a "Gate to the West", to underline the essence of the productive interaction of culture and civilisations in Europe. The EU Commission found Patras' plans very ambitious and also commented that a successful hosting of the title by a medium-sized city would make it possible to redefine the meaning of the term Cultural Capital.
The Selection Panel for 2006 noted in its final report:
The current cultural activity of the city includes the Patras International Festival (various artistic activities, mainly in the field of music), the Patras Carnival and the Poetry Symposium (organised each year for the 25 years by an ad hoc committee at the University of Patras).[54] The Patras 2006 proposal focuses on two central ideas: "bridges" and "dialogues". Cultural managers from Patras and the general public will be involved in developing these ideas. Further, four poles/programmes of cultural attraction will be developed. The first, "A city for Europe", will relate to the architectural heritage, the industrial revolution and similar subjects. "The counterpart cities" programme will be developed in the fields of human and social sciences and in diverse artistic fields. "The three sea battles" will present a cultural programme focusing on peace and understanding. The last theme, "The many homelands", is directly linked to the etymology of the name of the city. This programme will among other things concentrate on art workshops, the transfer of know-how, way of life and entertainment.[55][56]
In 2006 various cultural events were held in the context of the European Capital of Culture. Among the artists presenting their work in Patras were: Gary Burton, Maxim Shostakovich, Ian Anderson - with the Patras Municipal Orchestra, Jean Louis Trintignant, Roberto Benigni, Eros Ramazzotti and José Carreras.[57] With the completion of the Capital of Culture programme, a part of the old Ladopoulos factory was renovated to host exhibitions, a small theatre (named the Art Factory), was built and a number of neoclassical buildings around the city were renovated as part of a plan to preserve the city's architectural heritage and link it to its cultural life. The new Archaeological museum was completed in 2009. Its globe-like roof and modern architectural design enhances the town's northern entrance, taking its place among the other city landmarks.
Sports

.JPG.webp)

.jpg.webp)
Patras has several sports facilities and important teams in almost all the major Greek leagues. Panachaiki Gymnastiki Enosi, Apollon Patras, E.A. Patras and NO Patras are historically the major sports clubs based in the city, specialising in football, basketball, volleyball and water polo. The city's national stadium, Pampeloponnisiako Stadium, was renovated and expanded in 2004.[58] Since 2009, a new event, the Patras International Circuit Kart takes place every September, turning the city streets into a circuit.
The city has hosted several international sports events, such as the 1995 Basketball Under-19 World Cup (preliminaries), the 1995 Men's European Volleyball Championship (preliminaries), the 1997 Rhythmic Gymnastics European Championships, the 2001 World Wrestling Championships, the EuroBasket 2003 Women, the 2003 International Children's Games, a group stage of the football tournament in the 2004 Olympic Games, the 2007 World Rhythmic Gymnastics Championships, the 2008 World Deaf Football Championships and the 2019 Mediterranean Beach Games.
| Club | Sport | Current League | Venue | Location | Capacity | Established | Highest ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panachaiki G.E. | Football | Super League 2 | Kostas Davourlis Stadium | Agyia | 11,321 | 1891 | 4th (1973) |
| Volleyball | Volleyball League | Panachaiki Indoor Arena | 500 | 1928 | 8th (2016) | ||
| Apollon Patras | Basketball | Basket League | Apollon Patras Indoor Hall | Perivola | 3,500 | 1926 | 6th (1986) |
| E.A. Patras | Volleyball | A2 Ethniki | EAP Indoor Hall | Agios Dionysios | 2,200 | 1927 | Champion (1938) |
| NO Patras | Water polo | A1 Ethniki | NOP Aquatic Centre | Akti Dymeon | 3,000 | 1929 | Champion (x 8) |
| Thyella | Football | Delta Ethniki | Fotis Aravantinos Stadium | Glafkos | 3,000 | 1930 | 5th (B Ethniki) |
| Olympiada Patras | Basketball Volleyball |
A2 League A2 Ethniki |
