Section 5
Reaction Stoichiometry
By Boundless
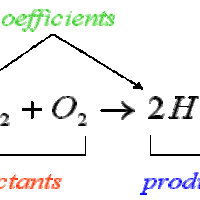
Stoichiometry is the study of the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions and how to calculate those quantities.
Molar ratios, or conversion factors, identify the number of moles of each reactant needed to form a certain number of moles of each product.
Mole-to-mole conversions can be facilitated by using conversion factors found in the balanced equation for the reaction of interest.
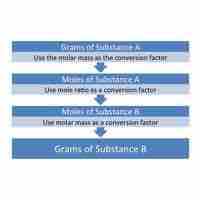
Mass-to-mass conversions cannot be done directly; instead, mole values must serve as intermediaries in these conversions.
Mass-to-mole conversions can be facilitated by employing the molar mass as a conversion ratio.
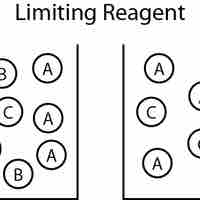
The reagent that limits how much product is produced (the reactant that runs out first) is known as the limiting reagent.
The percent yield of a reaction measures the reaction's efficiency. It is the ratio between the actual yield and the theoretical yield.