Spina bifida (Latin: "split spine") is a developmental congenital disorder caused by the incomplete closing of the embryonic neural tube. Some vertebrae overlying the spinal cord are not fully formed and remain unfused and open.
The protruded portion of the spinal cord and the nerves that originate at that level of the cord are damaged or not properly developed. As a result, there is usually some degree of paralysis and loss of sensation below the level of the spinal cord defect. Thus, the higher the level of the defect, the more severe the associated nerve dysfunction and resultant paralysis may be. People may have ambulatory problems; loss of sensation; deformities of the hips, knees, or feet; and loss of muscle tone.
Spina bifida
Location of spina bifida on an infant.
Treatment for Spina Bifida
Spina bifida can be surgically closed after birth, but this does not restore normal function to the affected part of the spinal cord. Intrauterine surgery for spina bifida has also been performed; the safety and efficacy of this procedure is currently being investigated. The spinal cord lesion or the scarring due to surgery may result in a tethered spinal cord. In some individuals, this causes significant traction and stress on the spinal cord. This may lead to a worsening of associated paralysis, scoliosis, back pain, and worsening bowel and/or bladder function.
Causes of Spina Bifida
There is neither a single cause of spina bifida nor any known way to prevent it entirely. However, dietary supplementation with folic acid prior to pregnancy has been shown to be helpful in reducing the incidence of spina bifida. Natural sources of folic acid include whole grains, fortified breakfast cereals, dried beans, leafy vegetables, and fruits. Neural tube defects can usually be detected during pregnancy by testing the mother's blood (AFP screening) or by a detailed fetal ultrasound. Ultrasound screening for spina bifida is partly responsible for the decline in new cases because many pregnancies are terminated out of fear that a newborn might have a poor future quality of life. With modern medical care, the quality of life of patients has greatly improved.
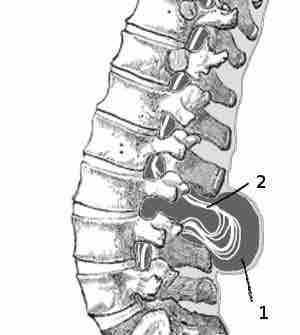
Spina Bifida
Spina bifida in the lumbar area. (1) External sac with cerebrospinal fluid. (2) Spinal cord wedged between the vertebrae.