Olympiada Indoor Hall | Taraboura | 2,500 | 1961 | 8th (2002) 10th (2007) |
| Promitheas Patras | Basketball | Basket League | Dimitris Tofalos Arena | Bozaitika | 4,500 | 1985 | 2nd (2019) |
| Ormi Patras | Handball | A1 Women's | National Indoor Hall | Koukouli | 1,000 | 2003 | Champion (x 6) |
| NE Patras | Water polo | A2 Ethniki A1 Women's |
Antonis Pepanos Aquatic Centre | Koukouli | 4,000 | 2006 | 4th (2009) 4th (x 3) |
Religion

The city is the seat of the Greek Orthodox Metropolis of Patras. As in the rest of the country, the largest denomination is the Orthodox Church, which represents the majority of the population. There is also a sizeable community of Roman Catholics and an Anglican church, part of the Church of England's Diocese in Europe.[59]

The most significant church in the city is the Orthodox Cathedral Church of Saint Andrew, in the south west of the city center. The construction of the church began in 1908 under the supervision of the architect Anastasios Metaxas, followed by Georgios Nomikos. It was inaugurated in 1974. It is the largest church in Greece and the third-largest Byzantine-style church in the Balkans, after the Cathedral of Saint Sava in Belgrade and Alexander Nevsky Cathedral in Sofia. It holds relics of Andrew the Apostle, which were returned to the city of Patras from St. Peter's Basilica, Rome in September, 1964, on the orders of Pope Paul VI. Other historical churches of the city are:
- The church of Pantokrator (1832), the old cathedral, in the upper town district
- The Metropolitan Church of Patras (1846) dedicated to Panayia Evangelistria, on Maisonos Street
- The church of Ayios Nikolaos (1885), next to the steps of Ayiou Nikolaou street
- The church of Pantanassa (1859), Ipsilanti street
- The church of Ayios Dimitrios, in the upper town district
- The Catholic Church of Saint Andrew (1937), on Maisonos Street
- The Anglican church of Saint Andrew (1878), on Odos Agiou Andreou [59]
- The old church of Ayios Andreas (1836–1843), next to the new temple. Situated in the site of Andrew the Apostle's martyrdom, it was built in basilica style by the architect Lysandros Kaftanzoglou.
- Girokomiou Monastery (Holy Monastery of Panagia Girokomitissa): This historic monastery was founded in the 10th century AD in the eastern part of Patras. It was built on the ruins of an ancient temple of the goddess Artemis and for this reason the monastery's cathedral is dedicated to Saint Artemiοs. It is obvious that the monastery maintained a nursing home during the Byzantine period.
- Monastery of Agios Nikolaos Bala (Paleomonastiro): Ιt is built at the foot of Panachaikos, at an altitude of 500 meters, near the village of Bala, 8 km northeast of Patras. This historic and picturesque monastery was founded at the end of the 17th century. A marble slab on the north outer side of the Cathedral tells of the restoration of the monastery in 1693. The monastery has also recently been renovated, numbering nineteen nuns and celebrating 6 December and 10 May.
Jewish community
The first Jewish presence in the city was dated back to the Hellenistic era (see Romaniotes). After World War II, the community almost disappeared and the last synagogue closed in 1950.
There is a district of the city named Evreomnimata, where the old Jewish cemetery was located.
Cuisine

Local specialities include:
- Bourjeto (similar to the Corfiot Bourdeto)
- Tilichtária Patrina, pork meat dish
- Galatopita
- Tiganites (type of pancakes)
- Patrina loukoumia
- Rodozachari
- Mavrodafni wine
- Tentura drink
People


The city has a significant political history in modern Greece; famous politicians from Patras include the prime ministers Dimitrios Gounaris, the main leader of the anti-venizelist party in the 1910s, Stylianos Gonatas, a high-ranking officer, politician and one of the leaders of the "1922 Revolution", Andreas Michalakopoulos, a prominent liberal party cadre, foreign minister and prime minister, and Dimitrios Maximos, a distinguished economist, minister and finally prime minister in the civil war era. More recent figures include the Papandreou family, arguably the most influential in post World War II Greece, Panagiotis Kanellopoulos, the last democratically elected head of government before the establishment of the 1967 junta, and Costis Stephanopoulos, the former president of the Hellenic Republic.
