Decision tree analysis provides a visual tool to help individuals quantify and weigh options against one another when making a decision. A decision tree calculates the expected values of competing alternative. This tells the decision maker which decision has the highest utility (i.e., is the most preferred) to the decision maker.
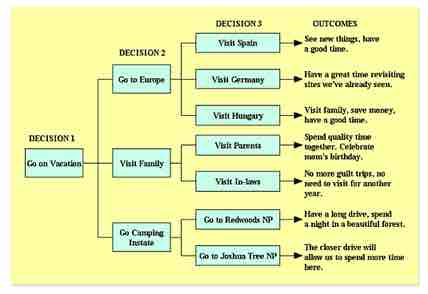
Decision tree
This example of a decision tree shows the decision maker trying to choose where to go on vacation.
Creating a Decision Tree
A decision tree consists of 3 types of nodes:
- Decision nodes: These are commonly represented by squares. Decision nodes are used when a decision needs to be made between at least two alternatives.
- Chance nodes: These may be represented by circles. Chance nodes represent points on the decision tree where there is uncertainty about outcomes (so there must be at least two possible outcomes represented).
- End nodes: These may be represented by triangles. An end node is where a decision is made and its value or utility is identified.
Applications of Decision Trees
Decision trees can be applied to ethical considerations. Consider an ethical dilemma involving a colleague. You are considering three options: report your colleague to a superior, confront the colleague yourself, or ignore the situation completely. The top box of the decision tree would state "Colleague Dilemma."
The next three nodes would then read: "Report colleague to superiors," "Confront colleague," and "Ignore situation. " Each of these nodes would then have a "Yes" arrow and a "No" arrow. For each "Yes" and "No," you would list what the outcome would be, realizing that in some cases the nodes may need to continue to account for potential outcomes, some of which may link back to previous options. For example, a "Yes" decision arrow for "Report colleague to superiors" may result in the situation being taken care of—or, it could result in an investigation that would impact your standing within the company and with your peers. If you chose to ignore the colleague and his unethical behavior is discovered in the future, you could end up in trouble for choosing not to act earlier.
A decision tree for a tough problem allows the decision maker to visually lay out each scenario and make a detailed consideration. Decision trees therefore support the evaluation process and can help clarify often-complex ethical dilemmas.