Free-Enterprise Defined
The definition of free enterprise is a business governed by the laws of supply and demand, where the government has no involvement in its decisions or actions. This economic system is based solely on private ownership as the means of production.
It is a private system in which all means of production are privately owned and operated.
Link to Capitalism
This is an example of capitalism in which government policies generally target the regulation and not the money.
Capitalism is generally considered to be an economic system that is based on private ownership of the means of production and the creation of goods or services for profit by privately-owned business enterprises.
Some have also used the term as a synonym for competitive markets, wage labor, capital accumulation, voluntary exchange, and personal finance. The designation is applied to a variety of historical cases, varying in time, geography, politics, and culture.
Variations of Capitalism
There are multiple variants of capitalism, including laissez faire, mixed economy, and state capitalism. There is, however, a general agreement that capitalism became dominant in the Western world following the demise of feudalism.
Economists, political economists, and historians have taken different perspectives on the analysis of capitalism. Economists usually emphasize the degree to which government does not have control over markets (laissez faire), as well as the importance of property rights.
Most political economists emphasize private property as well, in addition to power relations, wage labor, class, and the uniqueness of capitalism as a historical formation.
The extent to which different markets are free, as well as the rules defining private property, is a matter of politics and policy. Many states have what are termed mixed economies, referring to the varying degree of planned and market-driven elements in a state's economic system.
A number of political ideologies have emerged in support of various types of capitalism, the most prominent being economic liberalism.
Capitalism gradually spread throughout the Western world in the 19th and 20th centuries.
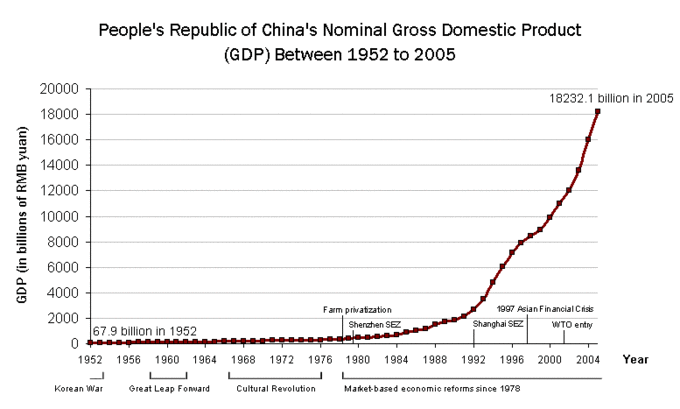
Peoples' Republic of China's Nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Between 1952 to 2005
Scatter graph of the People's Republic of China's GDP between years 1952 to 2005, based on publicly available nominal GDP data published by the People's Republic of China and compiled by Hitotsubashi University (Japan) and confirmed by economic indicator statistics from the World Bank.