|
Politics
|
Sports
|
Culture/Arts
|
Economy/Other
|
Transport






Seaport
The city has always been a sea-trade hub because of its strategic position. The port manages more than half of the foreign sea-passenger transportation in Greece,[60] and has excellent car-ferry links with the Ionian islands and the major Adriatic ports of Italy. Additionally, a new port was built in the southern section of the city to accommodate the increased traffic and relieve the city centre from port operations.[61] In 2011, this port went into operation. Ferries to Italy now dock there.[62]
The port is connected by a number of daily routes to the Ionian islands Kerkyra, Kefallonia and Zakynthos, to the port of Igoumenitsa and to the Italian cities Ancona, Bari, Brindisi, Trieste and Venice.[63]
Roads
A newly constructed, 20-kilometre (12 mi) ring road (the Bypass of Patras) was first opened in 2002 in order to alleviate heavy traffic throughout the city.[64] A mini ring road (known as the "Mini bypass" of Patras) is now complete (2019), alleviating heavy traffic-related problems in the city centre.[65] The mini-bypass is a two lanes mototway bridging the northern city entrance at the Zavlani neighborhood to the eastern entrance at the Aroi, Synora and Upper town (Ano poli) neighborhoods reducing the city centre crossing time to less than 4 minutes drive.
Two large highways were also constructed, connecting the seacoast and the new port with the Bypass of Patras. The first is over the small Diakoniaris river (from Eleftheriou Venizelou street until the Bypass'es exit in Eglykada), while the second consists of two roads, 4 km (2 mi) each, that run in parallel with the Glafkos river entering at the city' s New Port.[66][67] Another project was completed recently, leading to an additional entrance to the downtown area after expanding and widening Kanakari street. This work led to a fast, direct connection of the city's mini bypass road with the city centre.
The highway connection with Athens was recently upgraded to a 220km closed highway (Olympia odos), with a speed limit of 130km/hour, reducing the transit time to 1 hour and 45 minutes. The highway was connected to the Large bypass highway and is expected to extend all the way to Pyrgos by the end of 2023.[68] Patras will also be the central hub of the Ionia Odos highway, intended to bridge western Greece from Kalamata to Ioannina and the Kakavia border station. The Rio-Antirio bridge is north of the city and links the Peloponnese to mainland Greece. It was completed in August 2004.
Additional work was recently announced to begin in 2023 in order to connect via highway the Rion Antirrion bridge with Nafpaktos, Itea, Amfissa and Lamia. This project is expected to reduce the trip to Lamia to 90 minutes and its completion is expexted in 2025.
Patras is bypassed by the Olympia Odos (A8) motorway, which is also part of the E55 route that crosses the Rio-Antirio Bridge, dominating the sealine across the Gulf of Corinth.
- GR-5/E55
- GR-8/E55 and E65 (partly Panepistimiou Street)
- GR-8A
- GR-9/E55 (partly Akti Dymaion)
- GR-33 (partly Kalavryton, Georgiou Papandreou Street and Akrotiriou)
- Bypass of Patras
Rail
A rudimentary single, narrow gauge railway track crosses the city and connects it to Rio. In the past regional rail links were provided by the Hellenic Railways Organisation, connecting Patras to Athens and Piraeus as well as to Pyrgos and Kalamata.[63] OSE announced the suspension of all the rail service in the Peloponnese in January 2011[69] so today (2018) the railway track is in use only by suburban trains that connect Patras with the adjacent villages of Rion and Agios Vasileios. The central passenger train station of Patras which is a small building constructed in 1954, lies to the west of the downtown area, between Othonos-Amalias Avenue and the north port. The main freight station of Aghios Andreas lies further to the south, next to the homonymous church and it is not in use any more. Finally, the old depot of Aghios Dionysios, consisting of about ten tracks, offers basic turntable and roundhouse facilities; it is about 400 m (1,312.34 ft) long. A new double standard gauge railway line to Korinth and further to Athens is under construction. The construction works are currently (2018) in progress close to the suburbs of Patras, but the remaining few Kilometres till the city centre and the new port are still under study because of various financial and technical problems.[70]
Public transport
Patras is served by buses. There are two transport lines to and from the University of Patras and some nearby lines to city suburbs like Saravali, Glafkos, and Paralia. All the urban bus lines are about 40, with three numbers.
Commuter rail services have recently been established by Proastiakos, with one line currently connecting Patras, Rio, and Agios Vasileios.
Regional bus links are provided by the KTEL bus company and connect the city to most of Greece.
Tram
Patras was the first Greek city to introduce public electrified tramways in the past. Before the economic crisis, there were proposals for reestablishment of tram lines.
Air
Seasonal civilian air transport is provided by the military Patras Araxos Airport, about 40 km (25 mi) from the city's centre.
