Hormones
A hormone is a chemical released by a cell or a gland in one part of the body that sends out messages that affect cells in other parts of the organism. Only a small amount of hormone is required to alter cell metabolism. In essence, it is a chemical messenger that transports a signal from one cell to another. All multicellular organisms produce hormones; plant hormones are also called phytohormones. Hormones in animals are often transported in the blood.
How Hormones Work
Hormones mediate changes in target cells by binding to specific hormone receptors. In this way, even though hormones circulate throughout the body and come into contact with many different cell types, they only affect cells that possess the necessary receptors. Receptors for a specific hormone may be found on many different cells or may be limited to a small number of specialized cells. For example, thyroid hormones act on many different tissue types, stimulating metabolic activity throughout the body. Cells can have many receptors for the same hormone, but often also possess receptors for different types of hormones. The number of receptors that respond to a hormone determines the cell's sensitivity to that hormone and the resulting cellular response. Additionally, the number of receptors that respond to a hormone can change over time, resulting in increased or decreased cell sensitivity. In up-regulation, the number of receptors increases in response to rising hormone levels, making the cell more sensitive to the hormone, allowing for more cellular activity. When the number of receptors decreases in response to rising hormone levels, called down-regulation, cellular activity is reduced.
Cells respond to a hormone when they express a specific receptor for that hormone. The hormone binds to the receptor protein, resulting in the activation of a signal transduction mechanism that ultimately leads to cell type-specific responses. Receptor binding alters cellular activity, resulting in an increase or decrease in normal body processes . Depending on the location of the protein receptor on the target cell and the chemical structure of the hormone, hormones can mediate changes directly by binding to intracellular hormone receptors and modulating gene transcription, or indirectly by binding to cell surface receptors and stimulating signaling pathways.
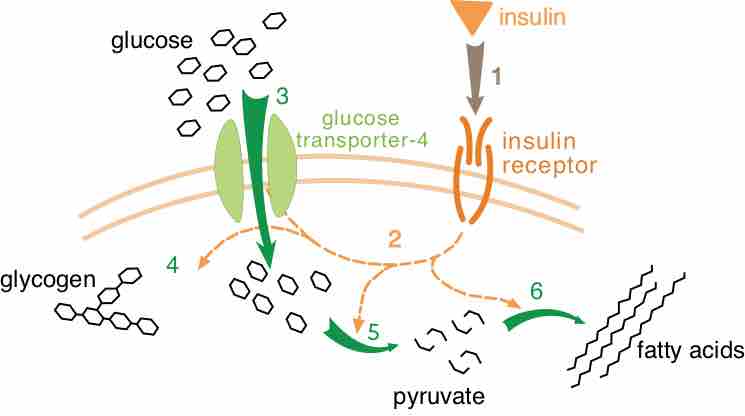
Hormone functioning
The hormone insulin binds to its receptor (1), which starts many protein activation cascades (2). These include translocation of Glut-4 transporter to the plasma membrane and influx of glucose (3), glycogen synthesis (4), glycolysis (5), and triglyceride (6).