Section 1
Human Resources and Relevant Laws
By Boundless

The National Labor Relations Act establishes the right of most private-sector workers to form unions, bargain with management and strike.

The Labor-Management Relations Act (or the Taft-Hartley Act) is a U.S. federal law that monitors the activities and power of labor unions.
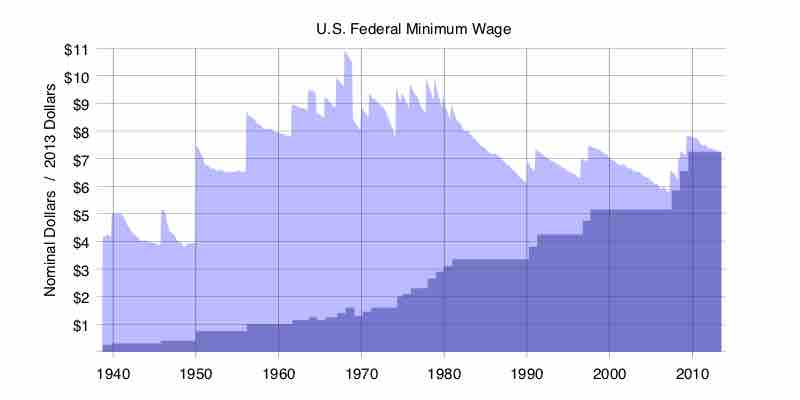
The Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 established a national minimum wage, forbade "oppressive" child labor, and provided for overtime pay in designated occupations.

The Equal Pay Act of 1963 is a U.S. Federal law amending the Fair Labor Standards Act aimed at abolishing wage disparity based on sex.
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 outlawed major forms of discrimination against African Americans and women, including racial segregation.

Under this act both employees and applicants who are 40 years old or over are protected from employment discrimination based on their age.

The goal of the OSHA Act is to make sure employers provide employees a place to work that is free from recognized hazards.

Businesses who voluntarily set up pension and health plans in private industry must adhere to rules ERISA rules that protect employees.
Affirmative action prevents discrimination against employees on the basis of race, religion, gender, or nationality.

The ADA makes it illegal to discriminate against people with disabilities in employment, public transportation, and communications.