Concept
Version 10
Created by Boundless
Amino Acids
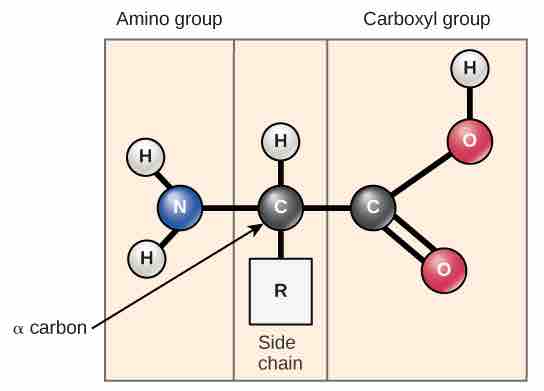
Amino acid structure
Amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (R group) are attached. This amino acid is unionized, but if it were placed in water at pH 7, its amino group would pick up another hydrogen and a positive charge, and the hydroxyl in its carboxyl group would lose and a hydrogen and gain a negative charge.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
"OpenStax College, Proteins. October 16, 2013."
http://cnx.org/content/m44402/latest/Figure_03_04_01.jpg
OpenStax CNX
CC BY 3.0.