Reconnaissance satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications.


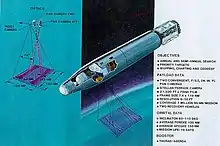


The first generation type (i.e., Corona[1][2] and Zenit) took photographs, then ejected canisters of photographic film which would descend back down into Earth's atmosphere. Corona capsules were retrieved in mid-air as they floated down on parachutes. Later, spacecraft had digital imaging systems and downloaded the images via encrypted radio links.
In the United States, most information available about reconnaissance satellites is on programs that existed up to 1972, as this information has been declassified due to its age. Some information about programs before that time is still classified information, and a small amount of information is available on subsequent missions.
A few up-to-date reconnaissance satellite images have been declassified on occasion, or leaked, as in the case of KH-11 photographs which were sent to Jane's Defence Weekly in 1984.[3]
History
On 16 March 1955, the United States Air Force officially ordered the development of an advanced reconnaissance satellite to provide continuous surveillance of "preselected areas of the Earth" in order "to determine the status of a potential enemy’s war-making capability".[4]
Types
There are several major types of reconnaissance satellite.[5]
- Missile early warning
- Provides warning of an attack by detecting ballistic missile launches. Earliest known are Missile Defense Alarm System.
- Nuclear explosion detection
- Detects nuclear detonation from space. Vela is the earliest known.
- Electronic reconnaissance
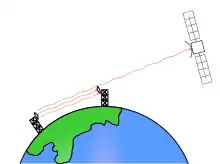
- Signals intelligence, intercepts stray radio waves. SOLRAD is the earliest known.[6]
- Optical imaging surveillance
- Earth imaging satellites. Satellite images can be a survey or close-look telephoto. Corona is the earliest known. Spectral imaging is commonplace.
- Radar imaging surveillance
- Most space-based radars use synthetic-aperture radar. Can be used at night or through cloud cover. Earliest known are the Soviet US-A series.
Missions
Examples of reconnaissance satellite missions:
- High resolution photography (IMINT)
- Measurement and Signature Intelligence (MASINT)
- Communications eavesdropping (SIGINT)
- Covert communications
- Monitoring of nuclear test ban compliance (see National Technical Means)
- Detection of missile launches
On 28 August 2013, it was thought that "a $1-billion high-powered spy satellite capable of snapping pictures detailed enough to distinguish the make and model of an automobile hundreds of miles below"[7] was launched from California's Vandenberg Air Force Base using a Delta IV Heavy launcher, America's highest-payload space launch vehicle at the time.
On 17 February 2014, a Russian Kosmos-1220 originally launched in 1980 and used for naval missile targeting until 1982, made an uncontrolled atmospheric entry.[8]
Benefits
Reconnaissance satellites have been used to enforce human rights, through the Satellite Sentinel Project, which monitors atrocities in Sudan and South Sudan.
During his 1980 State of the Union Address, President Jimmy Carter explained how all of humanity benefited from the presence of American spy satellites:
...photo-reconnaissance satellites, for example, are enormously important in stabilizing world affairs and thereby make a significant contribution to the security of all nations.[9]
Additionally, companies such as GeoEye and DigitalGlobe have provided commercial satellite imagery in support of natural disaster response and humanitarian missions.[10]
During the 1950s, a Soviet hoax had led to American fears of a bomber gap. In 1968, after gaining satellite photography, the United States' intelligence agencies were able to state with certainty that "No new ICBM complexes have been established in the USSR during the past year."[11] President Lyndon B. Johnson told a gathering in 1967:
I wouldn't want to be quoted on this ... We've spent $35 or $40 billion on the space program. And if nothing else had come out of it except the knowledge that we gained from space photography, it would be worth ten times what the whole program has cost. Because tonight we know how many missiles the enemy has and, it turned out, our guesses were way off. We were doing things we didn't need to do. We were building things we didn't need to build. We were harboring fears we didn't need to harbor.[11]
In fiction
Spy satellites are commonly seen in spy fiction and military fiction. Some works of fiction that focus specifically on spy satellites include:
- The OMAC Project
- Enemy of the State
- Body of Lies
- Ice Station Zebra
- Parmanu: The Story of Pokhran
- Patriot Games
See also
- Aerial reconnaissance
- Defense Support Program (U.S.)
- European Union Satellite Centre
- List of intelligence gathering disciplines
- List of Kosmos satellites
- National Reconnaissance Office (U.S.)
- Satcom on the Move
References
- "Corona History". National Reconnaissance Office]. Retrieved 15 February 2014.
- "Corona Program". Mission and Spacecraft Library. Archived from the original on 7 August 2011. Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- Wright, Michael; Herron, Caroline Rand (8 December 1985). "Two Years for Morison". The New York Times. Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- Erickson, Mark (2005). Into the Unknown Together – The DOD, NASA, and Early Spaceflight (PDF). ISBN 1-58566-140-6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2009.
- reconnaissance satellite, Infoplease, retrieved 17 February 2014
- "The Navy's Spy Missions in Space". U.S. Naval Research Laboratory. April 2008. Archived from the original on 21 April 2019. Retrieved 21 April 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - Hennigan, W.J. (27 August 2013). "Monster rocket to blast off from Pacific coast, rattle Southland". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 16 February 2014.
- Melissa Goldin (17 February 2014). "Fragments of Soviet-Era Satellite Burn Up in Earth's Atmosphere". Mashable. Retrieved 17 February 2014.
- "The State of the Union Annual Message to the Congress". 1980 State of the Union Address. The American Presidency Project. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
- "Commercial Satellite Imagery Companies Partner with the U.S. Geological Survey in Support of the International Charter "Space and Major Disasters"". USGS Newsroom. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 4 April 2014.
- Heppenheimer, T. A. (1998). The Space Shuttle Decision. NASA. pp. 191, 198.
Further reading
- Kupperberg, Paul (2003). Spy satellites. Rosen Publishing Group. ISBN 9780823938544. ISBN 0-8239-3854-9
- Richelson, Jeffrey (1990). America's Secret Eyes in Space: the U.S. Keyhole Spy Satellite Program. Harper & Row. ISBN 9780887302855. ISBN 0-88730-285-8
- Norris, Pat (2008). Spies in the Sky: Surveillance Satellites in War and Peace. Berlin; New York: Springer; Chichester, UK: In association with Praxis Publishing. Bibcode:2008spsk.book.....N. OCLC 154711855.