Sonic Booms
A sonic boom is the sound associated with the shock waves created by an object traveling through the air faster than the speed of sound. It can be viewed as a Doppler effect on steroids; sonic booms generate an enormous amount of energy, and sound like explosions. The first man made object to ever create this phenomenon was a bullwhip. The 'crack' of the whip is a result of this sonic boom. This version of a Doppler effect is demonstrated by .

Sonic Boom Gif
The sound source has now broken through the sound speed barrier, and is traveling at 1.4 times the speed of sound, (Mach 1.4). Since the source is moving faster (with a speed ) than the sound waves it creates, it actually leads the advancing wavefront. The sound source will pass by a stationary observer (with a speed ) before the observer actually hears the sound it creates.
When the sound source passes through the air, it creates a series of pressure waves. These waves are travelling at the speed of sound, and as the speed of the sound source increases, the waves, not being able to get out of each other's way, are forced together. They eventually merge into a single shock wave traveling at the speed of sound. This is a critical speed, known as Mach. The shock waves radiate out from the sound source, and create a "Mach cone' . The half angle,
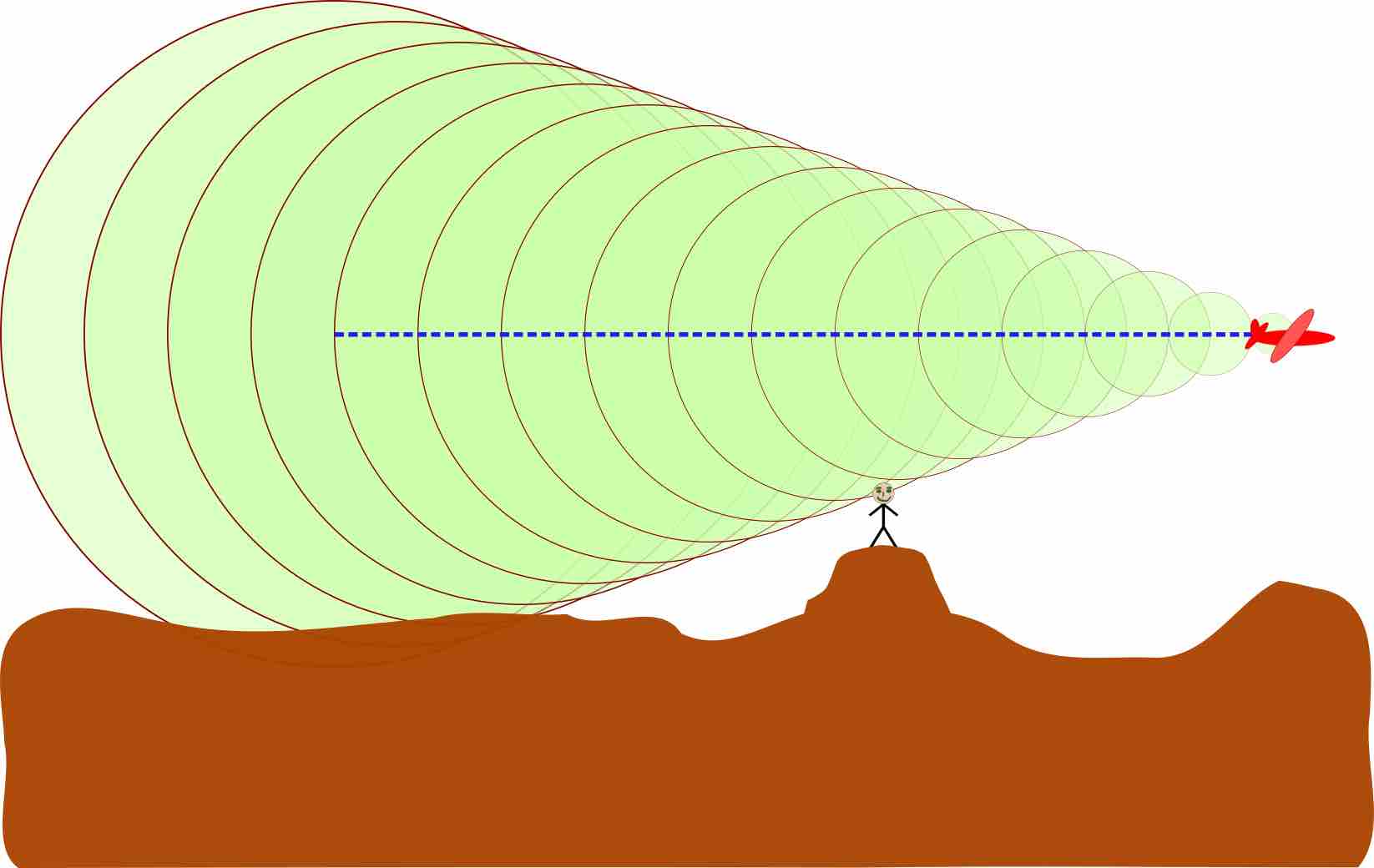
Sonic Boom
A sonic boom produced by an aircraft moving at M=2.92, calculated from the cone angle of 20 degrees. An observer hears the boom when the shock wave, on the edges of the cone, crosses his or her location
From previous atoms, we know that
At the front of the sound source, there is a sudden rise in pressure, while at the end of the source there is a decreasing pressure. This 'overpressure profile' is known as an N-wave. There is a big boom when there is a sudden change in pressure, and since the pressure changes twice, this is a double boom.