The Doppler Effect
The Doppler effect is a periodic event's change in frequency for an observer in motion relative to the event's source. Typically, this periodic event is a wave.
Most people have experienced the Doppler effect in action. Consider an emergency vehicle in motion, sounding its siren . As it approaches an observer, the pitch of the sound (its frequency) sounds higher than it actually is. When the vehicle reaches the observer, the pitch is perceived as it actually is. When the vehicle continues away from the observer, the pitch is perceived as lower than it actually is. From the perspective of an observer inside the vehicle, the pitch of the siren is constant.

The Doppler Effect and Sirens
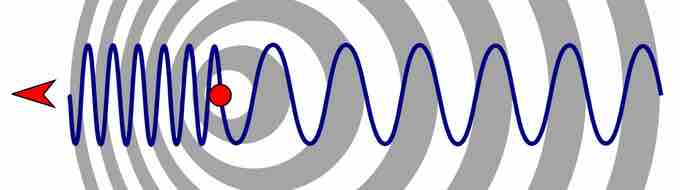
Waves emitted by a siren in a moving vehicle
The difference in the perceived pitch depending on observer location can be explained by the fact that the siren's position changes as it emits waves. A wave of sound is emitted by a moving vehicle every millisecond. The vehicle 'chases' each wave in one direction. By the time the next wave is emitted, it is closer (relative to an onlooker ahead of the vehicle) to the previous wave than the wave's frequency would suggest. Relative to an onlooker behind the vehicle, the second wave is further from the first wave than one would expect, which suggests a lower frequency.
The Doppler effect can be caused by any kind of motion. In the example above, the siren moved relative to a stationary observer. If the observer moves relative to the stationary siren, the observer will notice the Doppler effect on the pitch of the siren. Finally, if the medium through which the waves propagate moves, the Doppler effect will be noticed even for a stationary observer. An example of this phenomenon is wind.
Quantitatively, the Doppler effect can be characterized by relating the frequency perceived (f) to the velocity of waves in the medium (c), the velocity of the receiver relative to the medium (vr), the velocity of the source relative to the medium (vs), and the actual emitted frequency (f0):
The Doppler Effect
Wavelength change due to the motion of source