Applications and Problem Solving
As we should know by now, a hyperbola is an open curve with two branches, the intersection of a plane with both halves of a double cone. The plane may or may not be parallel to the axis of the cone.
Hyperbola
A hyperbola is an open curve with two branches, the intersection of a plane with both halves of a double cone. The plane may or may not be parallel to the axis of the cone.
Here are some examples of hyperbolas in the real world.
Sundials
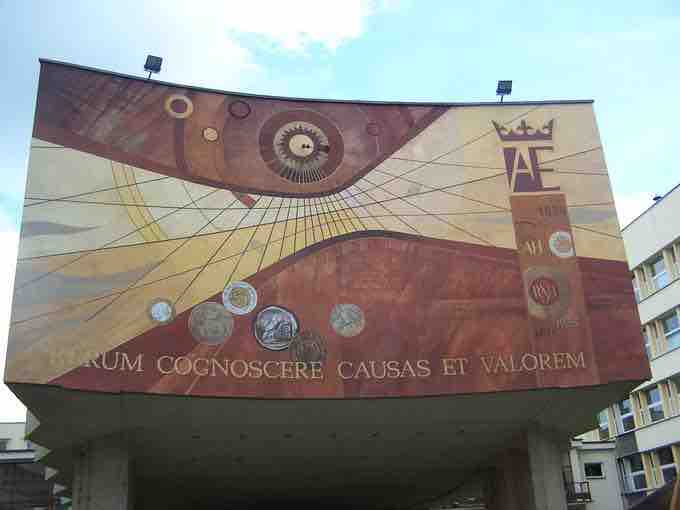
Hyperbolas may be seen in many sundials. Every day, the sun revolves in a circle on the celestial sphere, and its rays striking the point on a sundial traces out a cone of light. The intersection of this cone with the horizontal plane of the ground forms a conic section. The angle between the ground plane and the sunlight cone depends on where you are and the axial tilt of Earth, which changes seasonally. At most populated latitudes and at most times of the year, this conic section is a hyperbola.
Sundials work by casting the shadow of a vertical marker, sometimes called a gnomon, over a clock face on the horizontal surface. The angle between the sunlight and the ground will be the same as the angle formed by the line connecting the tip of the gnomon with the end of its shadow.
If we mark where the end of the shadow falls over the course of the day, the line traced out by the shadow forms a hyperbola on the ground (this path is called the declination line). The shape of this hyperbola varies with the geographical latitude and with the time of the year, since those factors affect the angle of the cone of the sun's rays relative to the horizon.
The parameters of the traced hyperbola, such as its asymptotes and its eccentricity, are related to the specific physical conditions that produced it, namely the angle between the sunlight and the ground, and the latitude at which the sundial exists.

Hyperbolas and sundials
Hyperbolas as declination lines on a sundial.
Trilateration
Trilateration is the a method of pinpointing an exact location, using its distances to a given points. The can also be characterized as the difference in arrival times of synchronized signals between the desired point and known points. These types of problems arise in navigation, mainly nautical. A ship can locate its position using the arrival times of signals from GPS transmitters. Alternatively, a homing beacon can be located by comparing the arrival times of its signals at two separate receiving stations. This can be used to track people, cell phones, internet signals, and many other things.
In the case in which a ship, or other object to be located, only knows the difference in distances between itself and two known points, the curve of possible locations is a hyperbola. One way of defining a hyperbola is as precisely this: the curve of points such that the absolute value of the difference between the distances to two focal points remains constant.
So if we call this difference in distances
The Kepler Orbit of Particles
The Kepler orbit is the path followed by any orbiting body. This can be applied to a particle of any size, as long as gravity is the only force causing the orbital trajectory. Depending on the orbital properties, including size and shape (eccentricity), this orbit can be any of the four conic sections. In particular, if the eccentricity e of the orbit is greater than
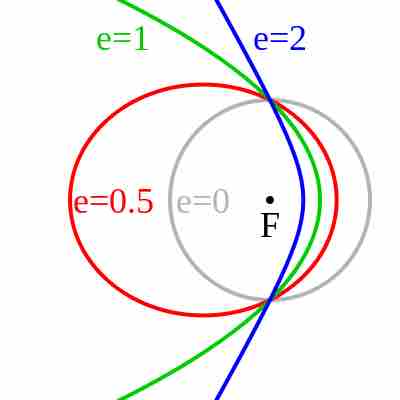
Kepler orbits
A diagram of the various forms of the Kepler Orbit and their eccentricities. Blue is a hyperbolic trajectory (
Physically, another way to understand hyperbolic orbits is in terms of the energy of the orbiting particle. Orbits which are circular or elliptical are bound orbits, which is to say the object never escapes its closed path around one of the focal points. This is associated with the particle's total energy
A parabolic trajectory does have the particle escaping the system. However, this is the very special case when the total energy
If there is any additional energy on top of the minimum (zero) value, the trajectory will become hyperbolic, and so