Sexual violence is any sexual act or sexual advance directed at one individual without their consent. The most commonly discussed form of sexual violence is rape. Rape is a form of sexual assault involving one or more persons who force sexual penetration with another individual without that individual's consent. Sexual violence is not limited to rape; it is a broad category that can include everything from verbal harassment to physical assault.
Forms of sexual violence include: rape by strangers, marital rape, date rape, war rape, unwanted sexual harassment, demanding sexual favors, sexual abuse of children, sexual abuse of disabled individuals, forced marriage, child marriage, denial of the right to use contraception, denial of the right to take measures to protect against sexually-transmitted diseases, forced abortion, genital mutilation, forced circumcision, and forced prostitution.
An act is deemed sexually violent if the individual to whom the attention is directed does not consent to the sexual activity, if they are members of a class of persons who cannot consent (the severely cognitively impaired, individuals who are inebriated, minors, etc.), or if consent is due to coercion or duress. Coercion can cover a whole spectrum of degrees of force. Apart from physical force, it may involve psychological intimidation, blackmail, or any other type of threat, like the threat of physical harm or of being dismissed from a job.
Sexual violence has a profound impact on physical and mental health. Sexual violence can cause severe physical injuries, including an increased risk of sexual and reproductive health problems, with both immediate and long-term consequences. Additionally, sexual violence can impact mental health, which can be as serious as its physical impact, and may be even longer lasting.
Acts of Power
Sexually violent acts are acts of power, not of sex. This can be seen most clearly when considering war rape and prison rape. War rape is the type of sexual pillaging that occurs in the aftermath of a war, typically characterized by the male soldiers of the victorious military raping the women of the towns they have just taken over. Prison rape is the type of rape that is common (and seriously under reported) in prisons all over the world, including the United States, in which inmates will force sex upon one another as a demonstration of power.
Tracking Sexual Violence
Sexual violence is particularly difficult to track because it is severely under reported. Records from police and government agencies are often incomplete or limited. Most victims of sexual violence do not report it because they are ashamed, afraid of being blamed, concerned about not being believed, or are simply afraid to relive the event by reporting it. Most countries and many NGOs are undertaking efforts to try to increase the reporting of sexual violence as it so obviously has serious physical and psychological impacts on its victims.
On a global scale, international sexual violence is difficult to track because of extreme variation in sexual mores. A good example of cultural variation with regards to sexual violence is the differing views associated with the practice of female circumcision/female genital mutilation (FGM). Female circumcision and FGM refer to the same practice, but the practice is called "female circumcision" by those who condone its usage. FGM has violent connotations and is used by individuals who conceive of the practice as a violation of human rights.
Female circumcision/FGM is a practice used in many parts of Africa in which parts of the female's vagina, usually the clitoris, are removed in order to decrease sexual pleasure. The operation is performed most commonly on young females. The practice has been the target of many human rights campaigns as a serious affront to the fundamental human rights of the girls undergoing the operation. However, many individuals in Africa view the practice as an acceptable component of their cultures. Neither vantage point is simple; some women in Africa accept the practice, while others have been vocal in speaking out against the practice. Nevertheless, the case demonstrates that cultural norms associated with sex / sex organs (and therefore sexual violence) can vary widely across cultures.
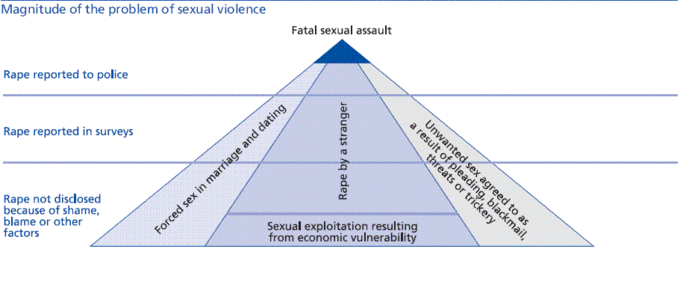
Sexual Violence Reporting
Sexual violence is severly under reported. This graphic illustrates the magnitude of the underreporting of sexual violence