Aggregate Supply
Aggregate supply is the total supply of goods and services that firms in a national economy plan to sell during a specific period of time. It is the total amount of goods and services that firms are willing to sell at a given price level.
Short-run Aggregate Supply Curve
In the short-run, the aggregate supply curve is upward sloping. There are two main reasons why the quantity supplied increases as the price rises:
- The AS curve is drawn using a nominal variable, such as the nominal wage rate. In the short-run, the nominal wage rate is fixed. As a result, an increasing price indicates higher profits that justify the expansion of output.
- An alternate model explains that the AS curve increases because some nominal input prices are fixed in the short-run and as output rises, more production processes encounter bottlenecks. At low levels of demand, large numbers of production processes do not make full use of their fixed capital equipment. As a result, production can be increased without much diminishing returns. The average price level does not have to rise much in order to justify increased production. In this case, the AS curve is flat. Likewise, when demand is high, there are few production processes that have unemployed fixed outputs. Any increase in demand production causes the prices to increase which results in a steep or vertical AS curve.
Short-run Aggregate Supply Equation
The equation used to calculate the short-run aggregate supply is: Y = Y* + α(P-Pe). In the equation, Y is the production of the economy, Y* is the natural level of production, coefficient is always positive, P is the price level, and Pe is the expected price level.
In the short-run, firms possess fixed factors of production, including prices, wages, and capital. It is possible for the short-run supply curve to shift outward as a result of an increase in output and real GDP at a given price . As a result, the short-run aggregate supply curve shows the correlation between the price level and output.
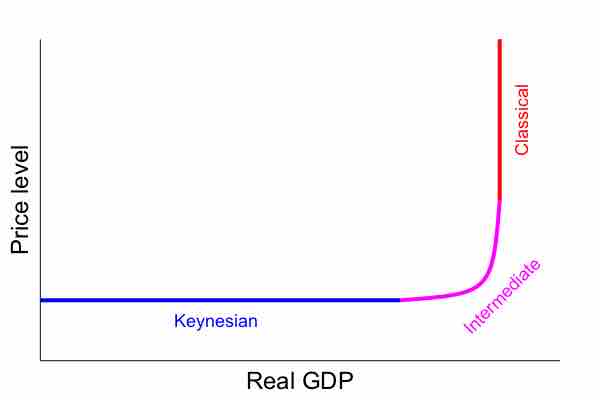
Aggregate Supply Curve
This graph shows the aggregate supply curve. In the short-run the aggregate supply curve is upward sloping. When the curve shifts outward, it is due to an increase in output and real GDP.