In a condensation reaction, two molecules or parts thereof combine, releasing a small molecule. When this small molecule is water, it is known as a dehydration reaction. Other possible lost molecules include hydrogen chloride, methanol, and acetic acid.
When two separate molecules react, their condensation is termed intermolecular. A simple example is the condensation of two amino acids to form a peptide. This reaction example is the reverse of hydrolysis, which splits a chemical entity into two parts through action from the polar water molecule, which itself splits into hydroxide and hydrogen ions.

Peptide bond formed during condensation reaction
The condensation (dehydration) of two amino acids to form a peptide bond (red) with expulsion of water (blue).
When a condensation is performed between different parts of the same molecule, the reaction is termed intramolecular condensation; in many cases, this leads to ring formation. An example is the Dieckmann condensation, in which the two ester groups of a single diester molecule react with each other to lose a small alcohol molecule and form a β-ketoester product.
Many condensation reactions follow a nucleophilic acyl substitution or an aldol condensation reaction mechanism (see previous concept for more information). Other condensations, such as the acyloin condensation, are triggered by radical conditions.
Condensation Polymerization Reactions
In one type of polymerization reaction, a series of condensation steps takes place whereby monomers or monomer chains add to each other to form longer chains. This is termed "condensation polymerization," or "step-growth polymerization," and occurs in such processes as the synthesis of polyesters or nylons. Nylon is a silky material used to make clothes made of repeating units linked by amide bonds, and is frequently referred to as polyamide. This reaction may be either a homopolymerization of a single monomer A-B with two different end groups that condense, or a copolymerization of two co-monomers A-A and B-B. Small molecules are usually liberated in these condensation steps, unlike polyaddition reactions.
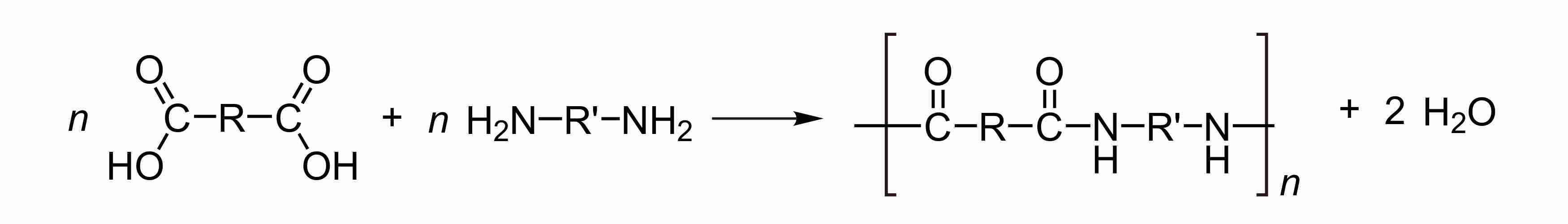
Condensation of diacid and diamine
The condensation of a diacid and diamine is an example of A-B polymerization.
Condensation polymers often require heat, form slower than do addition polymers, and are lower in molecular weight. This type of reaction is used as a basis for making many important polymers, such as nylon, polyester, and various epoxies. It is also the basis for the laboratory formation of silicates and polyphosphates. Many biological transformations, such as polypeptide synthesis, polyketide synthesis, terpene syntheses, phosphorylation, and glycosylations are condensations.

Nylon molecular structure
Nylon is a synthetic polymer produced by condensation polymerization.