Aliados (Primera Guerra Mundial)
En el contexto de la Primera Guerra Mundial, se entiende por Aliados a los países en conflicto con las Potencias Centrales. El bloque aliado tuvo su origen en la Triple Entente, integrada por: Francia, el Reino Unido y Rusia. En sentido estricto comenzaron a llamarse así tras la firma del Pacto de Londres, el 5 de septiembre de 1914, por el que los beligerantes se comprometían a no firmar una paz por separado.[1]

Mapamundi que muestra los participantes durante la Primera Guerra Mundial.
Entente y los Aliados (algunos entraron en la guerra y otros se mantuvieron neutral pero apoyaron a sus aliados)
Potencias Centrales
Países neutrales

Evolución de las alianzas durante la Primera Guerra Mundial:
Entente
Colonia, dominio y/o territorios ocupados por la Entente
Potencias centrales
Territorio ocupado por las potencias centrales y/o sus colonias
Neutral
Principales países aliados
- 8 países en total participaron durante la primera Gran Guerra.
.svg.png.webp) Reino de Bélgica (incluyendo sus fuerzas coloniales)
Reino de Bélgica (incluyendo sus fuerzas coloniales).svg.png.webp) Reino de Serbia
Reino de Serbia.svg.png.webp) Reino de Montenegro
Reino de Montenegro.svg.png.webp) Tercera República Francesa (incluyendo sus fuerzas coloniales)
Tercera República Francesa (incluyendo sus fuerzas coloniales) Imperio ruso (hasta marzo de 1917), el Gobierno Provisional Ruso capituló en noviembre de 1917.
Imperio ruso (hasta marzo de 1917), el Gobierno Provisional Ruso capituló en noviembre de 1917..svg.png.webp) Imperio británico
Imperio británico
.svg.png.webp) Reino de Italia (a partir de abril de 1915 e incluyendo sus fuerzas coloniales)
Reino de Italia (a partir de abril de 1915 e incluyendo sus fuerzas coloniales).svg.png.webp) Estados Unidos de América (con la Fuerza Expedicionaria Estadounidense a partir de 1917)
Estados Unidos de América (con la Fuerza Expedicionaria Estadounidense a partir de 1917)
.svg.png.webp)
 Puerto Rico (su desempeño fue en el canal de Panamá desde mayo de 1917 con el 65.º Regimiento de Infantería (Estados Unidos), conocido en inglés como 65th Infantry Regiment (United States)
Puerto Rico (su desempeño fue en el canal de Panamá desde mayo de 1917 con el 65.º Regimiento de Infantería (Estados Unidos), conocido en inglés como 65th Infantry Regiment (United States)
Otros países aliados
Otros países que tuvieron participación militar:
 Gran Imperio del Japón
Gran Imperio del Japón República Portuguesa (a partir de marzo de 1916 e incluyendo sus fuerzas coloniales)
República Portuguesa (a partir de marzo de 1916 e incluyendo sus fuerzas coloniales) Reino de Rumanía (de agosto de 1916 a mayo de 1918)
Reino de Rumanía (de agosto de 1916 a mayo de 1918).svg.png.webp) Reino de Grecia (el Gobierno de Defensa Nacional declaró la guerra a las Potencias Centrales en noviembre de 1916, el estado lo hizo en junio de 1917)
Reino de Grecia (el Gobierno de Defensa Nacional declaró la guerra a las Potencias Centrales en noviembre de 1916, el estado lo hizo en junio de 1917).svg.png.webp) Principado de Albania
Principado de Albania.svg.png.webp) Brasil (a partir de octubre de 1917)
Brasil (a partir de octubre de 1917) República Democrática de Armenia (a partir de mayo de 1918)
República Democrática de Armenia (a partir de mayo de 1918) Checoslovaquia (con la Legión Checoslovaca)
Checoslovaquia (con la Legión Checoslovaca) Reino de Finlandia (a partir de octubre de 1918)
Reino de Finlandia (a partir de octubre de 1918).svg.png.webp) Reino de Nepal (sus fuerzas se integraron en el Ejército Indio Británico)
Reino de Nepal (sus fuerzas se integraron en el Ejército Indio Británico).svg.png.webp) Reino de Siam
Reino de Siam San Marino (a partir de junio de 1915)
San Marino (a partir de junio de 1915)
Aliados nominales
Países que declararon la guerra a las Potencias Centrales pero que no participaron militarmente:
 Principado de Andorra (Desde 1914)[2]
Principado de Andorra (Desde 1914)[2].svg.png.webp) República de China (a partir de agosto de 1917, pero un año antes los ingleses los reclutaron para trabajos detrás de la Línea del Frente)[3]
República de China (a partir de agosto de 1917, pero un año antes los ingleses los reclutaron para trabajos detrás de la Línea del Frente)[3] Costa Rica (a partir de mayo de 1918)
Costa Rica (a partir de mayo de 1918) Cuba (a partir de abril de 1917)
Cuba (a partir de abril de 1917) Guatemala (a partir de abril de 1918)
Guatemala (a partir de abril de 1918) Liberia (a partir de agosto de 1917)
Liberia (a partir de agosto de 1917) Haití (a partir de julio de 1918)
Haití (a partir de julio de 1918) Honduras (a partir de julio de 1918)
Honduras (a partir de julio de 1918) Panamá (en abril de 1917 declaró la guerra a Alemania, en diciembre de 1917 al Imperio Austrohúngaro).
