The production of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) is primarily regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) that is released from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH release, in turn, stimulates the hypothalamus to secrete thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). This results in increased metabolism, growth, development and the activation of numerous other systems controlled by thyroid hormones.
Thyroid hormones also provide negative feedback to the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland. When thyroid levels in the blood are elevated TSH and TRH production is reduced. Excessive TRH can also inhibit the production of further TRH.
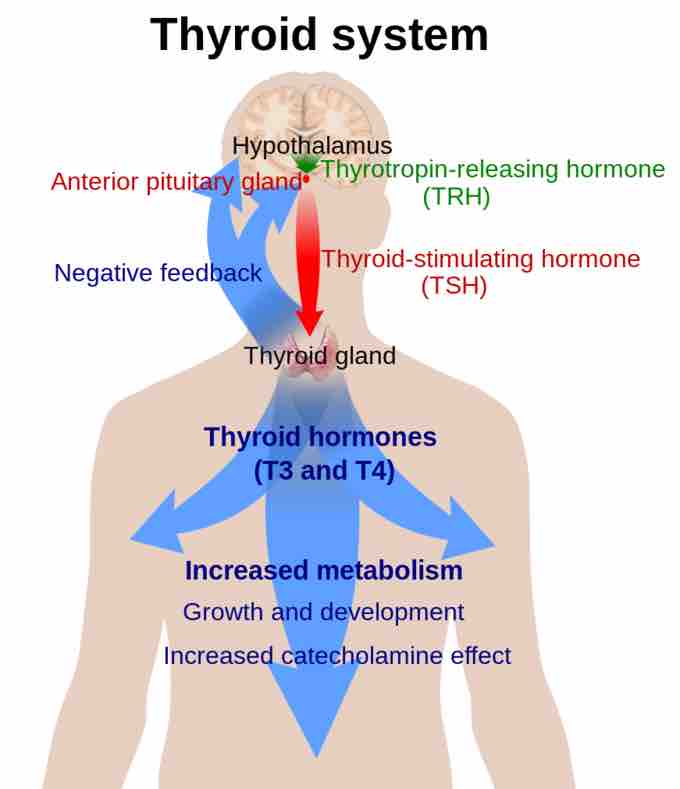
The thyroid system
Thyroid hormones are produced from the thyroid under the influence of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary gland, which is itself under the control of thyroptropin-releasing hormone (TRH) secreted by the hypothalamus. Thyroid hormones provide negative feedback, inhibiting secretion of TRH and TSH when blood levels are high.