Section 2
Theoretical Perspectives in Modern Psychology
By Boundless
Abnormal psychology seeks to study, understand, diagnose, and treat psychological disorders.
Positive psychology stems from the humanistic psychology of the 20th century and focuses on optimizing psychological health and well-being.
Psychodynamic theory studies the psychological forces underlying human behavior, feelings, and emotions.

Behaviorism is an approach to psychology that focuses on observable behaviors that people learn from their environments.

Cognitive psychology examines internal mental processes such as problem-solving, memory, and language.
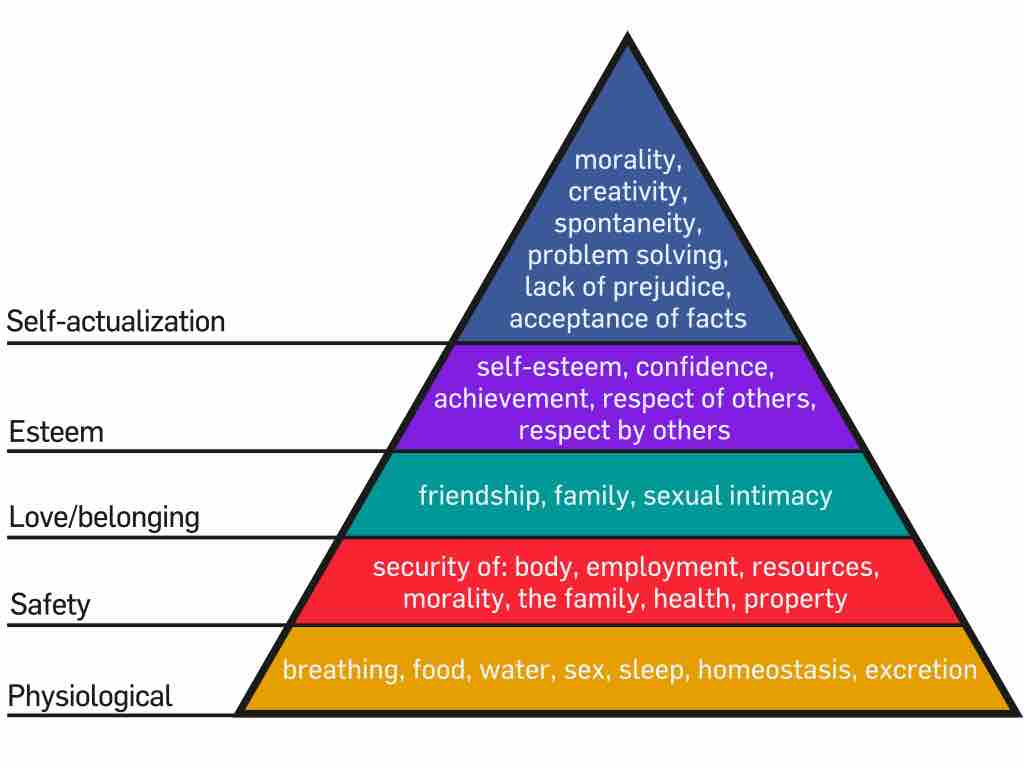
Humanistic psychology adopts a holistic view of human existence through explorations of meaning, human potential, and self-actualization.
Personality psychology studies the long-standing traits and patterns that propel individuals to consistently think, feel, and behave in specific ways.
Educational psychology is the study of how humans learn in educational settings.
Social psychology studies individuals in a social context and examines how situational variables influence behavior.

Cultural psychology seeks to understand how forces of society and culture influence individuals' thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
Biopsychology is the application of the principles of biology to the study of mental processes and physical behavior.
Developmental psychologists study the physical, cognitive, and psychosocial development of humans from conception through adulthood.

Evolutionary psychology seeks to understand human behavior as the result of psychological adaptation and natural selection.
Comparative psychology is the scientific study of animal behavior and mental processes, which can lead to a deeper and broader understanding of human psychology.