In algebra, equations can undergo scaling, meaning they can be stretched horizontally or vertically along an axis. This is accomplished by multiplying either
Vertical Scaling
First, let's talk about vertical scaling. Multiplying the entire function
where
As an example, consider the initial sinusoidal function presented below:
If we want to vertically stretch the function by a factor of three, then the new function becomes:
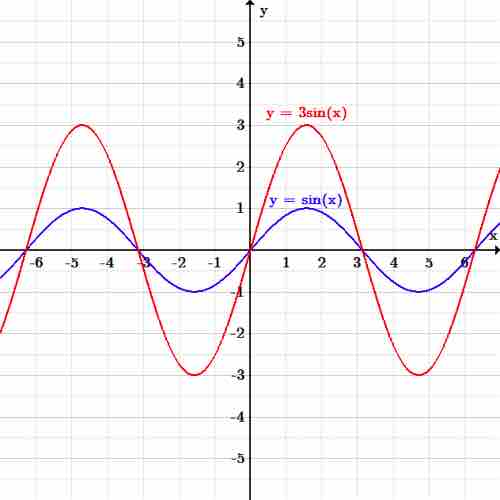
Vertical scaling
The function
Horizontal Scaling
Now lets analyze horizontal scaling.
Multiplying the independent variable
where
As an example, consider again the initial sinusoidal function:
If we want to induce horizontal shrinking, the new function becomes:
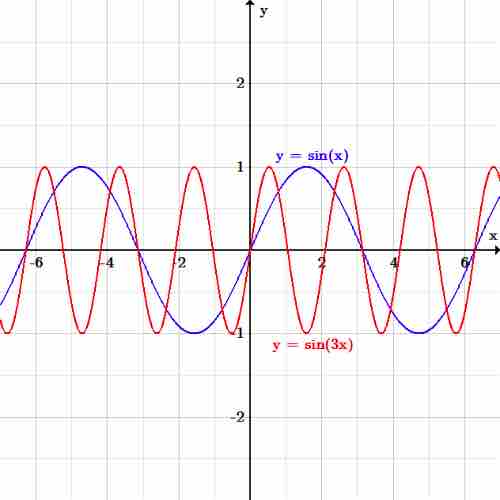
Horizontal scaling
The function