Marginal Cost
In economics, marginal cost is the change in the total cost when the quantity produced changes by one unit. It is the cost of producing one more unit of a good. Marginal cost includes all of the costs that vary with the level of production. For example, if a company needs to build a new factory in order to produce more goods, the cost of building the factory is a marginal cost. The amount of marginal cost varies according to the volume of the good being produced. Economic factors that impact the marginal cost include information asymmetries, positive and negative externalities, transaction costs, and price discrimination. Marginal cost is not related to fixed costs. An example of calculating marginal cost is: the production of one pair of shoes is $30. The total cost for making two pairs of shoes is $40. The marginal cost of producing the second pair of shoes is $10.
Average Cost
The average cost is the total cost divided by the number of goods produced. It is also equal to the sum of average variable costs and average fixed costs. Average cost can be influenced by the time period for production (increasing production may be expensive or impossible in the short run). Average costs are the driving factor of supply and demand within a market. Economists analyze both short run and long run average cost. Short run average costs vary in relation to the quantity of goods being produced. Long run average cost includes the variation of quantities used for all inputs necessary for production.
Relationship Between Average and Marginal Cost
Average cost and marginal cost impact one another as production fluctuate :
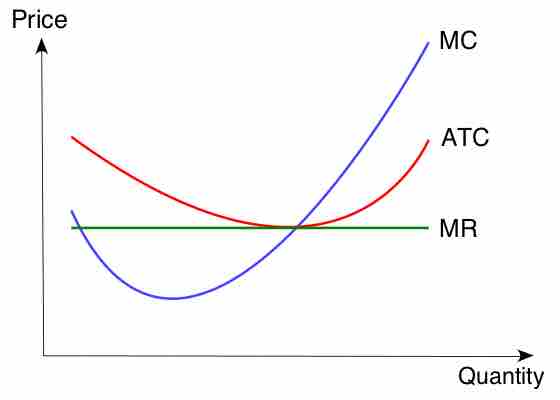
Cost curve
This graph is a cost curve that shows the average total cost, marginal cost, and marginal revenue. The curves show how each cost changes with an increase in product price and quantity produced.
- When the average cost declines, the marginal cost is less than the average cost.
- When the average cost increases, the marginal cost is greater than the average cost.
- When the average cost stays the same (is at a minimum or maximum), the marginal cost equals the average cost.