Johnson–Nyquist noise
Johnson–Nyquist noise (thermal noise, Johnson noise, or Nyquist noise) is the electronic noise generated by the thermal agitation of the charge carriers (usually the electrons) inside an electrical conductor at equilibrium, which happens regardless of any applied voltage. Thermal noise is present in all electrical circuits, and in sensitive electronic equipment (such as radio receivers) can drown out weak signals, and can be the limiting factor on sensitivity of electrical measuring instruments. Thermal noise increases with temperature. Some sensitive electronic equipment such as radio telescope receivers are cooled to cryogenic temperatures to reduce thermal noise in their circuits. The generic, statistical physical derivation of this noise is called the fluctuation-dissipation theorem, where generalized impedance or generalized susceptibility is used to characterize the medium.
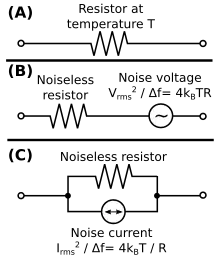
Thermal noise in an ideal resistor is approximately white, meaning that the power spectral density is nearly constant throughout the frequency spectrum, but does decay to zero at extremely high frequencies (terahertz for room temperature). When limited to a finite bandwidth, thermal noise has a nearly Gaussian amplitude distribution.[1]
History
This type of noise was discovered and first measured by John B. Johnson at Bell Labs in 1926.[2][3] He described his findings to Harry Nyquist, also at Bell Labs, who was able to explain the results.[4]
Derivation
As Nyquist stated in his 1928 paper, the sum of the energy in the normal modes of electrical oscillation would determine the amplitude of the noise. Nyquist used the equipartition law of Boltzmann and Maxwell. Using the concept potential energy and harmonic oscillators of the equipartition law,[5]
where is the noise power density in (W/Hz), is the Boltzmann constant and is the temperature. Multiplying the equation by bandwidth gives the result as noise power.
where N is the noise power and Δf is the bandwidth.
Noise voltage and power
Thermal noise is distinct from shot noise, which consists of additional current fluctuations that occur when a voltage is applied and a macroscopic current starts to flow. For the general case, the above definition applies to charge carriers in any type of conducting medium (e.g. ions in an electrolyte), not just resistors. It can be modeled by a voltage source representing the noise of the non-ideal resistor in series with an ideal noise free resistor.
The one-sided power spectral density, or voltage variance (mean square) per hertz of bandwidth, is given by
where kB is Boltzmann's constant in joules per kelvin, T is the resistor's absolute temperature in kelvins, and R is the resistor value in ohms (Ω). Using this equation for quick calculation, at room temperature:
For example, a 1 kΩ resistor at a temperature of 300 K has
For a given bandwidth, the root mean square (RMS) of the voltage, , is given by
where Δf is the bandwidth in hertz over which the noise is measured. For a 1 kΩ resistor at room temperature and a 10 kHz bandwidth, the RMS noise voltage is 400 nV.[6] A useful rule of thumb to remember is that 50 Ω at 1 Hz bandwidth correspond to 1 nV noise at room temperature.
A resistor in a short circuit dissipates a noise power of
The noise generated at the resistor can transfer to the remaining circuit; the maximum noise power transfer happens with impedance matching when the Thévenin equivalent resistance of the remaining circuit is equal to the noise-generating resistance. In this case each one of the two participating resistors dissipates noise in both itself and in the other resistor. Since only half of the source voltage drops across any one of these resistors, the resulting noise power is given by
where P is the thermal noise power in watts. Notice that this is independent of the noise-generating resistance.
