Section 2
Pollination and Fertilization
By Boundless
Plants can transfer pollen through self-pollination; however, the preferred method is cross-pollination, which maintains genetic diversity.

Plants have developed adaptations to promote symbiotic relationships with insects that ensure their pollination.

Non-insect methods of pollination include pollination by bats, birds, wind, and water.
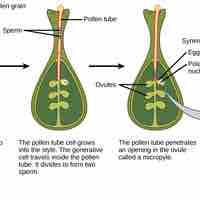
Angiosperms undergo two fertilization events where a zygote and endosperm are both formed.

Monocot and dicot seeds develop in differing ways, but both contain seeds with a seed coat, cotyledons, endosperm, and a single embryo.

Fruits are categorized based on the part of the flower they developed from and how they release their seeds.
Some fruits can disperse seeds on their own, while others require assistance from wind, water, or animals.