Poly(succinate de butyle)
Le poly(succinate de butyle), parfois francisé par calque de l'anglais en poly(butylène succinate) (PBS), est un polyester aliphatique biodégradable avec des propriétés similaires à celles des polyoléfines[2].
| Poly(butylène succinate) | |
| |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | poly(succinate de tétraméthylène) |
| Synonymes |
PBS |
| No CAS | |
| Apparence | solide de forme variable blanc |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
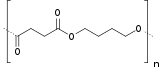
| Formule | (C8H12O4)n |
| Masse molaire | du motif de répétition : 172,18 g·mol-1 |
| Propriétés physiques | |
| T° fusion | 115 °C[1] |
| Solubilité | chloroforme, dichlorométhane |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
Applications : films, emballages, sacs.
Références
- Rongyuan Chen, Wei Zou, Haichen Zhang, Guizhen Zhang and Jinping Qu, Crystallization Behavior and Thermal Stability of Poly(butylene succinate)/Poly(propylene carbonate) Blends Prepared by Novel Vane Extruder, AIP Conference Proceedings 1713, 050002 (2016).
- N. Jacquel et al., « Synthesis and properties of poly (butylene succinate): Efficiency of different transesterification catalysts », J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem., vol. 49, no 24, , p. 5301-5312 (DOI 10.1002/pola.25009)
- Portail de la chimie
Cet article est issu de Wikipedia. Le texte est sous licence Creative Commons - Attribution - Partage dans les Mêmes. Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s'appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.