Section 3
Conflict in Europe
By Boundless
However, the 1941 German invasion of the Soviet Union and the exhausting offensive on the Eastern Front stalled Nazi Germany's gains and paved the way for the Allies' victory.
Blitzkrieg (German "lightning war") was a German military strategy whereby an attacking force spearheaded by a dense concentration of armored and motorized or mechanized infantry formations with close air support, breaks through the opponent's line of defense by short, fast, powerful attacks and then dislocates the defenders, using speed and surprise to encircle them.
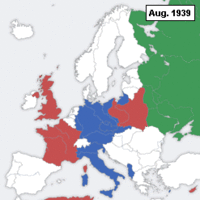
Britain's strategy military strategy evolved from the early idea of Appeasement to the active involvement on the three fronts of the European theater as a follower of the Joint Allied strategy.
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was a genocide in which Adolf Hitler's Nazi Germany and its collaborators killed about six million Jews during World War II.