Panamá (en abril de 1917 declaró la guerra a Alemania, en diciembre de 1917 al Imperio Austrohúngaro).
Fuerzas y pérdidas de las potencias aliadas
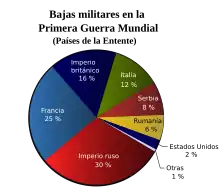
Gráfica circular mostrando las bajas de las fuerzas aliadas.
| País | Fuerzas movilizadas | Muertos en combate | Heridos en combate | Pérdidas totales | Porcentaje de pérdidas respecto al total de fuerzas movilizadas |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | 412 953 | 61 928[4] | 152 171 | 214 099 | 52% |
| Bélgica | 267 000 | 38 172[5] | 44 686 | 82 858 | 31% |
| Canadá | 28 964 | 56 639[6] | 149 732 | 214 676 | 34% |
| Estados Unidos | 4 355 000 | 116 708[7] | 205 690 | 322 398 | 7% |
| Francia | 8 410 000 | 1 186 000[8] | 4 266 000 | 5 663 800 | 67% |
| Grecia | 230 000 | 26 000[9] | 21 000 | 47 000 | 20% |
| India | 1 440 437 | 74 187[10] | 143 401 | 217 588 | 15% |
| Italia | 5 615 000 | 651 010[11] | 953 886 | 1 604 896 | 29% |
| Japón | 800 000 | 415[12] | 907 | 1322 | <1% |
| Montenegro | 50 000 | 3000 | 10 000 | 13 000 | 26% |
| Nueva Zelanda | 128 525 | 18 050[13] | 41 317 | 59 367 | 46% |
| Terranova | 11 922 | 1204[14] | 2314 | 3518 | 30% |
| Portugal | 100 000 | 7222[15] | 13 751 | 20 973 | 21% |
| Reino Unido | 6 200 000 | 885 138[16] | 1 663 435 | 2 548 573 | 41% |
| Rumanía | 750 000 | 250 000[17] | 120 000 | 370 000 | 43% |
| Rusia | 12 000 000 | 1 811 000[18] | 4 950 000 | 6 761 000 | 59% |
| Serbia | 707 343 | 275 000[19] | 133 148 | 408 148 | 20% |
| Sudáfrica | 136 070 | 9463[20] | 12 029 | 21 492 | 16% |
| Total | 42 243 214 | 5 691 241 | 12 809 280 | 18 500 521 | 44% |
| Rusia | 173,2 | 21.700
km² |
257,7 |
| Francia | 39,8 | 500.000 km² | 138,7 |
| Reino Unido | 46 | 300.000 km² | 226,4 |
| Italia | 35.6 | 300.000 km² | 93,3 |
| Estados Unidos | 95,5 | 7.800.000 km² | 511,6 |
| Total | 793,3 | 67.500.000 km² | 1.096,5 |
Referencias
- Stevenson, 2013, p. 106.
- https://adadabsurdum.blogspot.com/2015/03/andorra-vs-alemania-39-anos-en-guerra.html
- https://www.lavanguardia.com/internacional/20150405/54429433004/el-olvidado-papel-de-los-chinos-en-la-i-guerra-mundial.html
- Pérdidas australianas
Included in total are 55,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds-.
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.-
Totals include 2,005 military deaths during 1919-21-. The 1922 War Office report listed 59,330 Army war dead. - Belgium casualties
Included in total are 35,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds Figures include 13,716 killed and 24,456 missing up until Nov.11, 1918. "These figures are approximate only, the records being incomplete.". - Canada casualties
Included in total are 53,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds.
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.
