 |
Cocoa
Scientific name:
Theobroma cacao
Family:
Malvales: Sterculiaceae
Pests and Diseases: Aphids
Cocoa bud or black rot
Fruit flies
Helopeltis bugs
Leafhoppers
Mealybugs
Pod borers
Pod rot
Snails (Giant East African Snail)
Spiny bollworm
Thrips
Ants, Anthracnose
|
 |
| Geographical Distribution of Cocoa in Africa |
Today, cocoa is cultivated in all humid, tropical countries.
The main products made from cocoa beans are chocolate, cocoa powder and butterfat, which are all used for human consumption. Butterfat is also used in cosmetics and pharmaceutical products but the amount used for these purposes is insignificant in relation to that used in chocolate manufacture. On the international market, raw cocoa (dried cocoa seeds) is the most sought product, which is used for production of cocoa butter, chocolate, and cocoa powder.
Nutritive Value per 100 g of edible Portion
| Raw or Cooked Cocoa | Food Energy (Calories / %Daily Value*) |
Carbohydrates (g / %DV) |
Fat (g / %DV) |
Protein (g / %DV) |
Calcium (g / %DV) |
Phosphorus (mg / %DV) |
Iron (mg / %DV) |
Potassium (mg / %DV) |
Vitamin A (I.U) |
Vitamin C (I.U) |
Vitamin B 6 (I.U) |
Vitamin B 12 (I.U) |
Thiamine (mg / %DV) |
Riboflavin (mg / %DV) |
Ash (g / %DV) |
| Cocoa Powder unsweetened | 228 / 11% | 57.9 / 19% | 13.7 / 21% | 19.6 / 39% | 128 / 13% | 734 / 73% | 13.9 / 77% | 1524 / 44% | 0.0 IU / 0% | 0.0 / 0% | 0.1 / 6% | 0.0 / 0% | 0.1 / 6% | 0.2 / 14% | 5.8 |
With an even annual distribution of rainfall (100 mm per month), the plantations can survive on 1250 mm per year. Short drought periods can be compensated for by heavy clouds and high humidity. The average annual temperature should be around 25°C. In regions with extensive wet periods or large seasonal temperature fluctuations, the harvesting periods are reduced to only a few months per year. In regions with a balanced climate, and only slight temperature and rainfall fluctuations, cocoa produces fruit practically throughout the year. Cocoa is thus a typical crop of the tropical lowlands. It can also be grown at higher altitudes if other conditions are favourable. Especially in areas without a dry season, cocoa has shown to develop more quickly than in the major production areas of West Africa, where growth is stopped by drought during certain months of the year.
The soil on cocoa plantations should be deep, well-drained, and have sufficient water-retaining capacity. Soils with a high available moisture-storage capacity can compensate for periodic lack of rain, while excessive rainfall will cause fewer problems on well-drained soils. The pH-value should lie between 4.0 and 7.5. Care must be taken that sufficient organic material is available.
Cocoa trees can live for over 100 years. Naturally occurring cocoa crops propagate themselves through lateral shoots, which can occur at any height on the trunk. The natural vegetative proliferation occurs when the seeds are spread by small rodents and apes.
Cocoa is usually planted as seedlings, which are easy and cheap to produce. Vegetative propagation by rooted cuttings or budding is used to establish seed gardens. Seedlings are usually raised in polythene bags in a shaded nursery. Young plants are planted in the field 3 - 4 m apart or about 1100 trees/ha at an age of 4 - 6 months. Young trees need shade to reduce irradiance, to buffer the microenvironment and to promote the right shape and habit of the trees. When a closed canopy has been formed, the need for shade is reduced. Only under most favourable conditions of soil and nutrient supply can cocoa be grown without shade. It is normally necessary to retain some shade to reduce moisture stress and incidence of insect damage in order to prolong the economic life of plantations.
Shade can be provided either by thinning forest or by planting shade trees. Shade trees are common in South-East Asia, where mainly seedless Leucaena leucocephala and Mother of cocoa (Gliricidia sepium) are used. Often, hedges of leguminous shrubs are used for temporary side-protection between rows and as a source of mulch. Cocoa is also grown as an intercrop under coconuts.
 |
| Budding of cocoa plants |
| © Putter CA (Courtesy of EcoPort, www.ecoport.org) |
Any shells that are left over after the harvest must remain on the plantation. This means that the fruits should be broken open on site, if possible. The resulting shell material should be spread as evenly as possible. The cocoa pods harvested on a plot are first piled into a heap, and then broken open to provide around 50 kg of fresh cocoa. The cocoa pods should then be piled onto a different heap during the next harvest stage, and broken open there.
Many varieties of palms are capable of actively breaking down phosphorus, as well as binding heavy metals in the soil, which thereby reduces the amounts absorbed by the cocoa plants. This can be useful, because the amount of heavy metals in the cocoa seeds can be problematic. It is therefore recommended to integrate suitable palm varieties into the plantation.
Once the canopy has closed, lack of light will prevent weed growth. Young trees need no pruning during the first 2 - 3 years. Later, low-hanging branches should be pruned to facilitate harvesting. Vertical growth is usually restricted to the first jorquette (fan of branches). If the first jorquette is formed too low (below a height of 1.5 m), the tree is allowed to make a second one. To retain trees at the desired height, cocoa seedlings (chupons) should be removed at regular intervals.
 |
| © Naturland e.V. (www.naturland.de) |
 |
| © Naturland e.V. (www.naturland.de) |
 |
| © Naturland e.V. (www.naturland.de) |
 |
| © Naturland e.V. (www.naturland.de) |
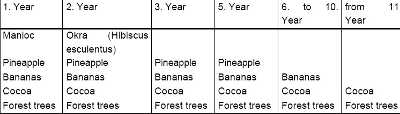
Rice as well as maize can be sown as a pioneer crop, depending on the starting conditions (soil fertility, market access, consumer habits, etc.), simultaneously with manioc (Manihot esculentum), new coco-jam (Xanthosoma sagittifolium) in Nigeria and Cameroon and pigeon peas (Cajanus cajan).
Before a pioneer crop is sown, bananas should be planted. The distance between each plant depends on the distances between the individual cocoa plants and the variety of banana. Along with standard commercial varieties of banana from the Cavendish group, other tall-growing local varieties which can tolerate shade should also be integrated into the plantation. The number of cocoa trees should lie between 600 and 1100 trees per ha.
During the first few years, on fertile soils, papaya (Carica papaya) can also be cultivated in addition to bananas within the system (2 x 2 m). Together with the papaya seeds or bananas, trees growing up to the middle storey (such as Inga ssp., Erytrina ssp., Gliricida sepium) as well as growing up to the upper storey must also be planted. This can be in seed form. Only in the cases of certain varieties (such as palm varieties that are old, or difficult to germinate), should the trees be first sown in a tree nursery. The choice of tree depends on which varieties are available in the region. In addition to the varieties listed above, it is recommended to integrate palm species at a density of 100-150 trees per ha in organic cultivation systems.
Many combinations are possible, in which other fruit trees such as avocado, jackfruit and many more can be integrated.
Monoculture plantations that already exist, and which have only very few shading trees can be improved. The best method is to re-forest wrongly cultivated spots, and also spaces that become available after unproductive single plants have been removed.
Depending on the region and weather conditions, there are usually 1 or 2 harvesting phases, which are spread out over several months. In order to achieve a uniform ripeness of the pods harvested, it is wise to harvest all of the ripened pods every 2-3 weeks. During peak production, pods are harvested each week. The best way to avoid harming the bark is to cut off the pods at the base of the blossom with a sharp knife or other suitable instrument.
The cocoa should be stored in air-permeable sacks on the production site for only a short time, whereby the sacks should be stacked on wooden planks or boards. The use of sacks made of organic material (jute) should be avoided, if these have been treated with pesticides. The cocoa butter part in the cocoa shell is an excellent solvent for chlorinated hydrocarbons which can diffuse through the outer shell when they come into contact with it, and into the cocoa seed. In such cases, tests have then shown limits for certain agricultural poisons being exceeded - although no pesticides had ever been used on the site.
The storage area should always be well-ventilated - the inside temperature should remain below the outside temperature.
On conventional plantations, it is quite usual to gas the cocoa with methyl bromide in order to protect them against storage pests. However, it is now not allowed to use methyl bromide. In addition, tetraline soap, hydrogen phosphide and prussic acid are also used. On organic cocoa plantations, it is not permitted to use either insecticides against storage pests, or to gas the beans.
Cocoa beans should be stored in dark, dry and well-ventilated rooms at low temperatures.
Short-term storage: about 16°C; relative humidity: 55%
Long-term storage: about 11°C; relative humidity: 55
-
Most diseases are caused by the following:
- Cultivation in monocropping systems with no or only very few varieties and number of shading trees (on conventional plantations, 25-40 trees of mostly one variety per ha recommended)
- Ignoring the natural rotation of the forest system. For example, cocoa plantations which grow beneath old shading trees from the secondary forest system (mostly Inga ssp., Gliricidia sepium etc.), are highly susceptible to diseases and pests. Cocoa, as a plant from the primary forest, can tolerate old primary forest trees above it, yet not trees from the secondary forest system.
- Too little distance between the different varieties in a system which have the same status; failure to thin out the agroforestry system
- Degraded and poor soils, lack of organic material
- Unsuitable site (water-logging, too dry, no possibility for deep root development)
Effective measures are often only possible in the form of improvements to the whole system. One possibility lies in radically cutting back the trees and subsequently replacing them with the correct varieties, or, with a complete renewal measure, whereby the trees are sawn down to a stump of around 40 cm. One to 3 of the resulting shoots which develop out of the stumps are left to develop. Opening up the plantation allows many new varieties to be included.
A tolerable loss at harvest time, which is also heavily dependant on weather conditions, is often caused by the fungus (Phytophtora palmivora). In addition to the measures described here, regular harvesting, which should then include diseased fruit, can reduce the infestation (many farmers only harvest the healthy fruits). In the case of a heavy infestation by Phytophtora palmivora, harvest losses can be alleviated with Bordeaux mixture, or other spray preparations containing copper, that are permitted on organic plantations. These methods should only be used in emergencies.
Fungal infections are caused by Botryodiplodia theobromae, Colletotrichum sp. (anthracnose) and Trachysphaera fructigena. On cocoa, infection with T. fructigena is an insignificant component of pod diseases.
Cocoa bud rot or Cocoa black rot (Phytophthora palmivora)
It is a foot rot disease caused by the fungus (Phytophthora palmivora) which results in large pod losses in West Africa and stem canker in Trinitario populations.
Cocoa bud rot attacks the whole plant. On pods, the disease begins with a circular brown lesion that enlarges to cover the whole pod. It eventually becomes black and mummified, and sometimes covered in a white mass of fungal growth (sporangia). Stem cankers are characterised by oval to round, rusty-brown discolouration of the external bark that looks purple when scraped. Attack of young shoots results in die-back.
Regular harvesting plays the greatest role, as it reduces spread to other pods and bark where stem canker and flower cushion infections may develop.
- Harvest pods regularly and remove diseased pods.
- Thin canopy to improve airflow and reduce humidity.
- Space planting in well drained sites.
- Avoid infested soil.

Cocoa black rot (Phytophthora palmivora)
© Jürgen Kranz (Courtesy of EcoPort, www.ecoport.org)
Pod rot of cocoa (Lasiodiplodia theobromae)
In cocoa pod rot the infected tissue shows brown necrosis with dark brown powdery spore masses. Such infected tissues show greyish-black mycelia.
The fungus is most important as a cause of postharvest food decay. It also causes damage in cocoa in the form of dieback disease.
A variety of insect pests are important during establishment, because they destroy the apical bud and delay or prevent canopy formation. In mature cocoa, mirids (Helopeltis and other regionally specific genera) are the major widely represented insect pests, causing severe damage to twigs, branches and young pods.
An infestation by pests in a cocoa plantation has the same causes as diseases which affect a system. The causes are listed under 'diseases'.
The losses caused by these pests world-wide is enormous. They result from the cocoa fruits being sucked dry in all stages of growth, after which, the plant dies off, depending to the amount of damage done.
Without losing sight of the need to combat the root causes, a solution which can be immediately utilised to save a harvest is by spraying with a 3% alkaline soap solution (potassium soap), which has proven itself in Bolivia in regulating different bug varieties. In addition, other preparations being permitted on organic farms can also be used.
Some common pests of cocoa are:
- Mealybugs (Planococcus, Stictococcus in Africa)
- Bollworms and various other psyllids
- Leafhoppers
- Thrips (Selenothrips rubrocinctus, Heliothrips rubrocinctus)
- Leaf cutter ants (Atta ssp.)
Helopeltis bugs (Helopeltis schoutedeni)
The cocoa mosquito (Helopeltis schoutedeni) also known as Helopeltis bug or mirid bugs are slender, delicate insects, about 7- 10 mm long with long legs and antennae, the antenna being nearly twice as long as the body. The females are red and the males brown to yellowish red. They lay eggs inserted into the soft tissue near the tips of flowering or vegetative shoots. Nymphs (immature bugs) are yellowish in colour. Both adults and nymphs feed on young leaves, young vegetative and flowering shoots, and developing fruits.
Typical feeding damage of Helopeltis species appears as a discoloured, necrotic (blackened) area or lesion around the affected plant tissue.
Heavy infestations by Helopeltis species can result in pod malformations and premature drop, thus providing a venue for secondary infection by microorganisms and serving to attract other pests to cacao.
- Monitor the crop regularly. Helopeltis attack occurs very suddenly and great vigilance is very important to control this pest, particularly during the rainy season or when water is available leading to flushing (production of young shoots) when Helopeltis populations normally build up.
- Conserve natural enemies. Weaver ants build nests on cashew trees providing good protection against this and other bug pests.
- Do not interplant cocoa with crops that are host for Helopeltis bugs, such as cashew, tea, sweet potato, guava, cotton and mango.
- Cultural practices including pruning, weeding and shading schemes have been used in the control of cocoa-mosquito.

