The theory of Special Relativity and its implications spurred a paradigm shift in our understanding of the nature of the universe, the fundamental fabric of which being space and time. Before 1905, scientists considered space and time as completely independent objects. Time could not affect space and space could not affect time. After 1905, however, the Special Theory of Relativity destroyed this old, but intuitive, view. Specifically, Special Relativity showed us that space and time are not independent of one another but can be mixed into each other and therefore must be considered as the same object, which we shall denote as space-time. The consequences of space/time mixing are:
Other important consequences which will be discussed in another section are
- Relativity of Simultaneity (for certain events, the sequence in which they occur is dependent on the observer)
- Nothing can move faster than the speed of light (we shall denote the value of the speed of light as
$c$ )
Why is there a mixing between space and time? In order to examine this we must know the founding principles of relativity. They are:
- The Principle of Relativity: The laws of physics for observers which are not accelerating relative to one another should be the same.
- The Principle of Invariant Light Speed: All observers, moving at constant speed, measure the same speed of light regardless of how fast they are moving.
If one accepts the second principle as fact then it immediately follows that space and time are not independent. Why? Let us look at the experiment in in which there is a light source, a fixed observer, and a rocket ship moving toward the light source. The two observers are related by a coordinate, or space-time, transformation. The second principle then tells us that no matter how fast the rocket is moving, both observers must measure the same light speed emanating from the source. The only way this can happen is if the clock of the rocket observer is ticking at a different rate than the stationary observer. How much different? This can be expressed in the time dilation equation:
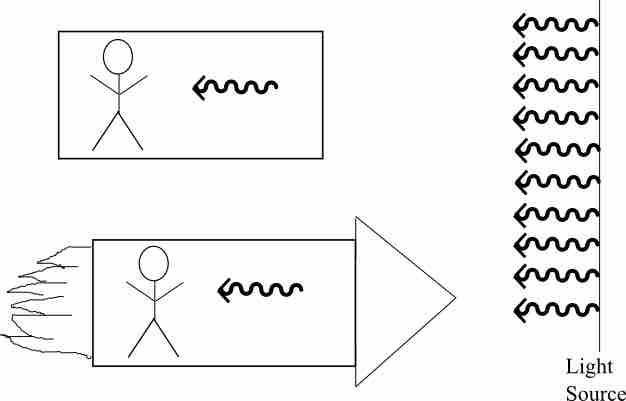
Measuring Light
A stationary observer will measure the same speed of light as an observer who is moving in a rocket ship even if that rocket is moving close to light speed.
Where
One of the more radical results of time dilation is the so-called "twin paradox. " The twin paradox is a thought experiment in special relativity that involves identical twins. One of the twins goes on a journey into space in a rocket that has a velocity near the speed of light. Upon returning home the twin finds that the twin that remained on Earth has aged more. This consequence altered the perception that aging is necessarily constant.
The square root factor in the time dilation equation is very important and we denote it as:
This factor shows up frequently in special relativity. For example the length contraction formula is:
where
Another radical finding that was made possible by the discovery of special relativity is the equivalence of energy and mass. Combined with other laws of physics, the postulates of special relativity predict that mass and energy are related by:
As a final note it is important to note how big the speed of light is compared to every day life. The speed of light is:
Thus in every day life