Totals include 3,789 military deaths during 1919-21 and 150 Merchant Navy deaths-. The losses of Newfoundland are listed separately on this table. The 1922 War Office report listed 56,639 Army war dead. - United States casualties
Official military war deaths listed by the US Dept. of Defense for the period ending Dec. 31, 1918 are 116,516; which includes 53,402 battle deaths and 63,114 other deaths., The US Coast Guard lost an additional 192 dead. - France casualties
Included in total are 1,186,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds. Totals include the deaths of 71,100 French colonial troops. -Figures include war related military deaths of 28,600 from 11/11/1918 to 6/1/1919. - Greece casualties
Jean Bujac in a campaign history of the Greek Army in World War One listed 8,365 combat related deaths and 3,255 missing, The Soviet researcher Boris Urlanis estimated total dead of 26,000 including 15,000 military deaths due disease - India casualties
British India included present-day India, Pakistán and Bangladés.
Included in total are 27,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds.
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.
Totals include 15,069 military deaths during 1919-21 and 1,841 Canadian Merchant Navy dea. The 1922 War Office report listed 64,454 Army war dead - Italy casualties
Included in total are 433,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds
Figures of total military dead are from a 1925 Italian report using official data. - War dead figure is from a 1991 history of the Japanese Army.
- New Zealand casualties
Included in total are 14,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds.
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.
Totals include 702 military deaths during 1919-21. The 1922 War Office report listed 16,711 Army war dead. - Newfoundland casualties
Newfoundland was a Dominion at the time, and not part of Canadá. The 1922 War Office report listed 1,204 Army war dead - Portugal casualties
Figures include the following killed and died of other causes up until Jan.1, 1920; 1,689 in France and 5,332 in Africa. Figures do not include an additional 12,318 listed as missing and POW. - UK and Crown Colonies casualties
Included in total are 624,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds.
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.
Military dead total includes 34,663 deaths during 1919-21 and 13,632 British Merchant Navy deaths. The losses of Newfoundland are listed separately on this table. The 1922 War Office report listed 702,410 war dead for the UK, 507 from "Other colonies" and the Royal Navy (32,287).
The British Merchant Navy losses of 14,661 were listed separately; The 1922 War Office report detailed the deaths of 310 military personnel due to air and sea bombardment of the UK. - Romania casualties
Military dead is "The figure reported by the Rumanian Government in reply to a questionnaire from the International Labour Office". Included in total are 177,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds. - Russia casualties
Included in total are 1,451,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds. The estimate of total Russian military losses was made by the Soviet researcher Boris Urlanis. - Serbia casualties
Included in total are 165,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds.The estimate of total combined Serbian and Montenegrin military losses of 278,000 was made by the Soviet researcher Boris Urlanis - South Africa casualties
Included in total are 5,000 killed or missing in action and died of wounds
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission Annual Report 2005-2006 is the source of total military dead.
Totals include 380 military deaths during 1919-21. The 1922 War Office report listed 7,121 Army war dead. - S.N. Broadberry, Mark Harrison. The Economics of World War I. illustrated ed. Cambridge University Press, 2005, pgs. 7-8.
Bibliografía
- Ellis, John and Mike Cox. The World War I Databook: The Essential Facts and Figures for All the Combatants (2002)
- Espositons, Vincent J. The West Point Atlas of American Wars: 1900-1918 (1997) despite the title covers entire war; online maps from this atlas
- Falls, Cyril. nkxiei
(1960), general military history
- Higham, Robin and Dennis E. Showalter, eds. Researching World War I: A Handbook (2003), historiography, stressing military themes
- Pope, Stephen and Wheal, Elizabeth-Anne, eds. The Macmillan Dictionary of the First World War (1995)
- Stevenson, David (2013). 1914-1918. Historia de la Primera Guerra Mundial. Barcelona: Círculo de Lectores/Penguin Random House. ISBN 978-84-672-5794-6.
- Strachan, Hew. The First World War: Volume I: To Arms (2004)
- Trask, David F. The United States in the Supreme War Council: American War Aims and Inter-Allied Strategy, 1917-1918 (1961)
- Tucker, Spencer, ed. The Encyclopedia of World War I: A Political, Social, and Military History (5 volumes) (2005), online at eBook.com
- Tucker, Spencer, ed. European Powers in the First World War: An Encyclopedia (1999)
Este artículo ha sido escrito por Wikipedia. El texto está disponible bajo la licencia Creative Commons - Atribución - CompartirIgual. Pueden aplicarse cláusulas adicionales a los archivos multimedia.