Nartheciaceae
La famille des Narthéciacées (Nartheciaceae) regroupe des plantes monocotylédones.
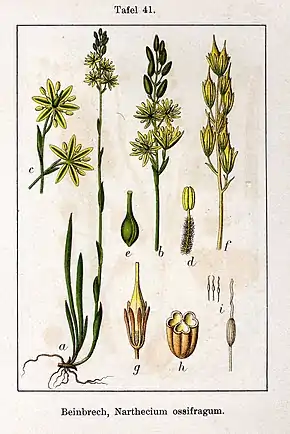
Voir le texte pour plus d'information.

| Clade | Angiospermes |
|---|---|
| Clade | Monocotylédones |
| Ordre | Dioscoreales |
En France on peut citer Narthecium ossifragum que l'on rencontre dans les tourbières de l'ouest de la France, ainsi que l'Ossifrage de Reverchon (Narthecium reverchonii), endémique de Corse.
Étymologie
Le nom vient du genre Narthecium boîte à parfum romaine, qui elle-même dérive du grec νάρθηξ (narthex), un fenouil géant aux feuilles parfumées, nom utilisé par Theophraste pour désigner l'espèce Ferula communis (Apiaceae). Le mot narthex est maintenant utilisé pour désigner le portique interne aménagé à l'entrée des églises byzantines, paléochrétiennes ou médiévales[1].
Description
Ce sont des plantes herbacées, à inflorescences en racème, à petites fleurs avec des tépales en partie libres qui persistent après la floraison.
Classification
En classification classique de Cronquist (1981)[2] cette famille n'existe pas et ces plantes étaient incluses dans les Liliacées.
Cette famille a été restaurée par la classification phylogénétique APG II (2003)[3] et comprend 41 espèces réparties en 5 genres : Aletris, Lophiola, Metanarthecium (en), Narthecium et Nietneria (en).
Liste des genres
Selon World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP) (15 avr. 2010)[4], Angiosperm Phylogeny Website (20 mai 2010)[5] et NCBI (15 avr. 2010)[6] :
- genre Aletris L. (1753)
- genre Lophiola Ker Gawl. (1813)
- genre Metanarthecium Maxim. (1867)
- genre Narthecium Huds. (1762)
- genre Nietneria Klotzsch ex Benth. (1883)
Liste des espèces
Selon World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP) (15 avr. 2010)[4] :
- genre Aletris L. (1753)
- Aletris alpestris Diels (1905)
- Aletris aurea Walter (1788)
- Aletris bracteata Northr. (1902)
- Aletris capitata F.T.Wang & Tang (1978)
- Aletris cinerascens F.T.Wang & Tang (1978)
- Aletris farinosa L. (1753)
- Aletris foliata (Maxim.) Makino & Nemoto, Fl. Japan (1931)
- Aletris foliolosa Stapf, Trans. Linn. Soc. London (1894)
- Aletris foliosa (Maxim.) Bureau & Franch. (1891)
- Aletris glabra Bureau & Franch. (1891)
- Aletris glandulifera Bureau & Franch. (1891)
- Aletris gracilis Rendle (1906)
- Aletris laxiflora Bureau & Franch. (1891)
- Aletris lutea Small (1899)
- Aletris megalantha F.T.Wang & Tang (1951)
- Aletris nana S.C.Chen (1981)
- Aletris obovata Nash (1903)
- Aletris pauciflora (Klotzsch) Hand.-Mazz. (1936)
- Aletris pedicellata F.T.Wang & Tang (1943)
- Aletris scopulorum Dunn, J. Linn. Soc. (1908)
- Aletris spicata (Thunb.) Franch. (1896)
- Aletris stenoloba Franch. (1896)
- Aletris × tottenii E.T.Br. (1961)
- Aletris yaanica G.H.Yang (1987)
- genre Lophiola Ker Gawl. (1813)
- Lophiola aurea Ker Gawl. (1813)
- genre Metanarthecium Maxim. (1867)
- Metanarthecium luteoviride Maxim. (1867)
- genre Narthecium Huds. (1762)
- Narthecium americanum Ker Gawl. (1812)
- Narthecium asiaticum Maxim. (1867)
- Narthecium balansae Briq. (1901)
- Narthecium californicum Baker, J. Linn. Soc. (1876)
- Narthecium ossifragum (L.) Huds. (1762)
- Narthecium reverchonii Celak. (1887)
- Narthecium scardicum Koanin (1913)
- genre Nietneria Klotzsch ex Benth. (1883)
- Nietneria corymbosa Klotzsch & M.R.Schomb. ex B.D.Jacks. (1894)
- Nietneria paniculata Steyerm., Fieldiana (1951)
Selon NCBI (15 avr. 2010)[6] :
- genre Aletris
- Aletris farinosa
- Aletris foliosa
- Aletris glabra
- Aletris laxiflora
- Aletris lutea
- Aletris pauciflora
- Aletris pauciflora var. khasiana
- Aletris rigida
- Aletris spicata
- Aletris stenoloba
- genre Lophiola
- Lophiola americana
- Lophiola aurea
- genre Metanarthecium
- Metanarthecium luteo-viride
- genre Narthecium
- Narthecium asiaticum
- Narthecium californicum
- Narthecium ossifragum
- genre Nietneria
- Nietneria paniculata
Notes et références
- (en) Maarten J M Christenhusz, Michael F Fay et Mark W. Chase, Plants of the World : An Illustrated Encyclopedia of Vascular Plants, Chicago, The University of Chicago Press, , 816 p. (ISBN 978-0-2265-2292-0, lire en ligne), p. 133
- (en) Arthur Cronquist, An Integrated System of Classification of Flowering Plants, New York, Columbia University Press, (ISBN 0-231-03880-1, OCLC 1136076363, lire en ligne)
- (en) Angiosperm Phylogeny Group, « An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG II », Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, Wiley-Blackwell, Linnean Society of London et OUP, vol. 141, no 4, , p. 399–436 (ISSN 0024-4074 et 1095-8339, DOI 10.1046/J.1095-8339.2003.T01-1-00158.X)
- WCSP. World Checklist of Selected Plant Families. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Published on the Internet ; http://wcsp.science.kew.org/, consulté le 15 avr. 2010
- Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 14, July 2017 [and more or less continuously updated since]." will do. http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb/, consulté le 20 mai 2010
- NCBI, consulté le 15 avr. 2010
Liens externes
- (en) Référence Monocot Families (USDA) : Nartheciaceae
- (en) Référence Kew Garden World Checklist : Nartheciaceae
- (en) Référence Angiosperm Phylogeny Website : Nartheciaceae ()
- (en) Référence BioLib : Nartheciaceae Bjurzon
- (en) Référence Catalogue of Life : Nartheciaceae (consulté le )
- (en) Référence Tree of Life Web Project : Nartheciaceae
- (en) Référence NCBI : Nartheciaceae (taxons inclus)
- (en) Référence GRIN : famille Nartheciaceae Fr. ex Bjurzon (+liste des genres contenant des synonymes)
- (fr) Référence Tela Botanica (France métro) : Nartheciaceae
- Voir aussi (en) Référence DELTA Angio : Melanthiaceae
- Portail de la botanique