The lac Operon: An Inducer Operon
A major type of gene regulation that occurs in prokaryotic cells utilizes and occurs through inducible operons. Inducible operons have proteins that can bind to either activate or repress transcription depending on the local environment and the needs of the cell. The lac operon is a typical inducible operon. As mentioned previously, E. coli is able to use other sugars as energy sources when glucose concentrations are low. To do so, the cAMP–CAP protein complex serves as a positive regulator to induce transcription. One such sugar source is lactose. The lac operon encodes the genes necessary to acquire and process the lactose from the local environment, which includes the structural genes lacZ, lacY, and lacA. lacZ encodes β-galactosidase (LacZ), an intracellular enzyme that cleaves the disaccharide lactose into glucose and galactose. lacY encodes β-galactoside permease (LacY), a membrane-bound transport protein that pumps lactose into the cell. lacA encodes β-galactoside transacetylase (LacA), an enzyme that transfers an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to β-galactosides. Only lacZ and lacY appear to be necessary for lactose catabolism.
CAP binds to the operator sequence upstream of the promoter that initiates transcription of the lac operon. The lac operon uses a two-part control mechanism to ensure that the cell expends energy producing β-galactosidase, β-galactoside permease, and thiogalactoside transacetylase (also known as galactoside O-acetyltransferase) only when necessary. However, for the lac operon to be activated, two conditions must be met. First, the level of glucose must be very low or non-existent. Second, lactose must be present. If glucose is absent, then CAP can bind to the operator sequence to activate transcription. If lactose is absent, then the repressor binds to the operator to prevent transcription. If either of these requirements is met, then transcription remains off. The cell can use lactose as an energy source by producing the enzyme b-galactosidase to digest that lactose into glucose and galactose. Only when both conditions are satisfied is the lac operon transcribed, such as when glucose is absent and lactose is present . This process is beneficial and makes most sense for the cell as it would be energetically wasteful to create the proteins to process lactose if glucose were plentiful or if lactose were not available.
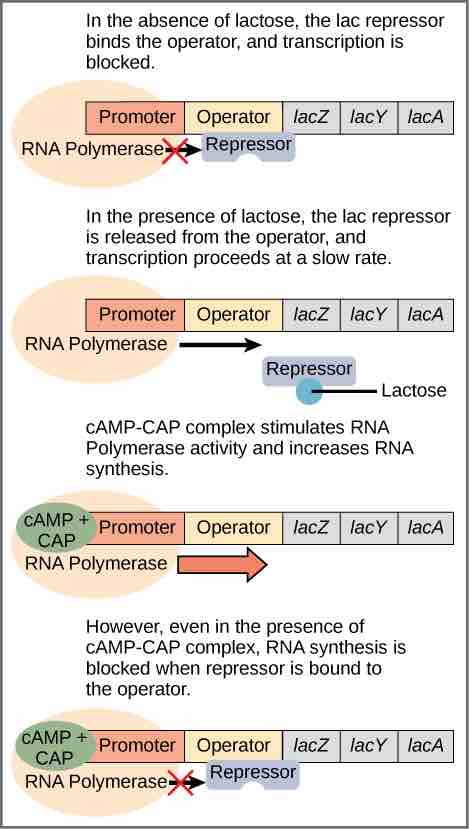
The lac Operon
Transcription of the lac operon is carefully regulated so that its expression only occurs when glucose is limited and lactose is present to serve as an alternative fuel source.