Banks operate by taking in deposits and making loans to lenders. They are able to do this because not every depositor needs her money on the same day. Thus, banks can lend out some of their depositors' money, while keeping some on hand to satisfy daily withdrawals by depositors. This is called the fractional-reserve banking system: banks only hold a fraction of total deposits as cash on hand.
Reserve Ratio
The fraction of deposits that a bank must hold as reserves rather than loan out is called the reserve ratio (or the reserve requirement) and is set by the Federal Reserve. If, for example, the reserve requirement is 1%, then a bank must hold reserves equal to 1% of their total customer deposits. These assets are typically held in the form of physical cash stored in a bank vault and in reserves deposited with the central bank.
Banks can also choose to hold reserves in excess of the required level. Any reserves beyond the required reserves are called excess reserves. Excess reserves plus required reserves equal total reserves. In general, since banks make less money from holding excess reserves than they would lending them out, economists assume that banks seek to hold no excess reserves.
Money Creation
Because banks are only required to keep a fraction of their deposits in reserve and may loan out the rest, banks are able to create money. To understand this, imagine that you deposit $100 at your bank. The bank is required to keep $10 as reserves but may lend out $90 to another individual or business. This loan is new money; the bank created it when it issued the loan. In fact, the vast majority of money in the economy today comes from these loans created by banks. Likewise when a loan is repaid, that money disappears from the economy until the bank issues another loan .
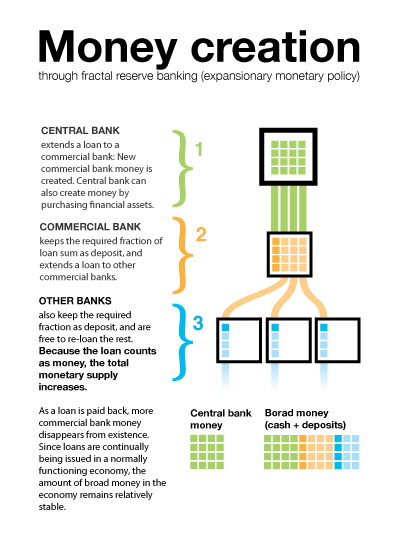
Money Creation in a Fractional Reserve System
The diagram shows the process through which commercial banks create money by issuing loans.
Thus, there are two ways that a central bank can use this process to increase or decrease the money supply. First, it can adjust the reserve ratio. A lower reserve ratio means that banks can issue more loans, increasing the money supply. Second, it can create or destroy reserves. Creating reserves means that commercial banks have more reserves with which they can satisfy the reserve ratio requirement, leading to more loans and an increase in the money supply.
Why Have Reserve Requirements?
Fractional-reserve banking ordinarily functions smoothly. Relatively few depositors demand payment at any given time, and banks maintain a buffer of reserves to cover depositors' cash withdrawals and other demands for funds. However, banks also have an incentive to loan out as much money as possible and keep only a minimum buffer of reserves, since they earn more on these loans than they do on the reserves. Mandating a reserve requirement helps to ensure that banks have the ability to meet their obligations.