ꜣḫt-ḫw.f-wj
Egyptian
Etymology
ꜣḫt (“Akhet”) + ḫw.f-wj (“Khufu”) in a direct genitive construction, thus literally “Akhet (place of sunrise) of Khufu”. The written form demonstrates honorific transposition.
Pronunciation
- (modern Egyptological) IPA(key): /ɑxɛt xuːʔɛf wi/, /ɑxɛt xuːfuː/
- Conventional anglicization: akhet-khu.ef-wi, akhet-khufu
Proper noun
f
- the Great Pyramid of Giza, including the surrounding complex of mortuary temples and tombs
- 6th Dynasty, Lintel of Neferi (Cleveland 1920.1992):[1]

![Aa1 [x]](../I/hiero_Aa1.png.webp)
![G43 [w]](../I/hiero_G43.png.webp)
![I9 [f]](../I/hiero_I9.png.webp)
![G43 [w]](../I/hiero_G43.png.webp)

![G25 [Ax]](../I/hiero_G25.png.webp)
![X1 [t]](../I/hiero_X1.png.webp)

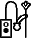
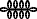
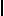
![F35 [nfr]](../I/hiero_F35.png.webp)
![I9 [f]](../I/hiero_I9.png.webp)
![D21 [r]](../I/hiero_D21.png.webp)
![M17 [i]](../I/hiero_M17.png.webp)
- zẖꜣw zꜣ ꜣḫt-ḫw.f-wj nfrj
- Scribe of a phyle of the Great Pyramid of Giza, Neferi
- 6th Dynasty, Lintel of Neferi (Cleveland 1920.1992):[1]
Alternative forms
Alternative hieroglyphic writings of ꜣḫt-ḫw.f-wj
| ꜣḫt-ḫw.f-wj |
References
- Berman, Lawrence M.; Bohač, Kenneth J. (1999) The Cleveland Museum of Art Catalogue of Egyptian Art, New York: Hudson Hills Press, page 132–133
This article is issued from Wiktionary. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.