International relations
Patras is a pilot city of the Council of Europe and the European Commission Intercultural cities programme.[71]
Twin towns — sister cities
|
|
Patras was selected as main motif for the €10 Greek Patras 2006 commemorative coin, minted in 2006. This coin was designed to commemorate an event signaling an enlightened course for Patras and serving as a reminder of the way in which culture can stimulate the economy and promote development, when Patras was appointed European Capital of Culture. On the obverse is the logo for Patras 2006 around the words "European Capital of Culture".
Consulates
The city hosts consulates from the following countries:
|
Gallery
 The flag raised by Andreas Londos in Patras at the outbreak of the Greek War of Independence.
The flag raised by Andreas Londos in Patras at the outbreak of the Greek War of Independence. Surrender of Patras to General Schneider by Hippolyte Lecomte.
Surrender of Patras to General Schneider by Hippolyte Lecomte. Postcard with King George I Square in the late 19th century.
Postcard with King George I Square in the late 19th century. A view of Panachaiko mountain.
A view of Panachaiko mountain. Inside the Mycenaean cemetery of Voudeni, outside the city
Inside the Mycenaean cemetery of Voudeni, outside the city Pantanassa church
Pantanassa church Ruins of the Roman and Medieval Aqueducts
Ruins of the Roman and Medieval Aqueducts_connecting_Patra_with_Aigio%252C_the_best_preserved_two-arched_bridge_in_Greece%252C_Patras%252C_Greece_(14331225575).jpg.webp) Part of the Roman bridge over river Kallinaos
Part of the Roman bridge over river Kallinaos Illustration of Patrasso, 1687
Illustration of Patrasso, 1687 Athanasios Kanakaris during the Siege of Patras by Peter von Hess (1821)
Athanasios Kanakaris during the Siege of Patras by Peter von Hess (1821)_(2).jpg.webp) Patras Castle, 1890
Patras Castle, 1890 Fountain in Georgiou I Square
Fountain in Georgiou I Square Alhambra mansion, Trion Navarchon Street
Alhambra mansion, Trion Navarchon Street Pantokrator church, uptown district
Pantokrator church, uptown district Catholic Church of Saint Andrew
Catholic Church of Saint Andrew The courthouse
The courthouse The house where Kostis Palamas and Matilde Serao were born.
The house where Kostis Palamas and Matilde Serao were born. Tzini's house (1832), Maisonos & Agiou Nikolaou street
Tzini's house (1832), Maisonos & Agiou Nikolaou street Prapopoulos building
Prapopoulos building Villa Crove at the old English (Egglezika) district of Patras
Villa Crove at the old English (Egglezika) district of Patras Patras Lighthouse
Patras Lighthouse.jpg.webp) Entrance of Agios Nikolaos (Bala) Monastery (Paleomonastiro)
Entrance of Agios Nikolaos (Bala) Monastery (Paleomonastiro) View to the Gulf of Patras
View to the Gulf of Patras City view from Agiou Nikolaou steps
City view from Agiou Nikolaou steps A view of Panagitsa (stream) in 2011.
A view of Panagitsa (stream) in 2011. The castle of Patras, photograph of the 19th century
The castle of Patras, photograph of the 19th century
See also
- University of Patras
- University of Peloponnese
- Apollon Theatre (Patras)
- List of settlements in Achaea
- Panachaiko
- Cities in Greece
References
- romanized: Pátrai, Ancient Greek: [pátrai̯], Katharevousa: [ˈpatre]
- [ˈpatrae̯]
- "Eurostat – Data Explorer". appsso.eurostat.ec.europa.eu.
- Population on 1 January by age groups and sex - functional urban areas, Eurostat, accessed 7 July 2020.
- Mansfield, Paul (29 January 2006). "Party town gets a culture kick". The Guardian. Retrieved 6 September 2017.
- "Region of Western Greece: Geography". Ditikiellda-region.com. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 9 February 2007.
- Thomopoulos, St. N, History of the City of Patras from Antiquity to 1821, Patrai 1952, (ed. Triantafyllou, K.N.)
- "Climate of Patras". Hellenic National Meteorological Service. Archived from the original on 18 March 2012. Retrieved 28 February 2013.
- Chris K. "Birds, birding and conservation in Greece". Hellenic Ornithological Society. Archived from the original on 25 December 2008. Retrieved 5 January 2009.
