Roburine A
La roburine A est un ellagitanin.
| Roburine A | |
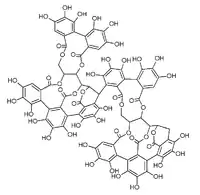
| |
| Formule développée. | |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| No CAS | |
| PubChem | 355200701 |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C82H50O51 |
| Masse molaire[1] | 1 851,243 8 ± 0,084 4 g/mol C 53,2 %, H 2,72 %, O 44,08 %, |
| Propriétés physiques | |
| T° fusion | Point de sublimation : |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
La roburine A peut être isolée du bois de chêne (Quercus robur, Q. petraea, Q. suber et Q. alba notamment). Elle peut aussi être trouvée dans certains vins élevés en fûts de chêne.
Les roburines A et D sont des dimères de la vescalagine.
Références
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Mosedale J.R., Feuillat F., Baumes R., Dupouey J-L. & Puech J-L., 1998. Variability of wood extractives among Quercus robur and Quercus petraea trees from mixed stands and their relation to wood anatomy and leaf morphology". Canadian Journal of Forest Research. 28 (7), pages 994–1006, DOI:10.1139/x98-066.
- (en) Glabasnia A. & Hofmann T., 2007. Identification and Sensory Evaluation of Dehydro- and Deoxy-ellagitannins Formed upon Toasting of Oak Wood (Quercus alba L.). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 55 (10), pages 4109–4118, DOI:10.1021/jf070151m, .
- (en) Cadahía E. Conde E., Fernández De Simon B. & García-Vallejo M.C., 1998. Changes in Tannic Composition of Reproduction Cork Quercus suber throughout Industrial Processing. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 46 (6), pages 2332–2336, DOI:10.1021/jf9709360.
- (en) Herve du Penhoat C.L.M., Michon V.M.F., Ohassan A. Peng S., Scalbert A. & Gage D., 1991. Roburin A, A dimeric ellagitannin from heartwood of Quercus robur. Phytochemistry. 30, pages 329–332, DOI:10.1016/0031-9422(91)84148-L.
Liens externes
- Portail de la chimie
Cet article est issu de Wikipedia. Le texte est sous licence Creative Commons - Attribution - Partage dans les Mêmes. Des conditions supplémentaires peuvent s'appliquer aux fichiers multimédias.