In the previous atom, we learned that a second-order linear differential equation has the form:
where
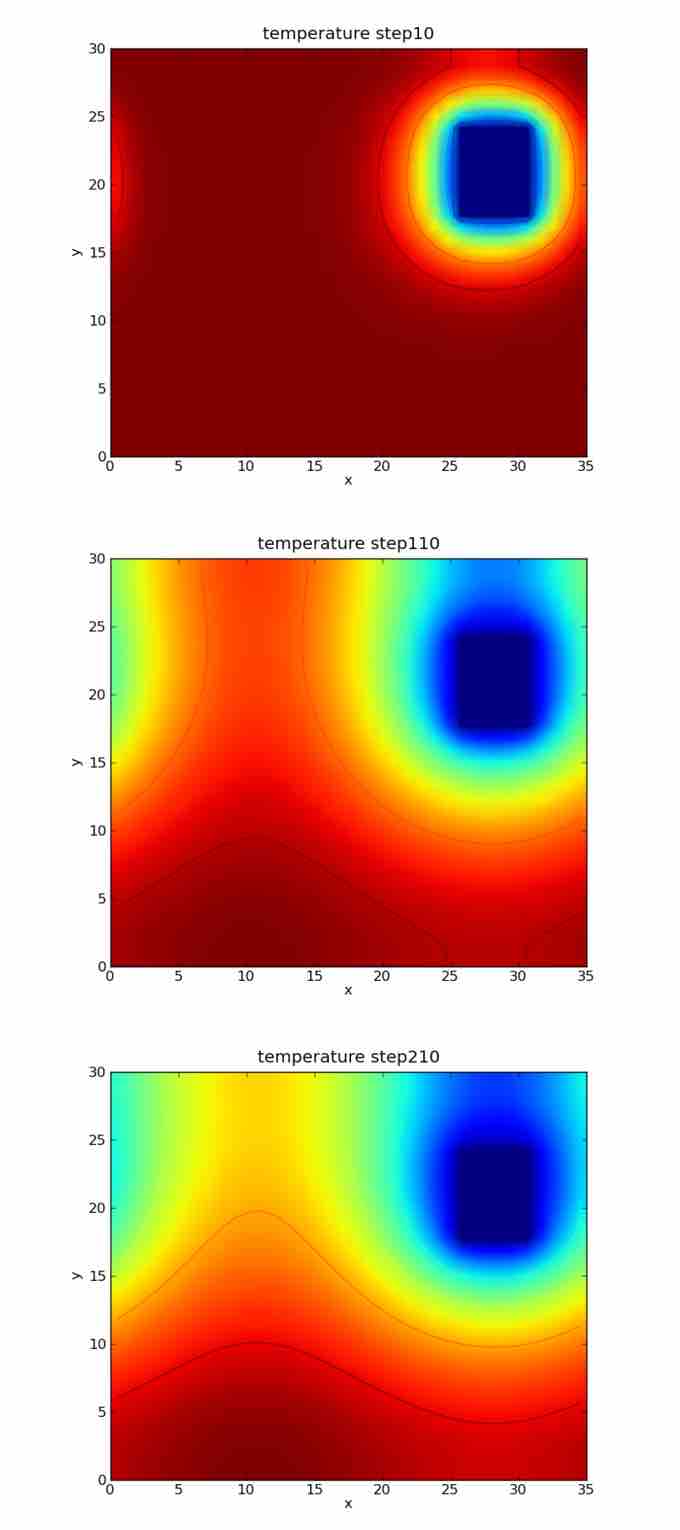
Heat Transfer
Phenomena such as heat transfer can be described using nonhomogeneous second-order linear differential equations.
In simple cases, for example, where the coefficients
Linearity
Linear differential equations are differential equations that have solutions which can be added together to form other solutions. If
then any arbitrary linear combination of