- Patra. From antiquity until today, Kotinos A.E. Editions, Athens 2005
- Encyclopaedia of Islam s.v. Baliabadra
- Strategus Makrygiannis. ""Memoirs", Book A, Chapter I, Athens, 1849". Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- Triantafyllou, Κ.Ν., Historic Lexicon of Patras
- Kounenaki Pegy. "19th Century Patras: how the character of the city changed with the development of the port after 1828". News.kathimerini.gr. Archived from the original on 15 February 2012. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- Thomopoulos
- "Contents". Archived from the original on 26 March 2012. Retrieved 10 February 2007., retrieved 9 February 2007
- ΕΤ1 TV, broadcast "Mεταμουσείο",The New Archaeological Museum of Patras,18/03/2013| http://9dim-patras.ach.sch.gr/images/2018-19/2018_11_25/video/mouseio.mp4
- "RC - Patras, Restoration and preservation of the Roman amphitheatre of Patras". Iiinstitute.nl. Archived from the original on 27 March 2012. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- Mentzini, Marilena. "Patras' Roman Aqueduct -Restoration". Retrieved 6 September 2017.
- "Ρωμαϊκό Υδραγωγείο". e-patras.gr. Archived from the original on 30 July 2012. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Info about St.Andrew Church". InfoCenterpatras.gr. Archived from the original on 5 October 2011. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Άγιος Ανδρέας". e-patras.gr. Archived from the original on 2 August 2012. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Πάτρα: Το αρχαιότερο σε λειτουργία χαμάμ της Ελλάδας - Εκεί που εξαγνίζονται ψυχές και σώματα ανελλιπώς απο τον 17ο αιώνα!". THE BEST. 23 February 2015.
- "WESTPOINT - Mια αρχιτεκτονική βόλτα στην Πάτρα". Westpoint.gr. Archived from the original on 26 March 2012. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- Αρχιτεκτονικοί θησαυροί της Πάτρας που έγιναν πολυκατοικίες
- "ΦΕΚ A 87/2010, Kallikratis reform law text" (in Greek). Government Gazette.
- "Population & housing census 2001 (incl. area and average elevation)" (PDF) (in Greek). National Statistical Service of Greece.
- 1928–1980 statistical data are from: "The population of Greece in the second half of the 20th century". Hellenic Republic. National Statistical Service of Greece. Athens 1980 & "Statistical Yearbook of Greece" Hellenic Republic. National Statistical Service of Greece. Athens 1980
- Population data from 1853 to 1920 are cited from: Kosta N. Triantafyllou, "Istorikon Lexikon ton Patron: Istoria tis poleos ton Patron apo arxaiotaton xronon eos simeron kata alphavitikin eidologikin katataksin" 3rd edition, Patrai 1995
- Data on municipal and urban population refer to permanent population and are taken from: the "2001 Census" of the National Statistical Service of Greece
- Loizos Bailas, Mixalis Kaplanidis. "MHXANIKH AE". Michaniki.gr. Archived from the original on 28 September 2007. Retrieved 5 January 2009.
- "Metropolitan Optical Network of Patras". Ru6.cti.gr. Archived from the original on 16 January 2009. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "European Culture Capital, Patras Venues". Patras2006.gr. Archived from the original on 23 July 2007. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Ktizon, Presentation of the Archaeological museum of Patras". Ktizon.blogspot.com. 28 March 2007. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Cultural Facilities in Patras". Infocenterpatras.gr. Archived from the original on 5 October 2011. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Παραδίδεται το έργο της ανάπλασης της Αγοράς Αργύρη - Οικονομία". Thebest.gr. 19 January 2010. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Greek Statistics Organization, Tourism data - 2006" (PDF).
- "Greek Statistics Organization, Tourism data - 2006" (PDF).
- "Abex Timber Manufacturing". Abex.gr. Archived from the original on 3 September 2011. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Andromeda Aquaculture". Andromeda aquaculture.gr. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Nireus Aquaculture". Nireus.gr. Archived from the original on 16 March 2011. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "λκμκ αρχιτέκτονες μηχανικοί - Βιομηχανικοί χώροι - Εργοστάσιο Παραγωγής Ιχθυοτροφών στην ΒΙ.ΠΕ. Πατρών". Lkmk.gr. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Kepenou mills". Tovima.dolnet.gr. Archived from the original on 7 December 2008. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Acciona Wind Parks". Acciona-energia.com. Archived from the original on 14 January 2009. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Glafkos Hydroelectric Power Station". Dei.gr. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Intracom Telecom: Infrastructure". Intracom-telecom.com. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- Intrasoft launched the new branch operation in the suburbs of Patras, an article in newspaper "GNOMI" (13/11/2018)
- "Corallia Innohub". Archived from the original on 29 March 2014.
