Section 4
Functions of the Integumentary System
By Boundless
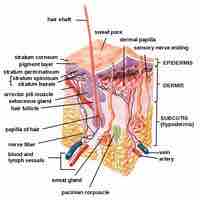
The skin provides an overlaying protective barrier from the environment and pathogens while contributing to the adaptive immune system.
The integumentary system keeps body temperature within limits even when environmental temperature varies; this is called thermoregulation.
The somatosensory system is composed of the receptors and processing centers to produce the sensory modalities, such as touch and pain.
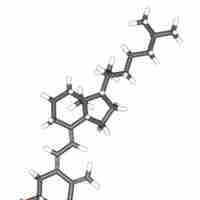
One of the metabolic functions of the skin is the production of vitamin D3 when ultraviolet light reacts with 7-dehydrocholesterol.
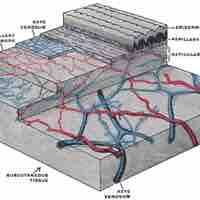
The blood vessels in the dermis provide nourishment and remove waste from its own cells and from the stratum basale of the epidermis.
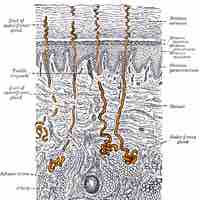
The integumentary system functions in absorption (oxygen and some medications) and excretion (e.g., perspiration via the eccrine glands).