Irreversibility
The second law of thermodynamics deals with the direction taken by spontaneous processes. Many processes occur spontaneously in one direction only—that is, they areirreversible, under a given set of conditions. Although irreversibility is seen in day-to-day life—a broken glass does not resume its original state, for instance—complete irreversibility is a statistical statement that cannot be seen during the lifetime of the universe. More precisely, an irreversible process is one that depends on path. If the process can go in only one direction, then the reverse path differs fundamentally and the process cannot be reversible.
For example, heat involves the transfer of energy from higher to lower temperature. A cold object in contact with a hot one never gets colder, transferring heat to the hot object and making it hotter. Furthermore, mechanical energy, such as kinetic energy, can be completely converted to thermal energy by friction, but the reverse is impossible. A hot stationary object never spontaneously cools off and starts moving. Yet another example is the expansion of a puff of gas introduced into one corner of a vacuum chamber. The gas expands to fill the chamber, but it never regroups in the corner. The random motion of the gas molecules could take them all back to the corner, but this is never observed to happen .
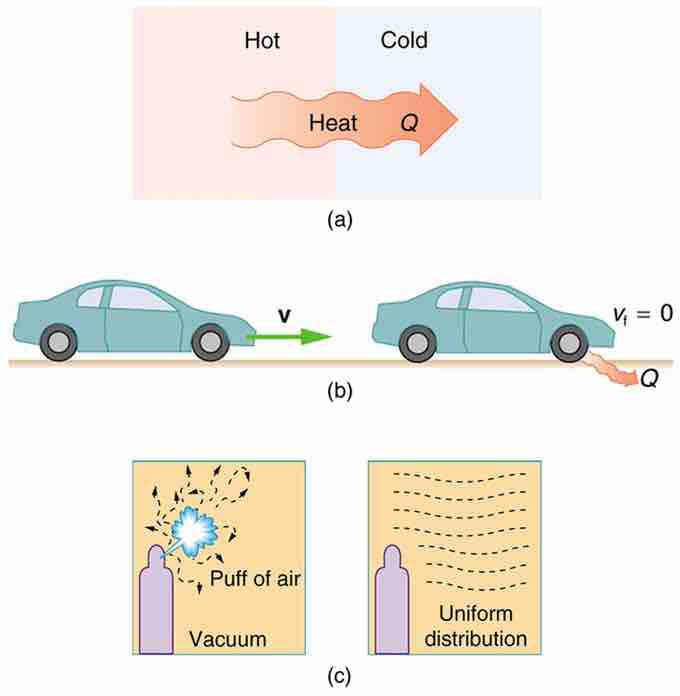
One-Way Processed in Nature
Examples of one-way processes in nature. (a) Heat transfer occurs spontaneously from hot to cold and not from cold to hot. (b) The brakes of this car convert its kinetic energy to heat transfer to the environment. The reverse process is impossible. (c) The burst of gas let into this vacuum chamber quickly expands to uniformly fill every part of the chamber. The random motions of the gas molecules will never return them to the corner.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
The fact that certain processes never occur suggests that there is a law forbidding them to occur. The first law of thermodynamics would allow them to occur—none of those processes violate conservation of energy. The law that forbids these processes is called the second law of thermodynamics . We shall see that the second law can be stated in many ways that may seem different, but these many ways are, in fact, equivalent. Like all natural laws, the second law of thermodynamics gives insights into nature, and its several statements imply that it is broadly applicable, fundamentally affecting many apparently disparate processes. The already familiar direction of heat transfer from hot to cold is the basis of our first version of the second law of thermodynamics.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics(first expression): Heat transfer occurs spontaneously from higher- to lower-temperature bodies but never spontaneously in the reverse direction.
The law states that it is impossible for any process to have as its sole result heat transfer from a cooler to a hotter object. We will express the law in other terms later on, most importantly in terms of entropy.