Cell Theory
The microscopes we use today are far more complex than those used in the 1600s by Antony van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch shopkeeper who had great skill in crafting lenses. Despite the limitations of his now-ancient lenses, van Leeuwenhoek observed the movements of protista (a type of single-celled organism) and sperm, which he collectively termed "animalcules. "
In a 1665 publication called Micrographia, experimental scientist Robert Hooke coined the term "cell" for the box-like structures he observed when viewing cork tissue through a lens. In the 1670s, van Leeuwenhoek discovered bacteria and protozoa. Later advances in lenses, microscope construction, and staining techniques enabled other scientists to see some components inside cells.
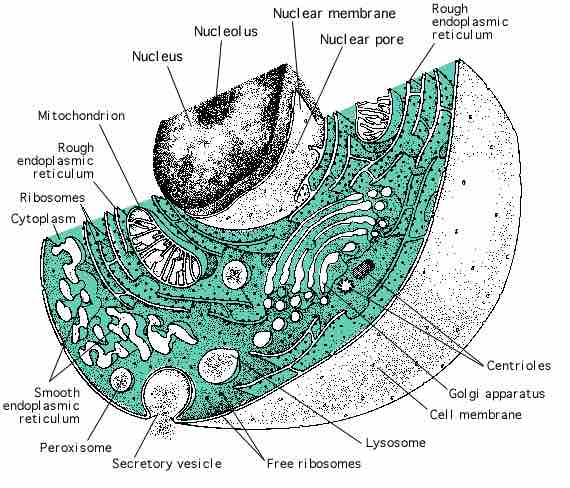
Structure of an Animal Cell
The cell is the basic unit of life and the study of the cell led to the development of the cell theory.
By the late 1830s, botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory. The unified cell theory states that: all living things are composed of one or more cells; the cell is the basic unit of life; and new cells arise from existing cells. Rudolf Virchow later made important contributions to this theory.
Schleiden and Schwann proposed spontaneous generation as the method for cell origination, but spontaneous generation (also called abiogenesis) was later disproven. Rudolf Virchow famously stated "Omnis cellula e cellula"... "All cells only arise from pre-existing cells. "The parts of the theory that did not have to do with the origin of cells, however, held up to scientific scrutiny and are widely agreed upon by the scientific community today. The generally accepted portions of the modern Cell Theory are as follows:
- The cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in living things.
- All organisms are made up of one or more cells.
- Cells arise from other cells through cellular division.
The expanded version of the cell theory can also include: