238 chapter 29
Phenytoin (diphenyIhydantoin, Dilantin)
For all types of seizures except brief seizures that suddenly throw the child out of balance (‘jolt
seizures’) or ‘minor seizures’ with staring, blinking, or fast movement of eyes. (Phenytoin may make
these kinds of seizures worse.)
Usually comes in: capsules or tablets of 25 mg., 50 mg., and 100 mg.
syrup with 30 mg. in each 5 ml. (1 teaspoon)
Dosage: Give 5 to 10 mg./kg./day in 2 divided doses, but do not exceed 300 mg./day.
Start with the following dose once a day:
children over 12 years ...................................100 to 300 mg.
children 7 to 12 years ....................................100 mg.
children 6 or under .........................................50 mg.
After 2 weeks, if the seizures are not completely prevented, the dose can be increased, but not to
more than twice the amount.
If child has no seizures during several weeks, try lowering the dose little by little until you find the
lowest dose that prevent the seizures.
SIDE EFFECTS AND COMPLICATIONS
WARNING: Watch for dizziness, eye-jerking, seeing double, and severe sleepiness. Lower
the dose if any of these occur. They are early signs of poisoning, which could cause permanent
brain damage.
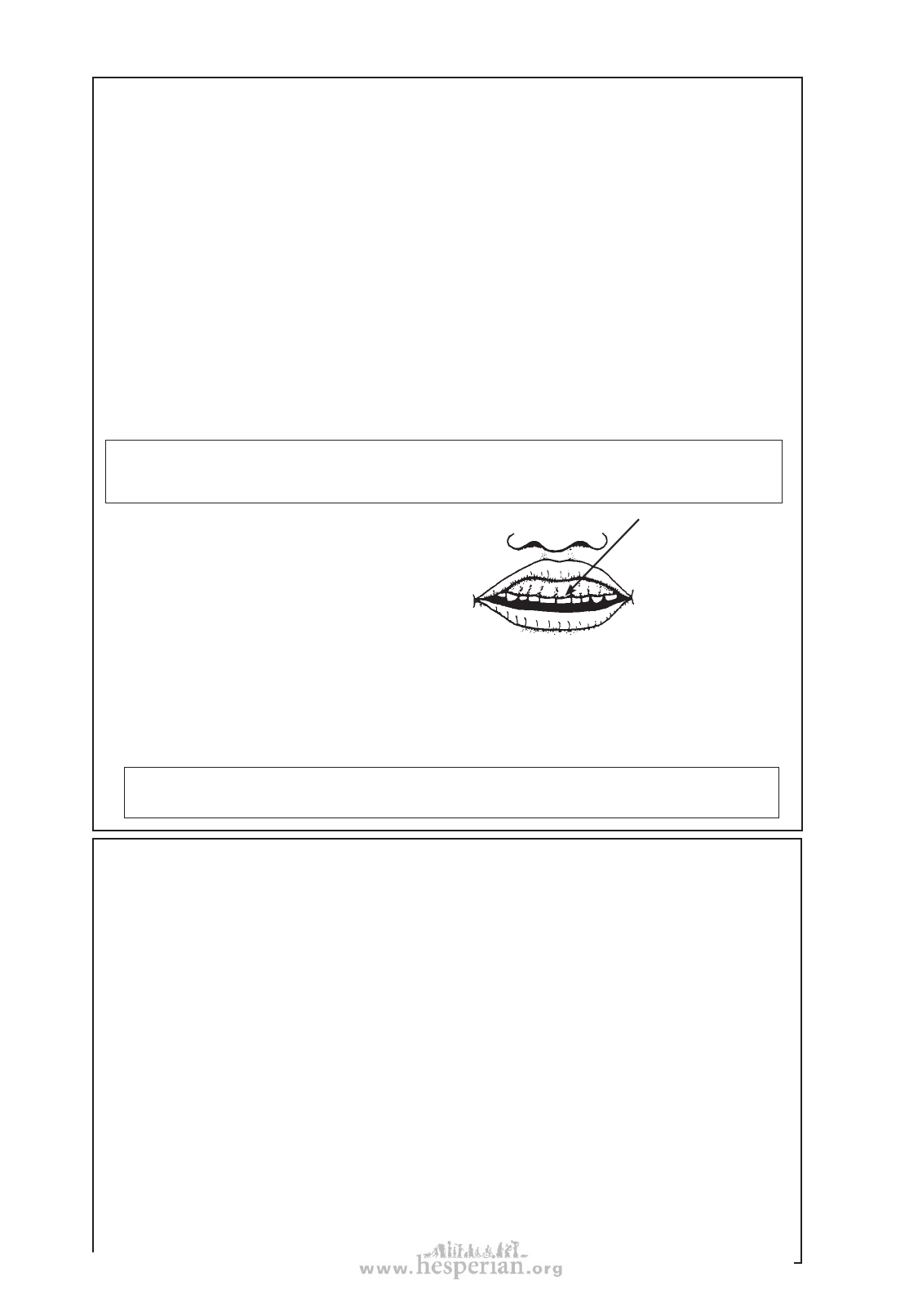
very swollen,
• Swelling and abnormal growth of the
sore gums
gums often occurs with long-time use. It
almost covering
can be partly prevented by good mouth care.
teeth—caused by
Be sure the child brushes or cleans his
not keeping teeth
teeth and gums well after eating. If he
clean while taking
cannot do it by himself, help him, or better,
phenytoin
teach him. If the gum problem is severe,
consider changing medicines. (See Where There Is No Dentist, p. 109.)
• Occasional side effects: increased body hair, rash, loss of appetite,vomiting.
• High dosage may cause liver damage.
• Bone growth problems sometimes occur—especially in children who are
mentally slow. Extra vitamin D may help.
WARNING: Sudden stopping of phenytoin may cause the child to have a long-lasting
seizure. Therefore, when stopping or changing the medicine, lower the dosage gradually.
Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
Useful for almost all types of seizures as a second choice, or in combination.
Especially useful for ’psychomotor’ seizures (see p. 241). High cost is a disadvantage.
(Unfortunately, many doctors prescribe it as first choice when cheaper drugs such as
phenobarbital are likely to work as well or better.)
Usually comes in: tablets of 100 mg. or 200 mg.
Dosage: 10 to 25 mg./kg./day divided into 2 to 4 doses. Or you can start with these doses 4 times a
day:
children 10 to 15 years ................................. 200 mg.
children 5 to 10 years ................................... 150 mg.
children 1 to 5 years ..................................... 100 mg.
children under 1 year old ................................ 50 mg.
It is best to take it with meals.
The dose of carbamazepine should be adjusted to the individual. Depending on how well it
controls the seizures, it can be raised to 30 mg./kg./day (but no higher) or dropped to 10 mg./
kg./day. Try to give the lowest amount of medicine that stops the seizures.
SIDE EFFECTS AND COMPLICATIONS
• Rarely causes liver damage or reduces ability of blood to clot.
Disabled village Children