Noise current
The noise source can also be modeled by a current source in parallel with the resistor by taking the Norton equivalent that corresponds simply to dividing by R. This gives the root mean square value of the current source as:
Noise power in decibels
Signal power is often measured in dBm (decibels relative to 1 milliwatt). From the equation above, noise power in a resistor at room temperature, in dBm, is then:
At room temperature (300 K) this is approximately
Using this equation, noise power for different bandwidths is simple to calculate:
| Bandwidth | Thermal noise power at 300 K (dBm) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Hz | −174 | |
| 10 Hz | −164 | |
| 100 Hz | −154 | |
| 1 kHz | −144 | |
| 10 kHz | −134 | FM channel of 2-way radio |
| 100 kHz | −124 | |
| 180 kHz | −121.45 | One LTE resource block |
| 200 kHz | −121 | GSM channel |
| 1 MHz | −114 | Bluetooth channel |
| 2 MHz | −111 | Commercial GPS channel |
| 3.84 MHz | −108 | UMTS channel |
| 6 MHz | −106 | Analog television channel |
| 20 MHz | −101 | WLAN 802.11 channel |
| 40 MHz | −98 | WLAN 802.11n 40 MHz channel |
| 80 MHz | −95 | WLAN 802.11ac 80 MHz channel |
| 160 MHz | −92 | WLAN 802.11ac 160 MHz channel |
| 1 GHz | −84 | UWB channel |
Thermal noise on capacitors
Ideal capacitors, as lossless devices, do not have thermal noise, but as commonly used with resistors in an RC circuit, the combination has what is called kTC noise. The noise bandwidth of an RC circuit is Δf = 1/(4RC).[9] When this is substituted into the thermal noise equation, the result has an unusually simple form as the value of the resistance (R) drops out of the equation. This is because higher R decreases the bandwidth as much as it increases the noise.
The mean-square and RMS noise voltage generated in such a filter are:[10]
The noise charge is the capacitance times the voltage:
This charge noise is the origin of the term "kTC noise".
Although independent of the resistor's value, 100% of the kTC noise arises in the resistor. Therefore, if the resistor and the capacitor are at different temperatures, the temperature of the resistor alone should be used in the above calculation.
An extreme case is the zero bandwidth limit called the reset noise left on a capacitor by opening an ideal switch. The resistance is infinite, yet the formula still applies; however, now the RMS must be interpreted not as a time average, but as an average over many such reset events, since the voltage is constant when the bandwidth is zero. In this sense, the Johnson noise of an RC circuit can be seen to be inherent, an effect of the thermodynamic distribution of the number of electrons on the capacitor, even without the involvement of a resistor.
The noise is not caused by the capacitor itself, but by the thermodynamic fluctuations of the amount of charge on the capacitor. Once the capacitor is disconnected from a conducting circuit, the thermodynamic fluctuation is frozen at a random value with standard deviation as given above. The reset noise of capacitive sensors is often a limiting noise source, for example in image sensors.
Any system in thermal equilibrium has state variables with a mean energy of kT/2 per degree of freedom. Using the formula for energy on a capacitor (E = ½CV2), mean noise energy on a capacitor can be seen to also be ½C(kT/C) = kT/2. Thermal noise on a capacitor can be derived from this relationship, without consideration of resistance.
| Capacitance | Electrons | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 fF | 2 mV | 2 aC | 12.5 e− |
| 10 fF | 640 µV | 6.4 aC | 40 e− |
| 100 fF | 200 µV | 20 aC | 125 e− |
| 1 pF | 64 µV | 64 aC | 400 e− |
| 10 pF | 20 µV | 200 aC | 1250 e− |
| 100 pF | 6.4 µV | 640 aC | 4000 e− |
| 1 nF | 2 µV | 2 fC | 12500 e− |
Generalized forms
The voltage noise described above is a special case for a purely resistive component for low frequencies. In general, the thermal electrical noise continues to be related to resistive response in many more generalized electrical cases, as a consequence of the fluctuation-dissipation theorem. Below a variety of generalizations are noted. All of these generalizations share a common limitation, that they only apply in cases where the electrical component under consideration is purely passive and linear.
Reactive impedances
Nyquist's original paper also provided the generalized noise for components having partly reactive response, e.g., sources that contain capacitors or inductors.[4] Such a component can be described by a frequency-dependent complex electrical impedance . The formula for the power spectral density of the series noise voltage is
The function is simply equal to 1 except at very high frequencies, or near absolute zero (see below).
The real part of impedance, , is in general frequency dependent and so the Johnson–Nyquist noise is not white noise. The rms noise voltage over a span of frequencies to can be found by integration of the power spectral density:
- .
Alternatively, a parallel noise current can be used to describe Johnson noise, its power spectral density being
where is the electrical admittance; note that
Quantum effects at high frequencies or low temperatures
Nyquist also pointed out that quantum effects occur for very high frequencies or very low temperatures near absolute zero.[4] The function is in general given by
where is Planck's constant and is a multiplying factor.
At very high frequencies , the function starts to exponentially decrease to zero. At room temperature this transition occurs in the terahertz, far beyond the capabilities of conventional electronics, and so it is valid to set for conventional electronics work.
