Sex Determination
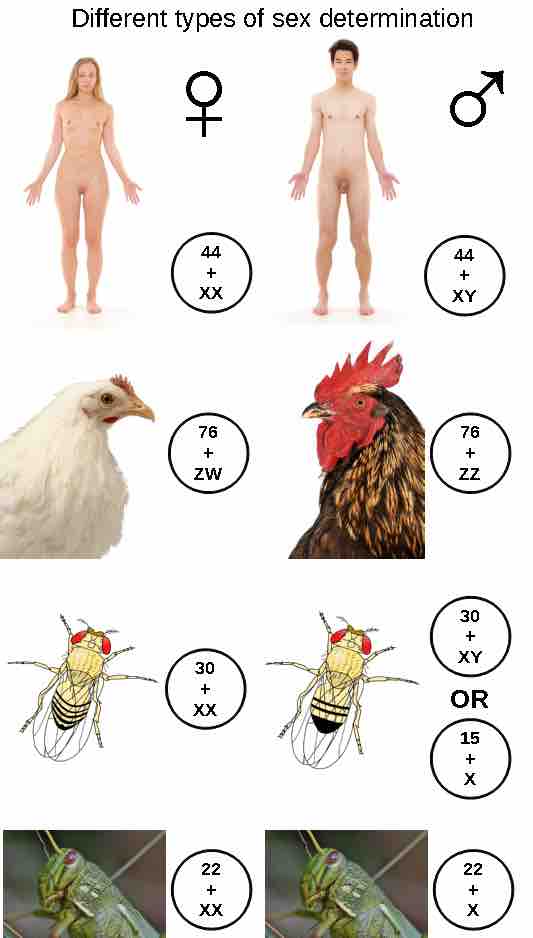
Mammalian sex is determined genetically by the presence of X and Y chromosomes . Individuals homozygous for X (XX) are female, while heterozygous individuals (XY) are male. The presence of a Y chromosome causes the development of male characteristics, while its absence results in female characteristics. The XY system is also found in some insects and plants.
Sex determination
The presence of X and Y chromosomes are one of the factors responsible for sex determination in mammals, with males being the heterozygous sex. In birds, Z and W chromosomes determine sex, with females being the heterozygous sex.
Avian sex determination is dependent on the presence of Z and W chromosomes. Homozygous for Z (ZZ) results in a male, while heterozygous (ZW) results in a female. The W appears to be essential in determining the sex of the individual, similar to the Y chromosome in mammals. Some fish, crustaceans, insects (such as butterflies and moths), and reptiles use this system.
The sex of some species is not determined by genetics, but by some aspect of the environment. Sex determination in some crocodiles and turtles, for example, is often dependent on the temperature during critical periods of egg development. This is referred to as environmental sex determination or, more specifically, as temperature-dependent sex determination. In many turtles, cooler temperatures during egg incubation produce males, while warm temperatures produce females. In some crocodiles, moderate temperatures produce males, while both warm and cool temperatures produce females. In some species, sex is both genetic- and temperature-dependent.
Individuals of some species change their sex during their lives, alternating between male and female. If the individual is female first, it is termed protogyny or "first female;" if it is male first, it is termed protandry or "first male." Oysters, for example, are born male, grow, become female, and lay eggs; some oyster species change sex multiple times.