A Double-Helix Structure
DNA has a double-helix structure, with sugar and phosphate on the outside of the helix, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone of the DNA. The nitrogenous bases are stacked in the interior in pairs, like the steps of a staircase; the pairs are bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. The two strands of the helix run in opposite directions, so that the 5′ carbon end of one strand faces the 3′ carbon end of its matching strand. This antiparallel orientation is important to DNA replication and in many nucleic acid interactions.
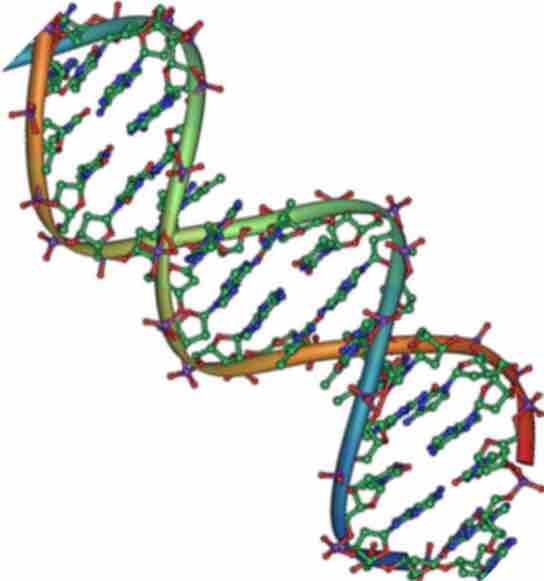
DNA is a Double Helix
Native DNA is an antiparallel double helix. The phosphate backbone (indicated by the curvy lines) is on the outside, and the bases are on the inside. Each base from one strand interacts via hydrogen bonding with a base from the opposing strand.
Base Pairs
Only certain types of base pairing are allowed. For example, a certain purine can only pair with a certain pyrimidine. This means Adenine pair with Thymine, and Guanine pairs with Cytosine. This is known as the base complementary rule because the DNA strands are complementary to each other. If the sequence of one strand is AATTGGCC, the complementary strand would have the sequence TTAACCGG.
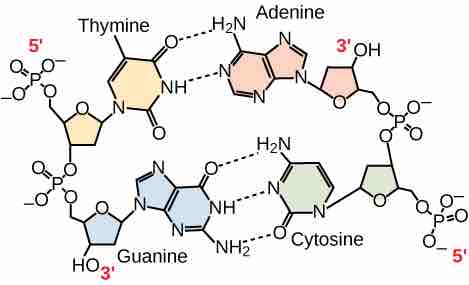
Antiparallel Strands
In a double stranded DNA molecule, the two strands run antiparallel to one another so that one strand runs 5′ to 3′ and the other 3′ to 5′. The phosphate backbone is located on the outside, and the bases are in the middle. Adenine forms hydrogen bonds (or base pairs) with thymine, and guanine base pairs with cytosine.
DNA Replication
During DNA replication, each strand is copied, resulting in a daughter DNA double helix containing one parental DNA strand and a newly synthesized strand. At this time it is possible a mutation may occur. A mutation is a change in the sequence of the nitrogen bases. For example, in the sequence AATTGGCC, a mutation may cause the second T to change to a G. Most of the time when this happens the DNA is able to fix itself and return the original base to the sequence. However, sometimes the repair is unsuccessful, resulting in different proteins being created.