Relation to Planck's law
Nyquist's formula is essentially the same as that derived by Planck in 1901 for electromagnetic radiation of a blackbody in one dimension—i.e., it is the one-dimensional version of Planck's law of blackbody radiation.[11] In other words, a hot resistor will create electromagnetic waves on a transmission line just as a hot object will create electromagnetic waves in free space.
In 1946, Dicke elaborated on the relationship,[12] and further connected it to properties of antennas, particularly the fact that the average antenna aperture over all different directions cannot be larger than , where λ is wavelength. This comes from the different frequency dependence of 3D versus 1D Planck's law.
Multiport electrical networks
Richard Q. Twiss extended Nyquist's formulas to multi-port passive electrical networks, including non-reciprocal devices such as circulators and isolators.[13] Thermal noise appears at every port, and can be described as random series voltage sources in series with each port. The random voltages at different ports may be correlated, and their amplitudes and correlations are fully described by a set of cross-spectral density functions relating the different noise voltages,
where the are the elements of the impedance matrix . Again, an alternative description of the noise is instead in terms of parallel current sources applied at each port. Their cross-spectral density is given by
where is the admittance matrix.
Continuous electrodynamic media
The full generalization of Nyquist noise is found in fluctuation electrodynamics, which describes the noise current density inside continuous media with dissipative response in a continuous response function such as dielectric permittivity or magnetic permeability. The equations of fluctuation electrodynamics provide a common framework for describing both Johnson–Nyquist noise and free-space blackbody radiation.[14]
See also
- Fluctuation-dissipation theorem
- Shot noise
- 1/f noise
- Langevin equation
- Rise over thermal
References
- John R. Barry; Edward A. Lee; David G. Messerschmitt (2004). Digital Communications. Sprinter. p. 69. ISBN 9780792375487.
- Anonymous (1927). "Minutes of the Philadelphia Meeting December 28, 29, 30, 1926". Physical Review. 29 (2): 350–373. Bibcode:1927PhRv...29..350.. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.29.350.
- Johnson, J. (1928). "Thermal Agitation of Electricity in Conductors". Physical Review. 32 (97): 97–109. Bibcode:1928PhRv...32...97J. doi:10.1103/physrev.32.97.
- Nyquist, H. (1928). "Thermal Agitation of Electric Charge in Conductors". Physical Review. 32 (110): 110–113. Bibcode:1928PhRv...32..110N. doi:10.1103/physrev.32.110.
- Tomasi, Wayne (1994). Electronic Communication. Prentice Hall PTR. ISBN 9780132200622.
- Google Calculator result for 1 kΩ room temperature 10 kHz bandwidth
- Pierce, J. R. (1956). "Physical Sources of Noise". Proceedings of the IRE. 44 (5): 601–608. doi:10.1109/JRPROC.1956.275123. S2CID 51667159.
- Vizmuller, Peter (1995), RF Design Guide, Artech House, ISBN 0-89006-754-6
- Lundberg, Kent H. "Noise Sources in Bulk CMOS" (PDF). p. 10.
- Sarpeshkar, R.; Delbruck, T.; Mead, C. A. (November 1993). "White noise in MOS transistors and resistors" (PDF). IEEE Circuits and Devices Magazine. 9 (6): 23–29. doi:10.1109/101.261888. S2CID 11974773.
- Urick, V. J.; Williams, Keith J.; McKinney, Jason D. (2015-01-30). Fundamentals of Microwave Photonics. p. 63. ISBN 9781119029786.
- Dicke, R. H. (1946-07-01). "The Measurement of Thermal Radiation at Microwave Frequencies". Review of Scientific Instruments. 17 (7): 268–275. Bibcode:1946RScI...17..268D. doi:10.1063/1.1770483. PMID 20991753.
- Twiss, R. Q. (1955). "Nyquist's and Thevenin's Theorems Generalized for Nonreciprocal Linear Networks". Journal of Applied Physics. 26 (5): 599–602. Bibcode:1955JAP....26..599T. doi:10.1063/1.1722048.
- Pitaevskii, L. P.; Lifshitz, E. M. (1980). "Chapter VIII. Electromagnetic Fluctuations". Statistical Physics, Part 2: Theory of the Condensed State. Vol. 9 (1st ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-7506-2636-1.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. (in support of MIL-STD-188).
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. (in support of MIL-STD-188).