Hispidín
Hispidina es una sustancia natural que también se puede sintetizar.[2]
| Hispidina | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Nombre IUPAC | ||
| 2-[(E)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethenyl]-6-hydroxypyran-4-one | ||
| General | ||
| Otros nombres | 6-(3,4-dihydroxystyrl)-4-hydroxy-2-pyrone | |
| Fórmula estructural |
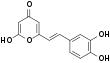 | |
| Fórmula molecular |
C 13H 10O 5 | |
| Identificadores | ||
| Número CAS | 555-55-5[1] | |
| ChEBI | 36332 | |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1224512 | |
| ChemSpider | 13975015 | |
| PubChem | 5353671 | |
| UNII | SSJ18CG55E | |
|
C1=CC(=C(C=C1C=CC2=CC(=O)C=C(O2)O)O)O
| ||
| Propiedades físicas | ||
| Masa molar | 246,21 g/mol | |
| Valores en el SI y en condiciones estándar (25 ℃ y 1 atm), salvo que se indique lo contrario. | ||
Hispidina 4-O-β-d-glucopiranosido se puede encontrar en Pteris ensiformis[3] mientras que los derivados de hispidina, tales como phellibaumin, se puede encontrar en el hongo comestible Inonotus xeranticus[4] o Phellinus.[5][6]
Referencias
- Número CAS
- Gonindard, C.; Bergonzi, C.; Denier, C.; Sergheraert, C.; Klaebe, A.; Chavant, L.; Hollande, E. (1997). «Synthetic hispidin, a PKC inhibitor, is more cytotoxic toward cancer cells than normal cells in vitro». Cell Biology and Toxicology 13 (3): 141-53. PMID 9088624. doi:10.1023/A:1007321227010.
- Identification of phenolic antioxidants from Sword Brake fern (Pteris ensiformis Burm.). Yung-Husan Chen, Fang-Rong Chang, Yih-Jer Lin, Lisu Wang, Jinn-Fen Chen, Yang-Chang Wu and Ming-Jiuan Wu, Food Chemistry, Volume 105, Issue 1, 2007, pp. 48-56, doi 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.03.055
- Hispidin Derivatives from the Mushroom Inonotus xeranticus and Their Antioxidant Activity. In-Kyoung Lee, Soon-Ja Seok, Wan-Kyu Kim and Bong-Sik Yun, J. Nat. Prod., 2006, 69 (2), pp. 299–301, doi 10.1021/np050453n
- Lee, In-Kyoung; Yun, Bong-Sik (2007). «Highly oxygenated and unsaturated metabolites providing a diversity of hispidin class antioxidants in the medicinal mushrooms Inonotus and Phellinus». Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 15 (10): 3309-14. PMID 17387019. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2007.03.039.
- Lee, Yeon Sil; Kang, Young-Hee; Jung, Ju-Young; Lee, Sanghyun; Ohuchi, Kazuo; Shin, Kuk Hyun; Kang, Il-Jun; Park, Jung Han Yoon et al. (octubre de 2008). «Protein glycation inhibitors from the fruiting body of Phellinus linteus» (Uso incorrecto de la plantilla enlace roto (enlace roto disponible en Internet Archive; véase el historial, la primera versión y la última).). Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 31 (10): 1968-72. PMID 18827365. doi:10.1248/bpb.31.1968.
Enlaces externos
- Esta obra contiene una traducción derivada de «Hispidín» de Wikipedia en inglés, publicada por sus editores bajo la Licencia de documentación libre de GNU y la Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-CompartirIgual 4.0 Internacional.
Este artículo ha sido escrito por Wikipedia. El texto está disponible bajo la licencia Creative Commons - Atribución - CompartirIgual. Pueden aplicarse cláusulas adicionales a los archivos multimedia.