Carbénium
Un ion carbénium est un carbocation dont l'atome de carbone qui porte la charge électrique est trivalent, ce qui lui donne une configuration plane trigonale résultant d'une hybridation sp2.

Configuration d'un ion carbénium tertiaire
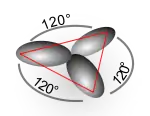
Trois orbitales sp2.
Outre l'ion méthylium CH3+, on distingue les ions carbénium primaires RCH2+, secondaires R2CH+ et tertiaires R3C+[1].
Références
- (en) « carbenium ion », IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology [« Gold Book »], Oxford, Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1997, version corrigée en ligne : (2019-), 2e éd. (ISBN 0-9678550-9-8)
- Stable carbocations. CXVIII. General concept and structure of carbocations based on differentiation of trivalent (classical) carbenium ions from three-center bound penta- of tetracoordinated (nonclassical) carbonium ions. Role of carbocations in electrophilic reactions George Andrew Olah; J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1972 94(3); 808-820. Abstract
Cet article est issu de Wikipedia. Le texte est sous licence Creative Commons - Attribution - Partage dans les Mêmes. Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s'appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.