- "Uni Systems opens Remote Development Center in cooperation with Knowledge Broadband Services | Unisystems". www.unisystems.gr.
- "Patras Science Park - Hosted Companies". Patras Science Park. Archived from the original on 5 December 2008. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Awards of the 7th International Venture Capital Forum" (in Greek). Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Vianex facilities in Patras". Vianex.gr. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Industrial Systems Institute". Isi.gr. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Institute of Chemical Engineering & High Temperature Chemical Processes". Iceht.forth.gr. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Institute of Biomedical Technology". Inbit.gr. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Συμπόσιο Ποίησης". Poetrysymposium.gr. 18 July 2012. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Patras Final Report" (PDF). Europa.eu.int. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 March 2006. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Patras Future Report". Europa.eu.int. Archived from the original on 4 May 2006. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Πολιτισμός". e-patras.gr. Archived from the original on 28 July 2012. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- George Xenides. "Παμπελοποννησιακό Εθνικό Στάδιο Πατρών". Stadia.gr. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- Diocese in Europe, Greece: Patras, accessed 5 September 2020
- ΟΛΠ - Στατιστικά στοιχεία (in Greek). Archived from the original on 4 April 2008.
- http://www.patrasport.gr: The Port Archived 22 October 2019 at the Wayback Machine
- "Southern Passenger Port | Οργανισμός Λιμένος Πατρών". www.patrasport.gr. Archived from the original on 10 November 2018. Retrieved 29 June 2019.
- "Πως θα έρθετε". e-patras.gr. Archived from the original on 17 February 2013. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Ring Road map" (PDF). Dikitiellada.gov.gr. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- "Works under construction in the region of Western Greece". Ditikiellada.gov.gr. Archived from the original on 23 February 2009. Retrieved 2 October 2012.
- Loizos Bailas, Mixalis Kaplanidis. "MHXANIKH AE". Michaniki.gr. Archived from the original on 28 September 2007. Retrieved 5 January 2009.
- Loizos Bailas, Mixalis Kaplanidis. "MHXANIKH AE". Michaniki.gr. Archived from the original on 28 September 2007. Retrieved 5 January 2009.
- "Road Axis Patra - Athens - Thessaloniki - Evzoni". Hellenic Ministry of Public Works. Archived from the original on 13 February 2012.
- "ΤΡΑΙΝΟΣΕ: Διακοπή δρομολογίων και αύξηση κομίστρων | naftemporiki.gr". www.naftemporiki.gr. 23 December 2010.
- "Rio – New Port of Patras".
- Council of Europe (2011). "Intercultural city: Patras, Greece". coe.int. Retrieved 22 May 2011.
- "e-patras.gr - Αδελφοποιημένες Πόλεις". Archived from the original on 26 October 2009.
- Градови партнери [City of Banja Luka - Partner cities]. Administrative Office of the City of Banja Luka (in Serbian). Archived from the original on 17 September 2011. Retrieved 9 August 2013.
- "Patras Municipality - Fraternize Cities". Patras Municipality. Archived from the original on 30 July 2012. Retrieved 4 June 2011.
- "Limassol Twinned Cities". Limassol (Lemesos) Municipality. Archived from the original on 1 April 2013. Retrieved 29 July 2013.
- Archived 23 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- "Online site translation into English and other languages – Yandex.Translate". translate.yandex.com. Retrieved 6 September 2017.
- Makris, A. (April 2015). "Russian Sailing Ship Docks in Patras for Twinning with Kaliningrad - GreekReporter.com". Retrieved 6 September 2017.
External links
 The dictionary definition of Patras at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of Patras at Wiktionary- The official website of the city Archived 13 August 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- official website of the Carnival of Patras Archived 15 March 2021 at the Wayback Machine
- Patras The Official website of the Greek National Tourism Organisation
- EΡΤ,ET1 TV,"Post-Museum" documentary - "The Patras New Archaeological Museum"
- "The Glaraki's School Complex of Patras"