Helopeltis bug (Helopeltis schoutedeni). Real size: 6 to 10 mm long.
© F. Haas, icipe

Helopeltis…

Helopeltis…
Pod-borers (Characoma stictigrapta)
Pod-borers are serious pests of cocoa. The pod husk borer (Characoma stictigrapta) for example, occurs in West Africa.
The damage is done by the larva which bores holes into pods of all sizes. It produces a mass of frass held together by silk at the entrance of the holes. If the pod is very young and soft (cherelle)
then it wilts. The insect is usually not controlled.
- Simple cultural methods, such as adjustment of shading level or improved soil drainage, will contain many of the most troublesome pests including pod borer.

Pod-borer Characoma stictigrapha damage on cocoa
© www.dropdata.net

Pod-borer

Pod-borer
The spiny bollworm (Earias biplaga)
It feeds on a wide range of plants and also attacks cocoa. It may prefer wild hosts to crops. If crops are grown while wild hosts are available nearby, the crops may not be badly affected. Wild hosts will also maintain a supply of natural enemies.
The larva eats the growing tips of the stems and young soft leaves. It's feeding activity prevents the plant from growing properly to form canopy.
The attack is more where there is no shade over the cocoa. It's attack therefore may be prevented if fast growing shade trees are provided over cocoa that has been freshly planted.
- Adjust shading level
- Improve soil drainage

Caterpillar of the spiny bollworm (Earias biplaga)(here on okra plant)
© A.M. Varela, icipe

Spiny boll…

Spiny boll…
Mealybugs
Mealybugs infest fruits and foliage. They can be serious pests in the warm season, if natural enemies, which usually control them, are destroyed by spraying with pesticides.
- Conserve natural enemies. Mealybugs are usually controlled by a wide range of natural enemies. However, use of pesticides may kill these natural enemies leading to mealybug outbreaks.

Mealybugs on underside of a leaf. Female mealybugs are 3 to 5 mm long and their body is usually covered with a waxy secretion.
© A.M. Varela, icipe
Leafhoppers (Empoasca spp)
Adult leafhoppers are small about 2 to 3 mm long and thin. The wings are held roof like over the abdomen. They are pale green to yellowish green in colour, shiny and more or less transparent. The legs are slender with bristles. The nymphs resemble the adults but are smaller and do not have fully developed wings. Adults and nymphs suck sap from the leaves, remaining on the underside during the day, but also moving to the upper surface during the evening. When disturbed they run sideways rapidly to reach a shady part of the host plant.
Feeding by leafhoppers causes discolouration, and leaf curl, the outer zone of the leaf turn yellow to reddish and whither later. Heavy leafhopper infestation may retard plant growth and may cause severe yield losses. In Africa, leafhopper damage is usually minor and does not warrant control.
- Look for leafhoppers on the undersides of leaves.
- Wash nymphs from plants with a strong jet of water. Wash the undersides of the leaves in particular.
- Set out yellow sticky traps near the infested plants if the infestation is severe. For more information on sticky traps click here
- If necessary spray insecticidal soap, neem or pyrethrum.

Leafhopper. Adults are small, about 2.5 mm long. Picture shows Empoasca fabae
© Steve L. Brown, University of Georgia, Bugwood.org
Red-banded thrips (Selenothrips rubrocinctus)
Adults of the red banded thrips are dark brown or blackish. Nymphs are pale yellow with a broad transverse red band on the dorsal side of the abdomen. Thrips attack older leaves, flowers and shoots. Attacked leaves drop off leaving bare shoots with few young leaves at the tip. Infestation of flowers causes poor fruit formation. Locally limited infestations may cause considerable damage.
- Conserve natural enemies. Anthocorid bugs are important in natural control of thrips.

Immature stage of the red banded thrips (Selenothrips rubrocinctus). Note a bright red band across the abdomen of immature thrips. Real size: about 1mm long.
© A. M. Varela, icipe
- CAB International (2005). Crop Protection Compendium, 2005 edition. Wallingford, UK www.cabi.org
- Naturland e.V. (2000). Organic Farming in the Tropics and Subtropics. Exemplary description of 20 crops. Cocoa. www.naturland.de
- Nutrition Data www.nutritiondata.com.