DNA and RNA
DNA and RNA
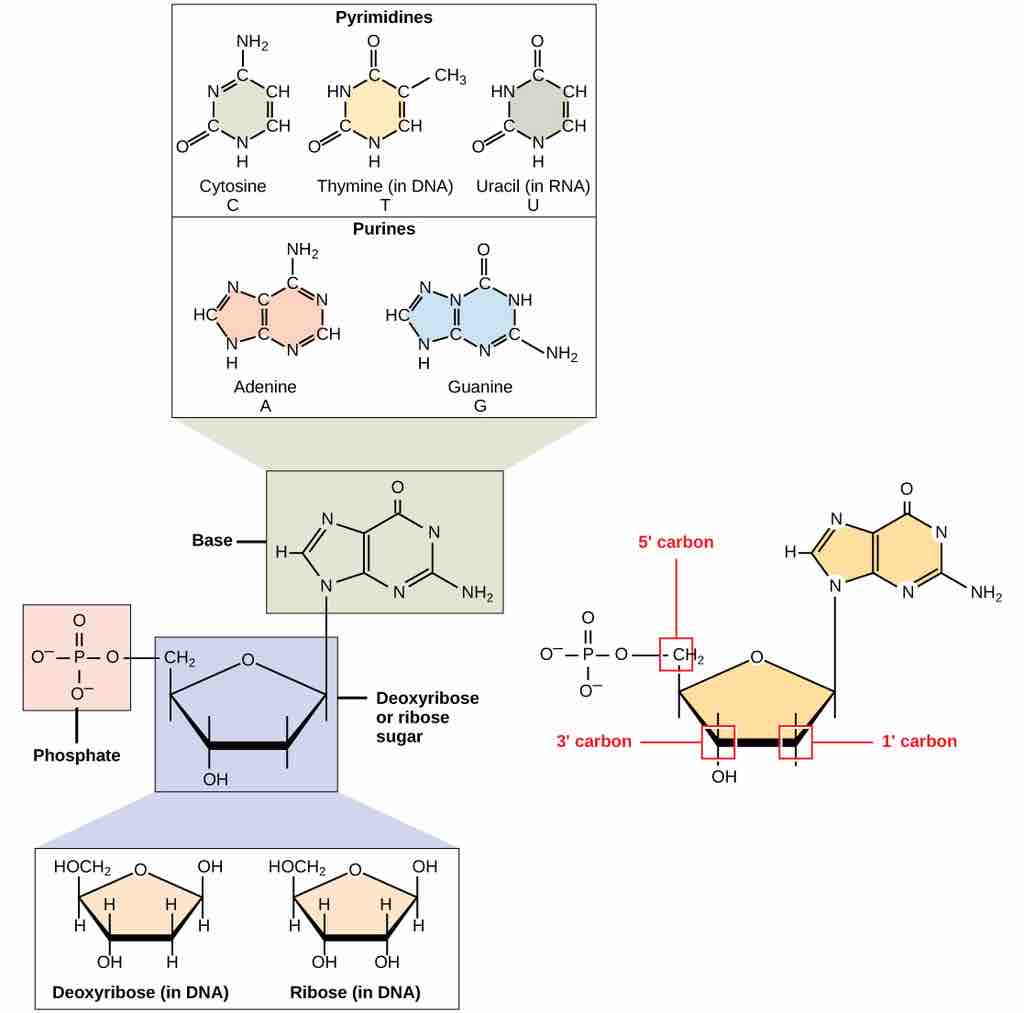
A nucleotide is made up of three components: a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. Carbon residues in the pentose are numbered 1′ through 5′ (the prime distinguishes these residues from those in the base, which are numbered without using a prime notation). The base is attached to the 1′ position of the ribose, and the phosphate is attached to the 5′ position. When a polynucleotide is formed, the 5′ phosphate of the incoming nucleotide attaches to the 3′ hydroxyl group at the end of the growing chain. Two types of pentose are found in nucleotides, deoxyribose (found in DNA) and ribose (found in RNA). Deoxyribose is similar in structure to ribose, but it has an H instead of an OH at the 2′ position. Bases can be divided into two categories: purines and pyrimidines. Purines have a double ring structure, and pyrimidines have a single ring.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources: