Section 2
Monetary Policy Tools
By Boundless
The reserve ratio is the percentage of deposits that a bank is required to hold in reserves, or funds that are not allowed to be loaned.
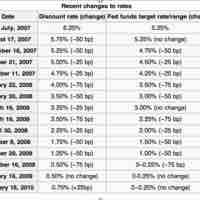
The rate that member banks charge each other is the federal funds rate and the rate the Fed charges is referred to as the discount rate.
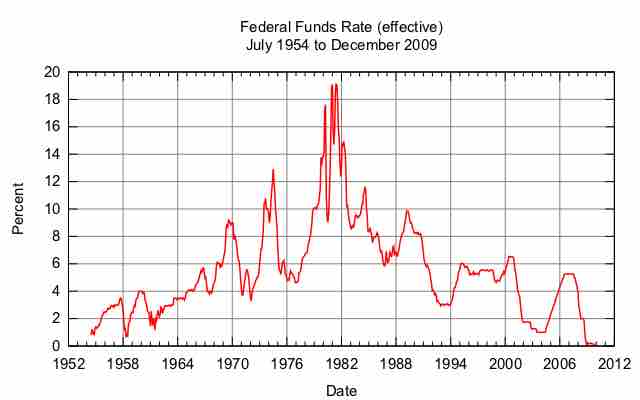
The Federal Funds rate is the interest rate at which depository institutions actively trade balances held at the Federal Reserve.
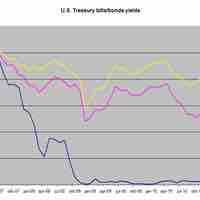
Open market operations (OMOs) are the purchase and sale of securities in the open market by a central bank.
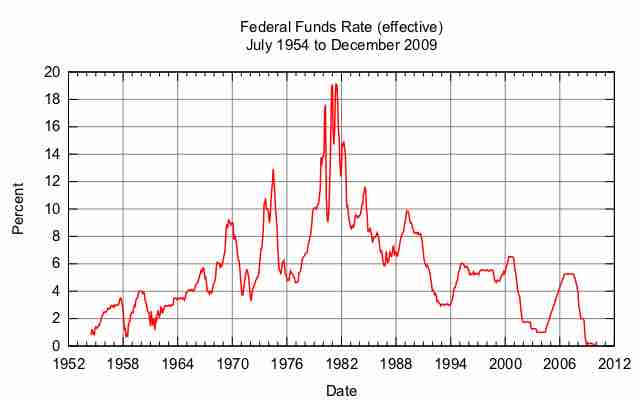
The Federal Reserve (Fed) has an ability to directly influence economic growth and stability through the use of monetary policy.
Central banks initiate expansionary policy during periods of economic slowing, increasing the money supply and reducing interest rates.
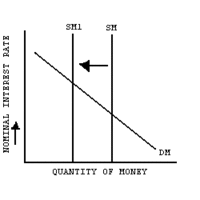
The central bank may initiate a contractionary or restrictive monetary policy to slow growth.
Taylor's rule was designed to provide monetary policy guidance for how a central bank should set short-term interest rates.